990 Due Date For 6 30 Year End

Nonprofit organizations with a June 30 fiscal year-end are reminded that their Form 990 series returns are due to the IRS by November 15, 2024. Failure to file on time can result in significant penalties, impacting an organization's ability to fulfill its mission and maintain its tax-exempt status.
This article clarifies the filing requirements for these organizations, outlines potential consequences of non-compliance, and offers resources for ensuring timely and accurate submission.
Understanding the Form 990 Filing Requirement
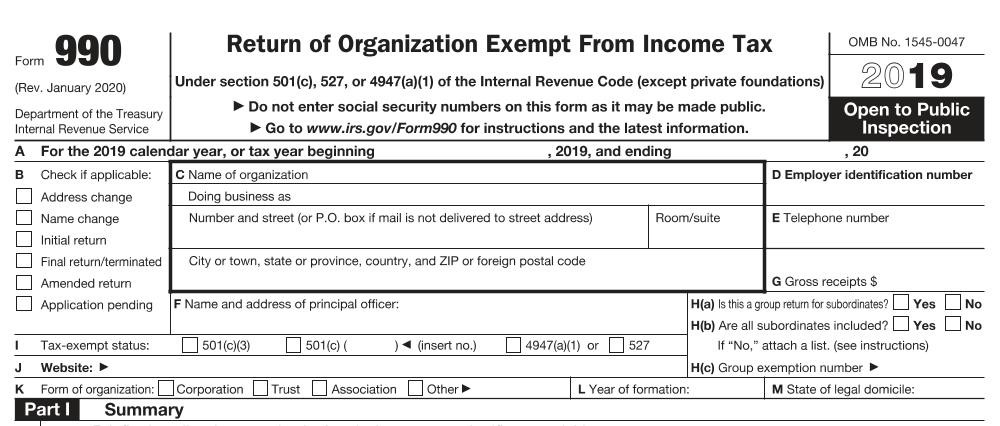
The Form 990, Return of Organization Exempt From Income Tax, is an annual information return that most tax-exempt organizations must file with the IRS.
It provides the IRS and the public with financial and operational information about the organization, including its mission, programs, finances, and governance. This transparency is crucial for maintaining public trust and accountability within the nonprofit sector.
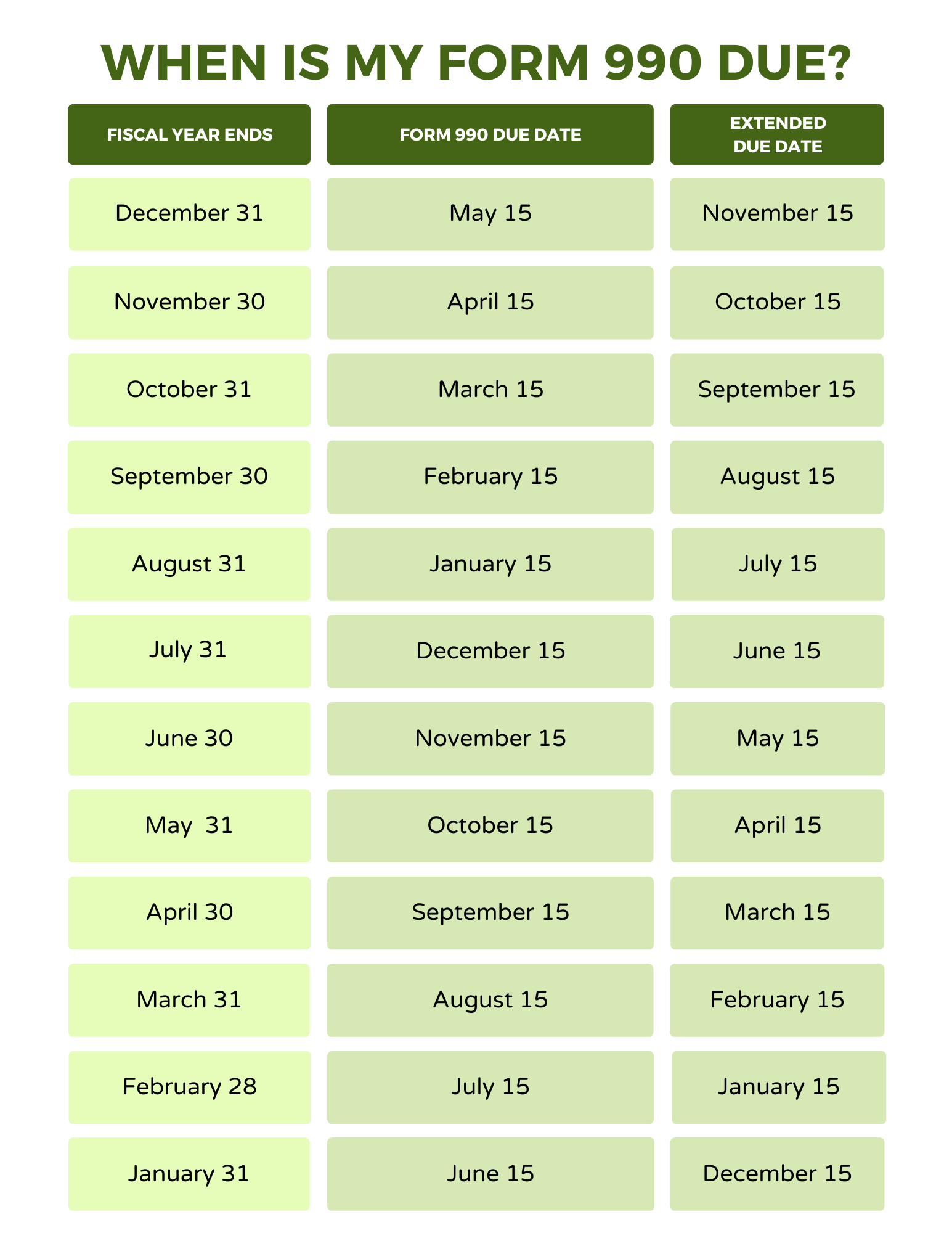
Organizations with a fiscal year ending June 30th must file their Form 990 by the 15th day of the fifth month following the end of their accounting period, which falls on November 15th.
Who Needs to File?
Generally, all organizations recognized as exempt under Internal Revenue Code Section 501(c)(3) are required to file Form 990, unless they meet specific exceptions.
Smaller organizations with gross receipts of less than $50,000 may be eligible to file Form 990-N (e-Postcard), a simplified online form. Organizations with gross receipts between $50,000 and $200,000 and total assets less than $500,000 may file Form 990-EZ, a shorter version of the Form 990. Larger organizations must file the full Form 990.
It's important to consult the IRS instructions or a qualified tax professional to determine the appropriate form and filing requirements for a specific organization.
What Information is Required?
The Form 990 requires detailed information about the organization's activities, finances, and governance.
This includes reporting revenue and expenses, assets and liabilities, program service accomplishments, compensation of officers and directors, and details about lobbying activities and political campaign involvement (if any). The level of detail required varies depending on the version of the form filed.
Organizations must also disclose information about related organizations and transactions with them.
Consequences of Late Filing or Non-Compliance
Failure to file Form 990 on time can result in significant penalties.
The IRS can assess penalties of $20 per day for organizations with gross receipts of less than $1,047,000, with a maximum penalty of $10,500. For larger organizations, the penalty increases to $105 per day, with a maximum penalty of $52,500.
More seriously, failure to file for three consecutive years can result in automatic revocation of an organization's tax-exempt status. This can have devastating consequences for the organization, including the loss of its ability to receive tax-deductible contributions and potential exposure to income tax.
The IRS emphasizes that accurate and timely filing is crucial for maintaining tax-exempt status.
How to Ensure Timely and Accurate Filing
Several steps can be taken to ensure timely and accurate filing of Form 990.
First, organizations should establish a system for tracking deadlines and gathering the necessary information. Assigning responsibility for filing to a specific individual or team is essential.
Second, utilizing accounting software or engaging a qualified tax professional can help ensure compliance with IRS regulations. Consulting with a CPA or enrolled agent can provide valuable guidance and support.
Finally, organizations should familiarize themselves with the Form 990 instructions and any applicable updates or changes. The IRS website provides comprehensive resources and guidance on filing requirements.
Resources Available to Nonprofits
The IRS offers a variety of resources to assist nonprofit organizations with their filing obligations.
The IRS website (www.irs.gov) provides access to Form 990 instructions, publications, and FAQs. The IRS also offers free educational webinars and workshops on various topics related to nonprofit tax compliance.
Additionally, many professional associations and nonprofit support organizations offer resources and training to help organizations comply with filing requirements. These organizations often provide templates, checklists, and other tools to simplify the filing process.
"Maintaining compliance with IRS regulations is a vital aspect of responsible stewardship for any nonprofit organization," said Sarah Miller, a CPA specializing in nonprofit tax compliance. "Proactive planning and access to reliable resources can help organizations avoid costly penalties and maintain their tax-exempt status."
Looking Ahead
The November 15th deadline is fast approaching for nonprofits with a June 30th year-end.
Taking proactive steps now to ensure timely and accurate filing can help organizations avoid penalties, maintain their tax-exempt status, and continue serving their communities effectively. Don't delay, gather your necessary documents and start preparing your 990 forms.
By prioritizing compliance, nonprofits can demonstrate their commitment to transparency and accountability, fostering trust with donors, stakeholders, and the public.
.jpg)