4 Phases Of Business Cycle Definition
Economic activity is fluctuating. Understanding the four phases of the business cycle is now crucial for businesses and investors navigating uncertain times.
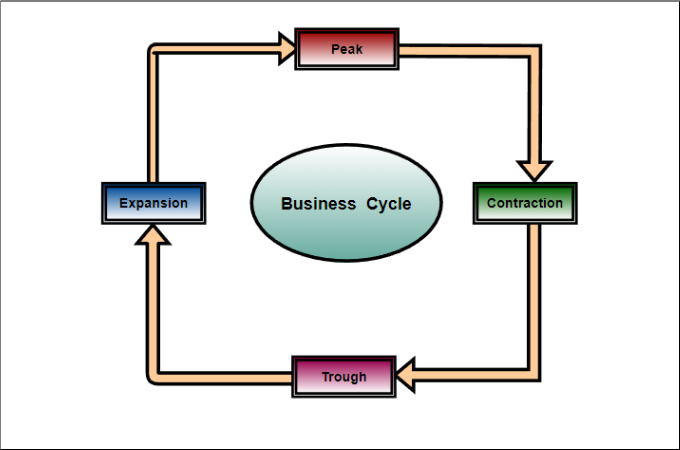
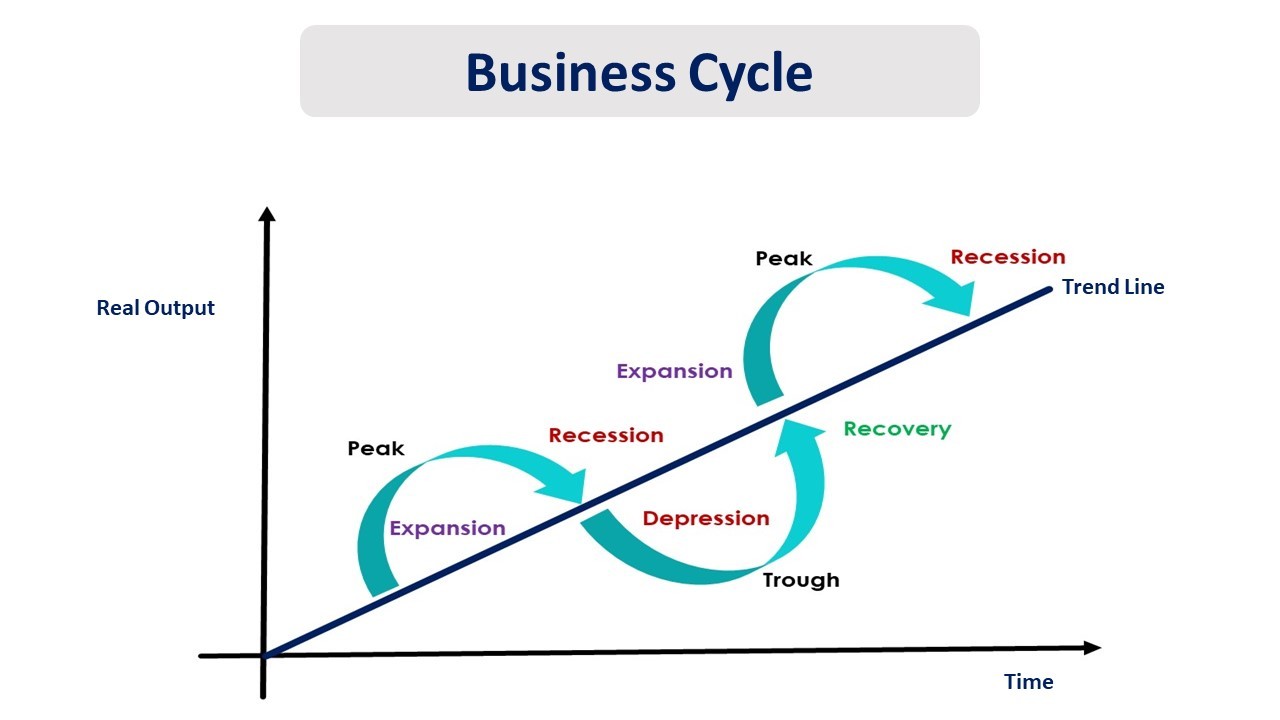
The business cycle describes the recurring pattern of expansion and contraction in an economy. Recognizing these phases helps anticipate market shifts and inform strategic decisions.
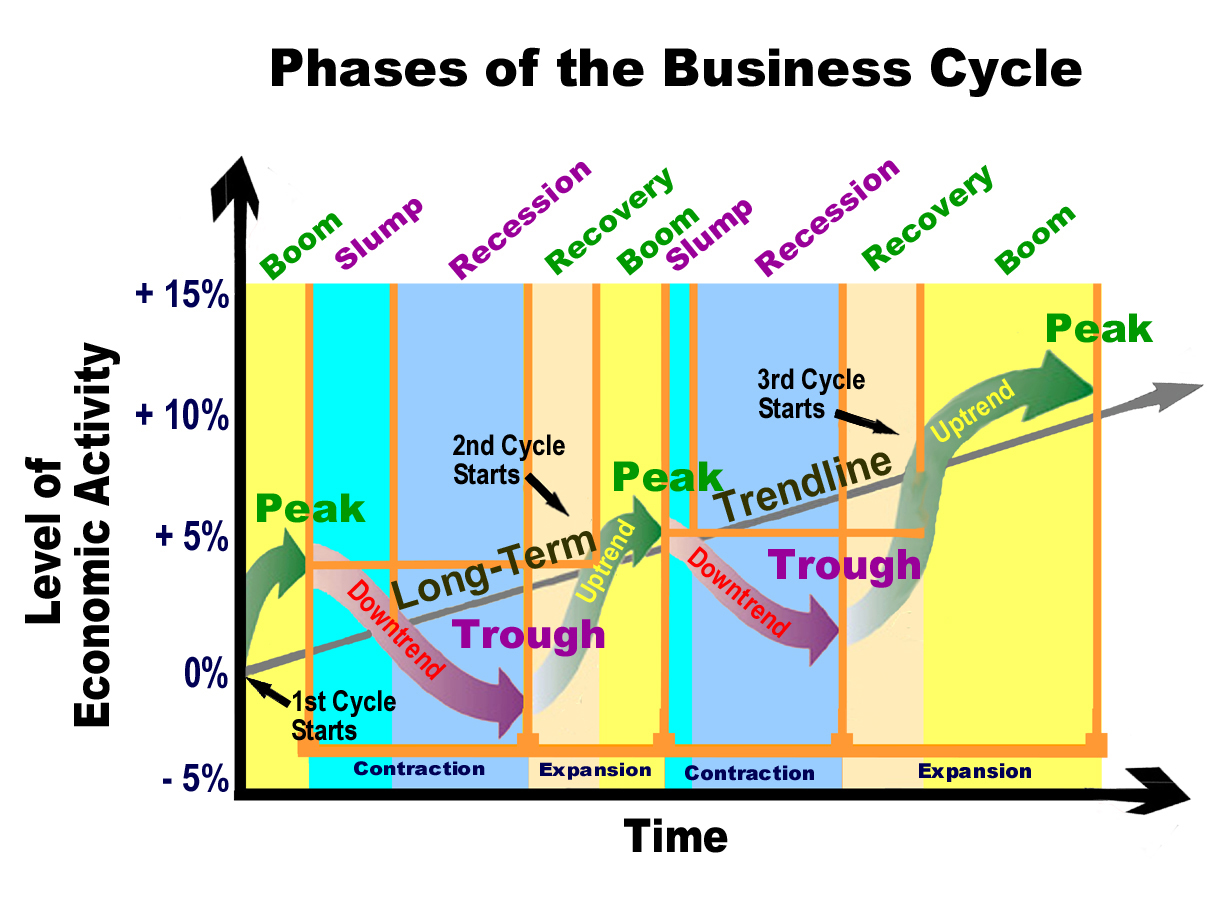
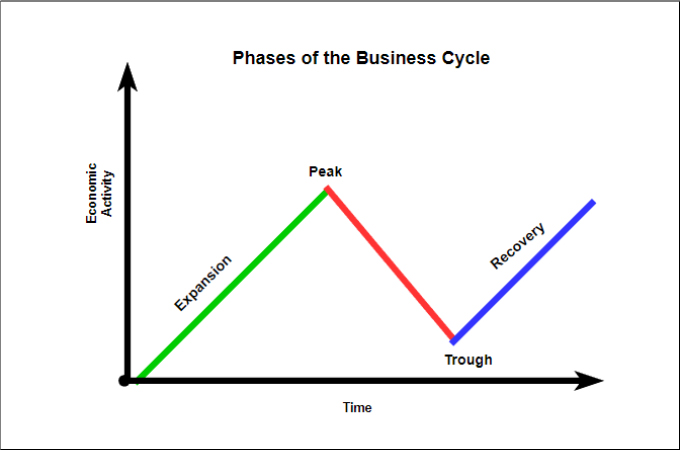
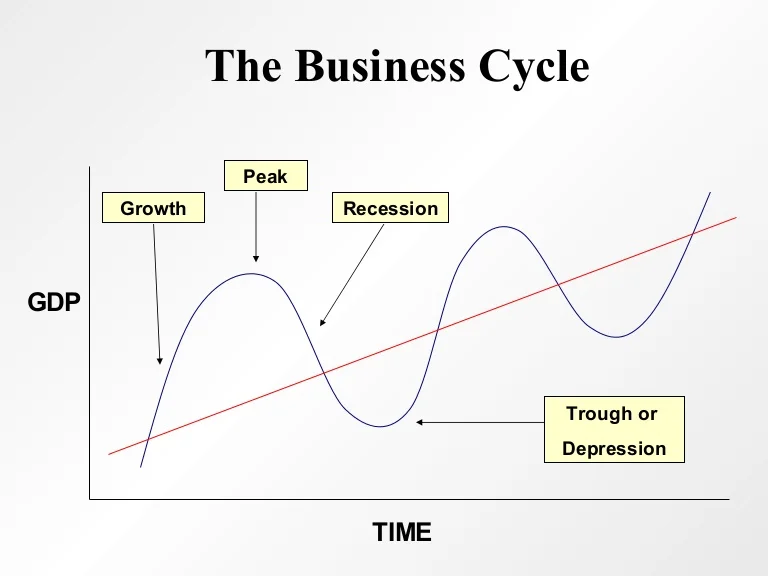
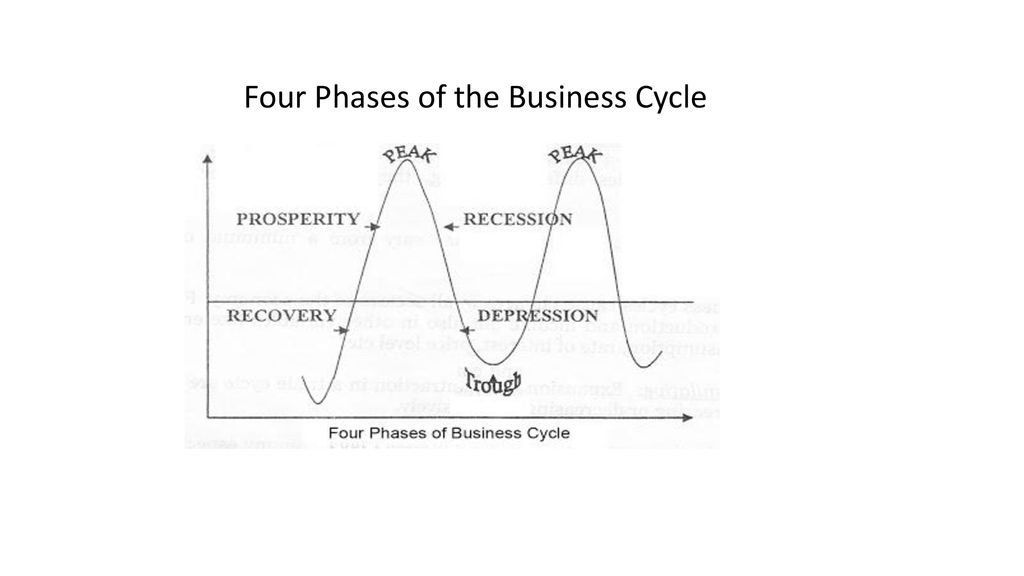
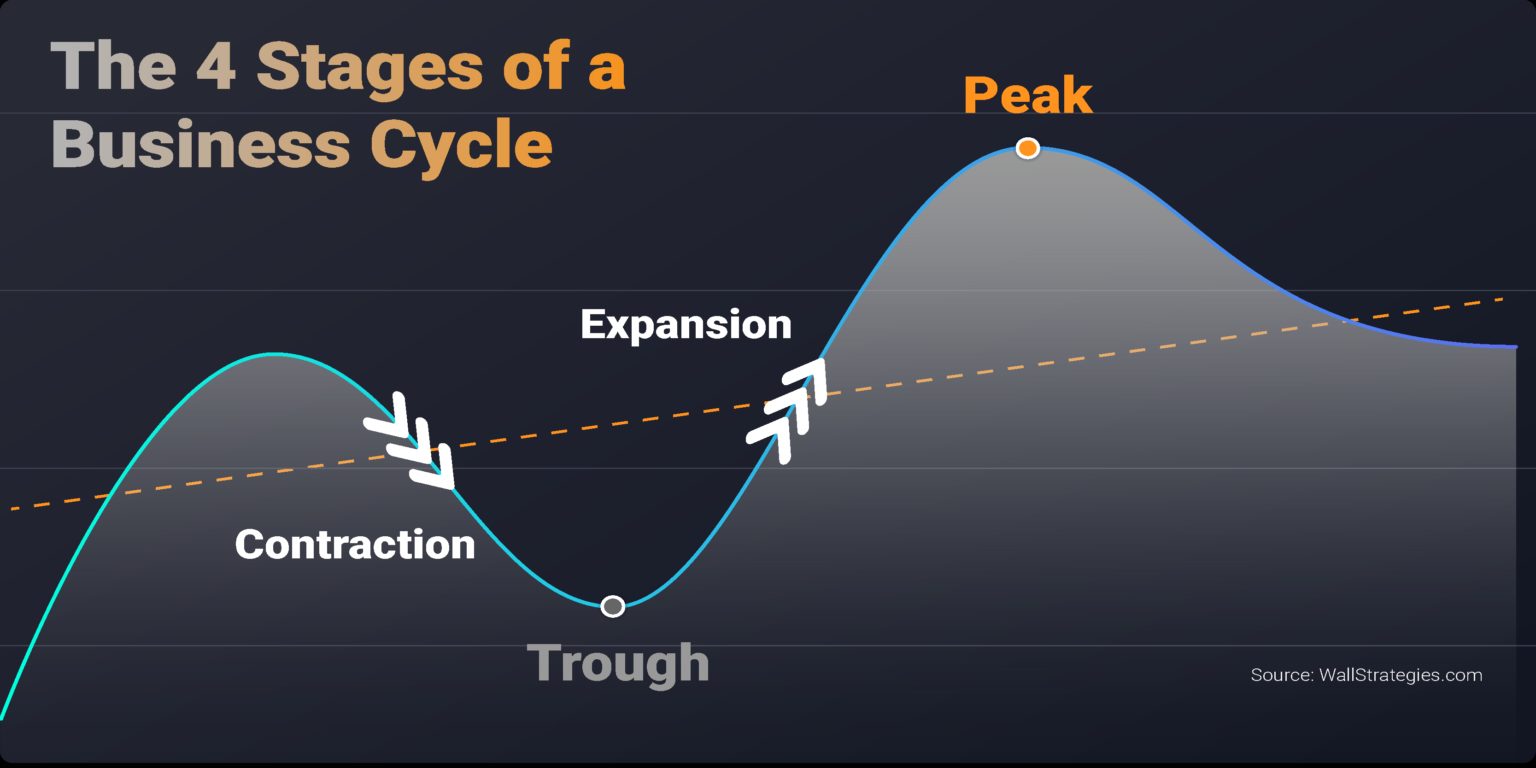
The Four Phases: A Breakdown
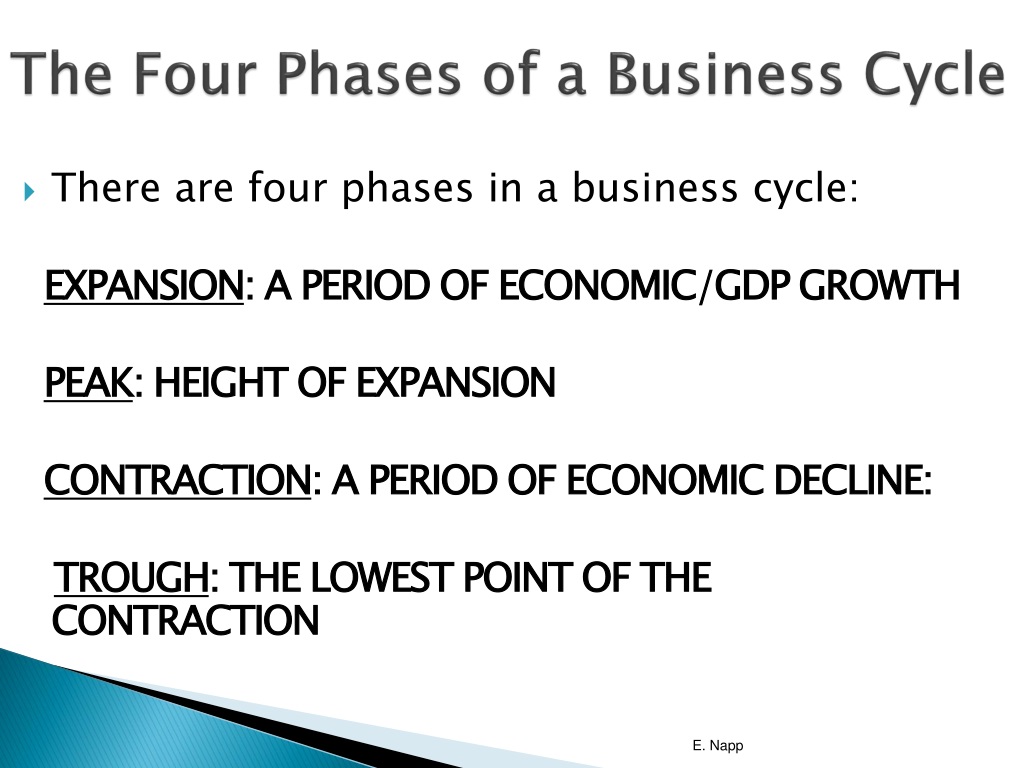
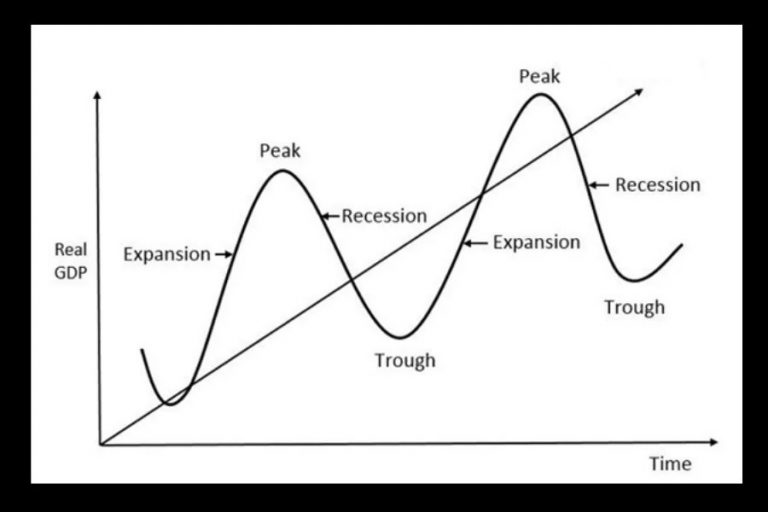
1. Expansion (Growth)
This phase marks a period of economic boom. During expansion, key indicators like GDP, employment, and consumer spending are all rising.
Businesses typically see increased profits and are more likely to invest in expansion and hiring.
Demand is high, leading to increased production and potential inflationary pressures. The NBER (National Bureau of Economic Research) generally identifies the peak of expansion.
2. Peak
The peak represents the highest point of economic activity in the cycle. Demand cannot keep up with supply, inflation is rampant.
It's a turning point where growth begins to slow. This phase is short-lived but critical for identifying an impending shift.
Indicators begin to show signs of fatigue, signaling a potential downturn.
3. Contraction (Recession)
A contraction, often referred to as a recession, is a period of economic decline. GDP, employment, and consumer spending all decrease during this phase.
Businesses may experience reduced profits, leading to layoffs and decreased investment.
The NBER defines a recession as "a significant decline in economic activity spread across the economy, lasting more than a few months, normally visible in real GDP, real income, employment, industrial production, and wholesale-retail sales."
4. Trough
The trough is the lowest point of economic activity in the cycle. This marks the end of the contraction and the beginning of a new expansion.
Economic indicators reach their lowest levels. Unemployment is usually at its highest during this phase.
This phase sets the stage for recovery and renewed growth. It is the best time to invest.
Navigating the Cycle: Key Considerations
Understanding these phases can inform investment strategies. During expansion, investing in growth stocks may be advantageous.
During contraction, investors might shift towards more defensive stocks. The market is unstable.
Businesses can use this knowledge to adjust their production, hiring, and pricing strategies.
Federal Reserve policies, like interest rate adjustments, can influence the business cycle. Government spending and tax policies also play a role.
Monitoring economic indicators is crucial for identifying the current phase. Keep updated with news.
Pay attention to GDP growth, employment figures, and inflation rates.
What's Next?
Economists are closely monitoring current data to determine the economy's trajectory. A new cycle is coming.
The Federal Reserve is expected to continue monitoring inflation and adjusting monetary policy accordingly. Their goal is stability.
Businesses and investors should stay informed and adapt their strategies to navigate the evolving economic landscape.
/businesscycle-013-ba572c5d577c4bd6a367177a02c26423.png)

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/businesscycle-013-ba572c5d577c4bd6a367177a02c26423.png)
.png)