Acetic Acid Industry Capacity And Capex Market

The global acetic acid industry is undergoing a period of significant transformation, driven by surging demand, particularly from the burgeoning Asian economies, and subsequently prompting substantial investments in capacity expansion. This expansion, however, is not without its challenges, as geopolitical uncertainties, fluctuating feedstock prices, and evolving sustainability concerns create a complex and dynamic landscape for producers and consumers alike.
At the heart of this narrative lies a surge in capital expenditure (CAPEX) aimed at bolstering production capacity to meet escalating global demand. This article delves into the intricate details of the acetic acid industry, examining the current capacity landscape, recent and planned CAPEX investments, the key drivers fueling growth, potential roadblocks, and the long-term outlook for this vital chemical compound. The analysis draws upon recent reports, official statements, and data from reputable industry organizations to provide a comprehensive and balanced perspective.
Current Global Acetic Acid Capacity
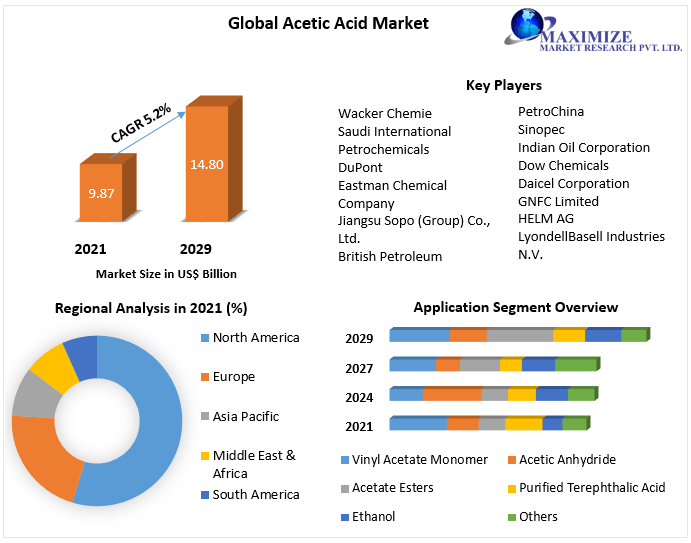
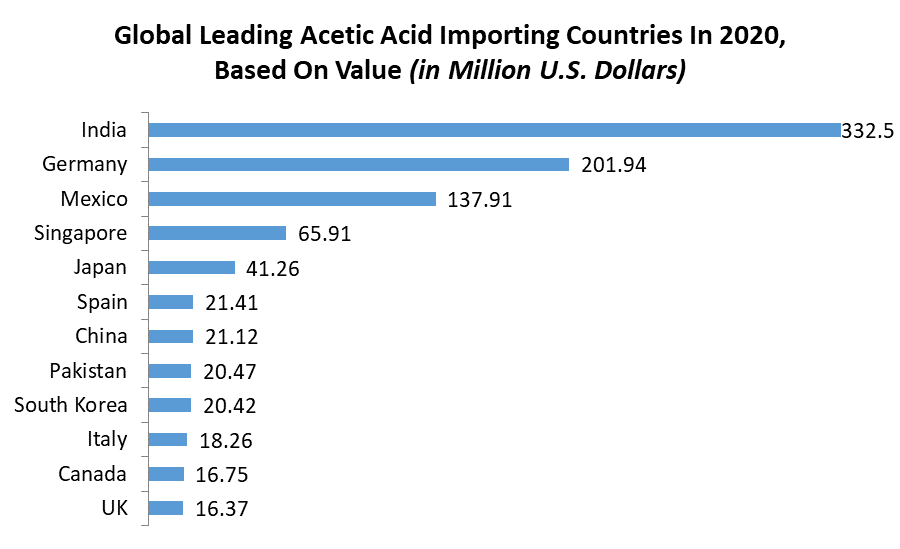
Global acetic acid production capacity is currently estimated to be in the range of 18-20 million metric tons per annum (MTPA). Asia dominates the production landscape, accounting for over 60% of the total global capacity. China stands out as the single largest producer, followed by the United States and Europe.
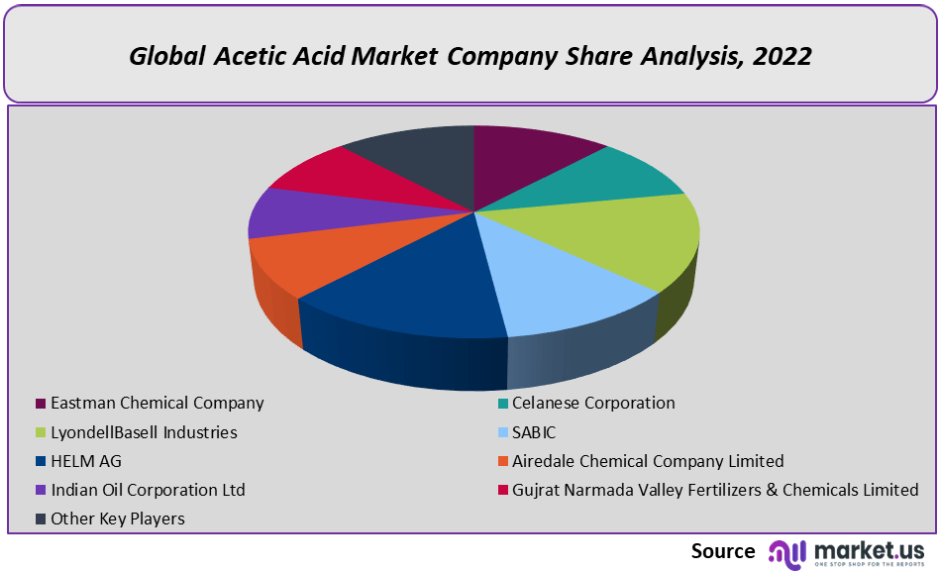
Major players in the acetic acid market include companies like BP, Celanese, LyondellBasell, and Jiangsu Sopo. These companies operate large-scale production facilities strategically located to serve key regional markets. Technological advancements, particularly in methanol carbonylation processes, have enabled these producers to achieve greater efficiency and higher yields.
CAPEX Investments: A Race to Meet Demand
Spurred by consistently increasing demand, several major producers have announced significant CAPEX investments in new acetic acid plants and expansions of existing facilities. A substantial portion of these investments is concentrated in Asia, reflecting the region's robust economic growth and increasing consumption of acetic acid derivatives.
For example, Celanese recently announced plans to expand its Clear Lake, Texas facility, adding approximately 600,000 MTPA of capacity. This expansion is aimed at serving the growing demand in North America and export markets. Similarly, several Chinese companies are undertaking large-scale expansions to capitalize on the domestic market's rapid growth.
Furthermore, greenfield projects are also being considered in regions with access to favorable feedstock supplies and emerging markets. These investments signal a long-term commitment to the acetic acid market and an anticipation of sustained demand growth.
Drivers of Market Growth
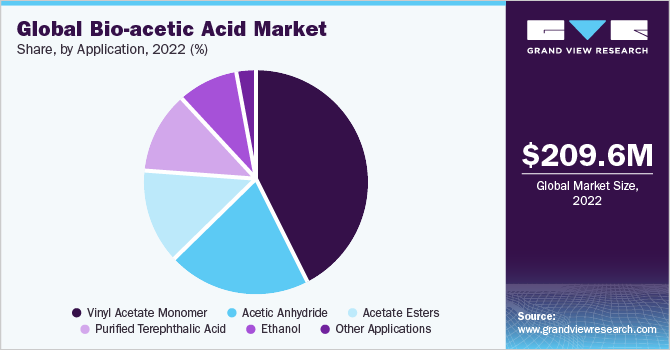
The acetic acid market is driven by a multitude of factors, foremost among them being the increasing demand for vinyl acetate monomer (VAM). VAM, a key derivative of acetic acid, is used extensively in the production of polymers, adhesives, coatings, and textiles.
The construction and packaging industries, both significant consumers of VAM-based products, are experiencing strong growth, particularly in developing economies. Consequently, the demand for acetic acid is directly correlated with the expansion of these sectors.
Another significant driver is the growing demand for purified terephthalic acid (PTA), another acetic acid derivative used in the production of polyester fibers and resins. The textile industry, a major consumer of polyester, is witnessing continuous expansion, particularly in Asia, further boosting acetic acid demand.
The Role of Feedstock Prices
Acetic acid production heavily relies on feedstocks like methanol and carbon monoxide. Fluctuations in the prices of these feedstocks can significantly impact the profitability of acetic acid producers.
Geopolitical instability and disruptions in supply chains can lead to volatile feedstock prices, creating uncertainty for producers. Strategies for mitigating feedstock price risk, such as long-term supply contracts and diversification of feedstock sources, are becoming increasingly important.
Challenges and Restraints
Despite the positive outlook, the acetic acid industry faces several challenges. Environmental regulations are becoming increasingly stringent, requiring producers to invest in cleaner production technologies and reduce emissions.
The disposal of acetic acid waste and the management of by-products are also growing concerns. Companies are exploring innovative solutions, such as carbon capture and utilization, to address these environmental challenges.
Furthermore, overcapacity can lead to price volatility and reduced profitability. The potential for oversupply, particularly if all planned expansions come online simultaneously, remains a key concern for the industry.
Sustainability and the Future
Sustainability is becoming a critical factor in the acetic acid industry. Consumers are increasingly demanding environmentally friendly products, and producers are responding by investing in sustainable production processes.
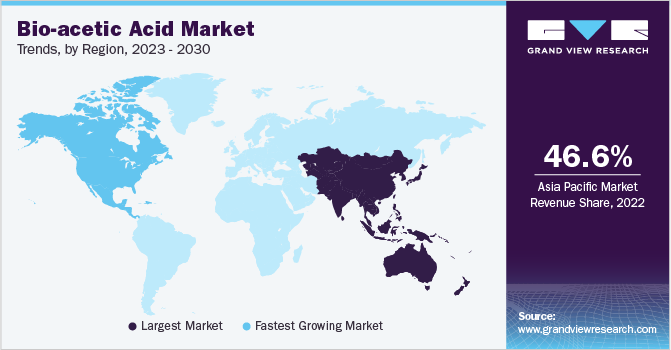
The development of bio-based acetic acid, derived from renewable resources, is gaining traction as a potential alternative to traditional fossil fuel-based production. Companies are actively researching and developing technologies to produce acetic acid from biomass and other sustainable feedstocks.
The future of the acetic acid industry will likely be shaped by a combination of factors, including technological innovation, environmental regulations, and evolving consumer preferences. Adapting to these changes will be crucial for companies to remain competitive and sustainable in the long term.
Regional Dynamics
Asia will continue to be the dominant force in the acetic acid market, driven by its robust economic growth and expanding downstream industries. China's role as both a major producer and consumer will remain pivotal.
North America and Europe will likely experience moderate growth, driven by demand in specific applications and the adoption of sustainable production practices. New capacity additions in these regions are expected to be more selective and focused on niche markets.
Emerging markets in Latin America and Africa offer potential growth opportunities, but infrastructure limitations and political instability may pose challenges. Companies will need to carefully assess the risks and opportunities in these regions before making significant investments.
Conclusion
The global acetic acid industry is poised for continued growth, fueled by strong demand from key end-use sectors and significant investments in new capacity. While challenges remain, particularly concerning feedstock prices, environmental regulations, and potential overcapacity, the long-term outlook for the industry is positive.
The increasing focus on sustainability and the development of bio-based acetic acid offer exciting opportunities for innovation and growth. Companies that can adapt to the evolving market dynamics and embrace sustainable practices will be best positioned to thrive in the years to come. The substantial CAPEX being deployed underscores the industry’s confidence in long-term demand and its commitment to meeting global needs.
Ultimately, the acetic acid market will remain a critical component of the global chemical industry, supporting a wide range of essential products and applications. Its future success hinges on the ability of producers to navigate the complexities of the market, embrace sustainability, and adapt to the changing needs of consumers worldwide.