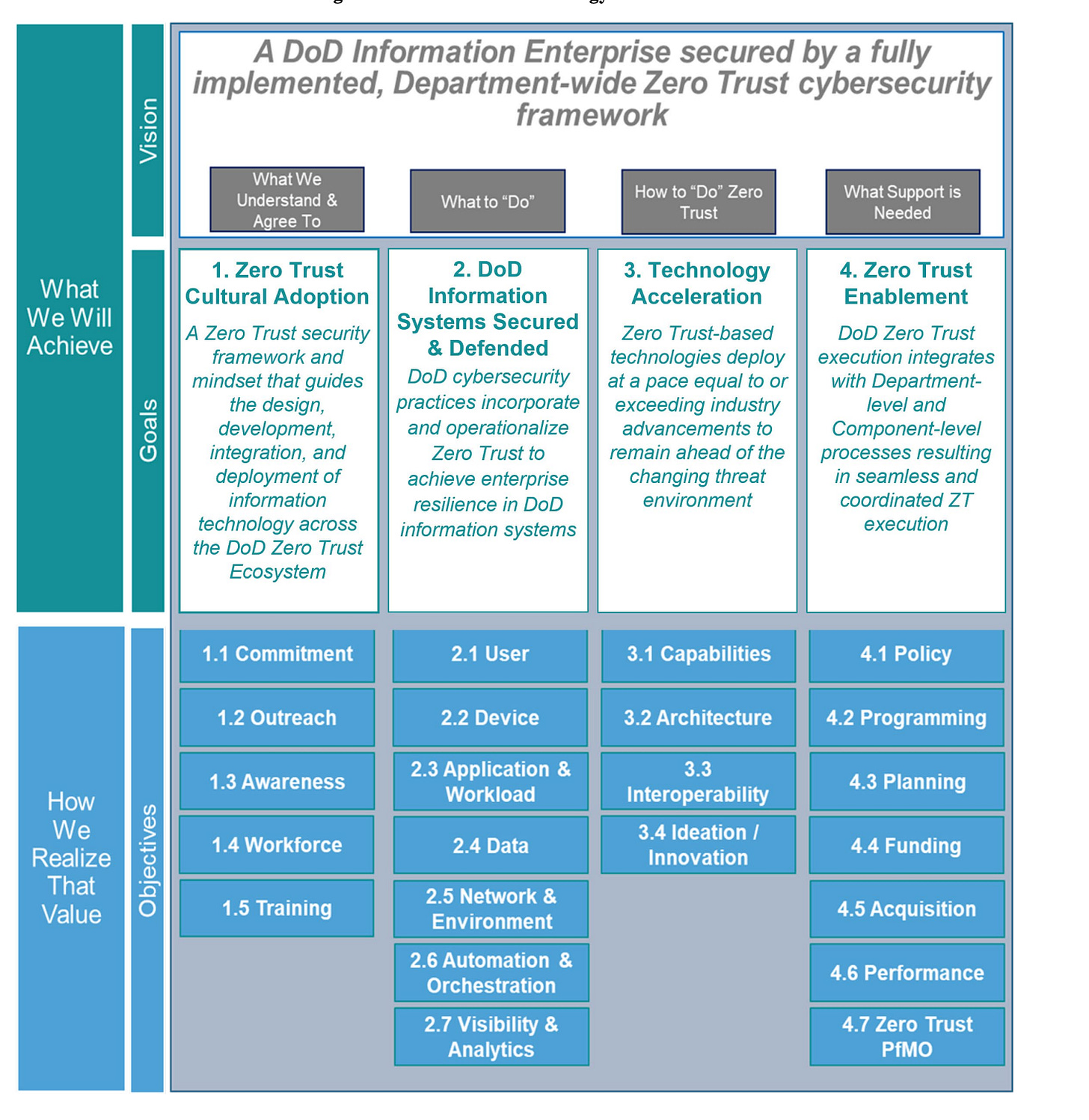
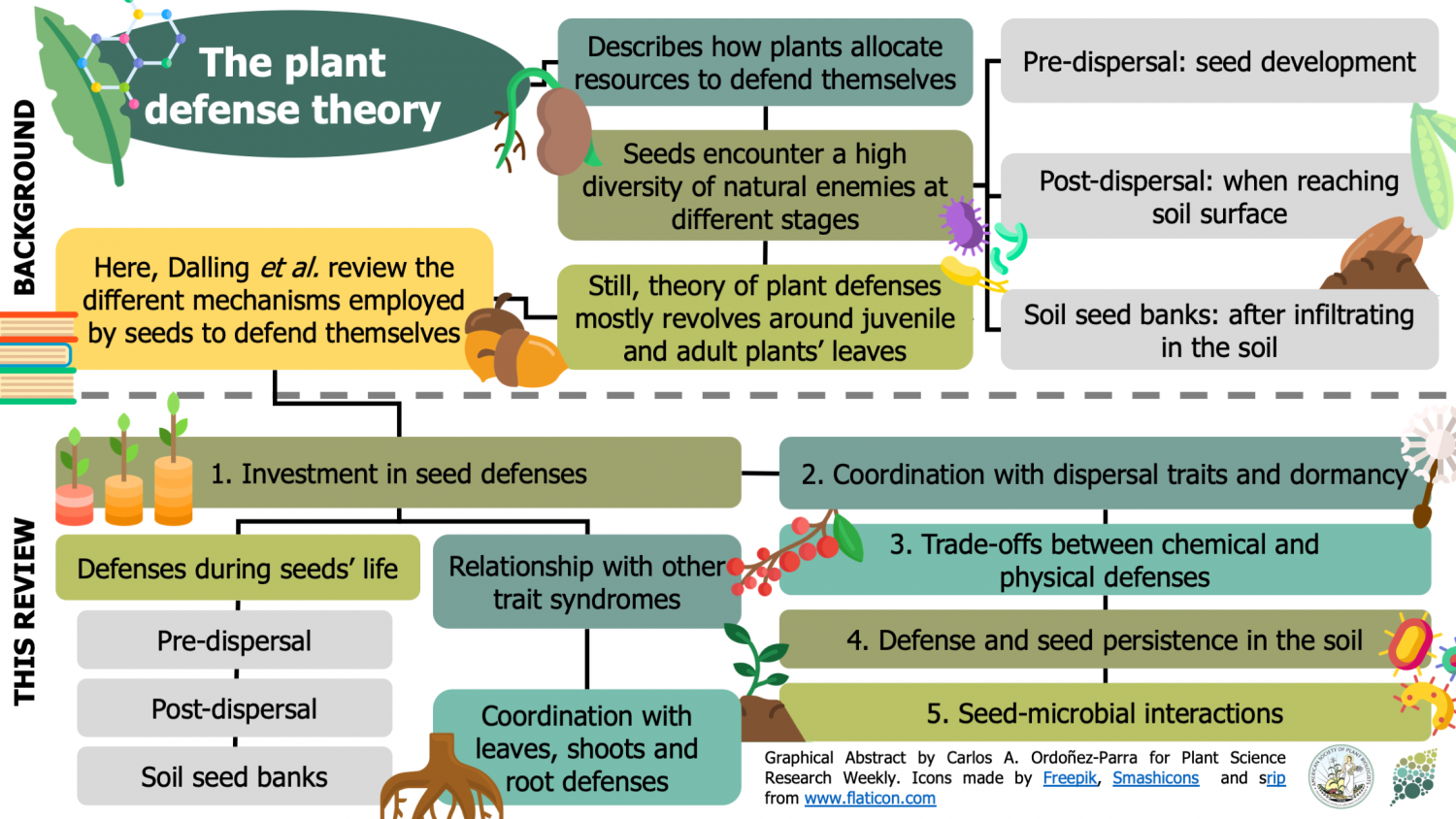
A Goal Of The Defense Plant Corporation Was

In the throes of World War II, the United States mobilized its industrial might with unprecedented speed and scale. A key instrument in this transformation was the Defense Plant Corporation (DPC), a government entity whose primary objective was to rapidly expand the nation's manufacturing capacity to meet the escalating demands of wartime production.
The DPC's story is a testament to the government's interventionist role in a time of national crisis. It offers valuable lessons about industrial policy, resource allocation, and the mobilization of national assets under extraordinary circumstances.
The Genesis of the Defense Plant Corporation
Established in August 1940 as a subsidiary of the Reconstruction Finance Corporation (RFC), the DPC was created to address the looming shortages of vital war materials and equipment. The initiative was led by Jesse H. Jones, then the head of the RFC.
The corporation was designed to finance the construction and operation of new plants and factories. The goal was to produce everything from airplanes and ammunition to synthetic rubber and machine tools.
Financing and Operation
The DPC operated primarily through lease agreements with private companies. The government financed the construction of the plants, and the companies managed the day-to-day operations.
This arrangement allowed private enterprise to leverage government resources while maintaining operational control. It also ensured that the government retained ownership of the facilities, providing flexibility after the war.
Key Areas of Investment
One of the most crucial areas of investment for the DPC was in the expansion of the aviation industry. Billions of dollars were allocated to build new aircraft factories and expand existing ones.
Another critical sector was the production of synthetic rubber. Access to natural rubber from Southeast Asia was severely curtailed due to the Japanese occupation, necessitating the development of a domestic synthetic rubber industry.
The DPC also invested heavily in the production of machine tools. These were essential for manufacturing all sorts of war materials.
Impact on Wartime Production
The DPC's investments had a transformative impact on American industry. It increased production capacity and introduced new technologies and manufacturing processes.
By the end of the war, the DPC owned or leased over 2,500 facilities. These facilities significantly contributed to the Allied victory.
The rapid expansion of industries like aviation and synthetic rubber not only supported the war effort but also laid the groundwork for postwar economic growth.
The Human Angle
The construction and operation of DPC-funded plants created millions of jobs. It brought economic opportunities to communities across the country.
Many of these jobs were filled by women and minorities, who entered the industrial workforce in unprecedented numbers due to the wartime labor shortage.
This shift in the demographics of the workforce had lasting social and economic consequences. It helped to break down traditional barriers and expand opportunities for previously excluded groups.
Postwar Legacy
Following the end of World War II, the DPC was dissolved. Its assets were sold off to private companies or repurposed for civilian use.
The sale of these assets helped to spur postwar economic growth. It also facilitated the transition from a wartime to a peacetime economy.
Some of the plants and facilities built by the DPC remain in operation today. They serve as a tangible reminder of the government's role in mobilizing the nation's industrial might during World War II.
Lessons Learned
The story of the Defense Plant Corporation offers valuable lessons for policymakers and economists. It demonstrates the potential of government intervention in stimulating industrial growth during times of national crisis.
It also highlights the importance of careful planning and coordination in managing large-scale industrial projects. The DPC's success was due, in part, to its ability to leverage the expertise and resources of both the public and private sectors.
However, the DPC's experience also raises questions about the appropriate role of government in the economy. It also raises questions about the potential risks of over-reliance on government intervention.
Conclusion
The Defense Plant Corporation played a pivotal role in the American war effort. It fueled industrial expansion and contributed significantly to the Allied victory.
Its legacy extends beyond the war years, influencing postwar economic growth and shaping the landscape of American industry. The DPC's achievements serve as a reminder of the nation's capacity for innovation and resilience in the face of adversity.
By understanding the DPC's purpose, we gain insight into a crucial chapter in American history. We see the intersection of industrial policy, wartime mobilization, and the enduring impact of governmental actions on the economy and society.