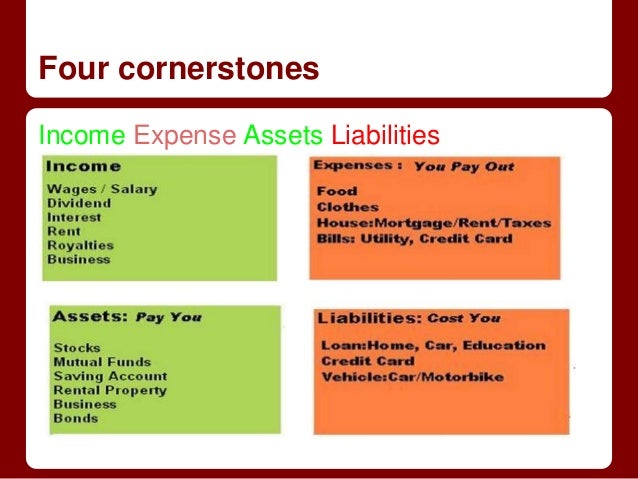
Assets Liabilities Equity Revenue Expenses Examples
Businesses face critical junctures in understanding their financial standing. Mastering the fundamental concepts of assets, liabilities, equity, revenue, and expenses is now crucial for survival and growth.
This article breaks down these key financial terms, providing practical examples to illustrate their importance in assessing a company's fiscal health. Understanding these concepts is no longer optional—it's essential for making informed decisions.
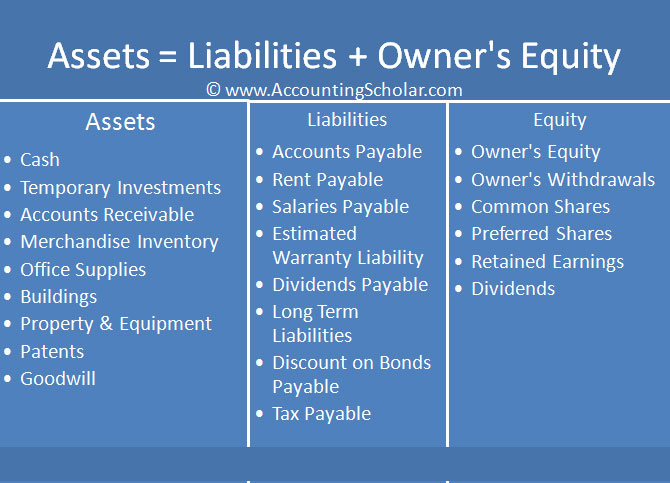
What are Assets?
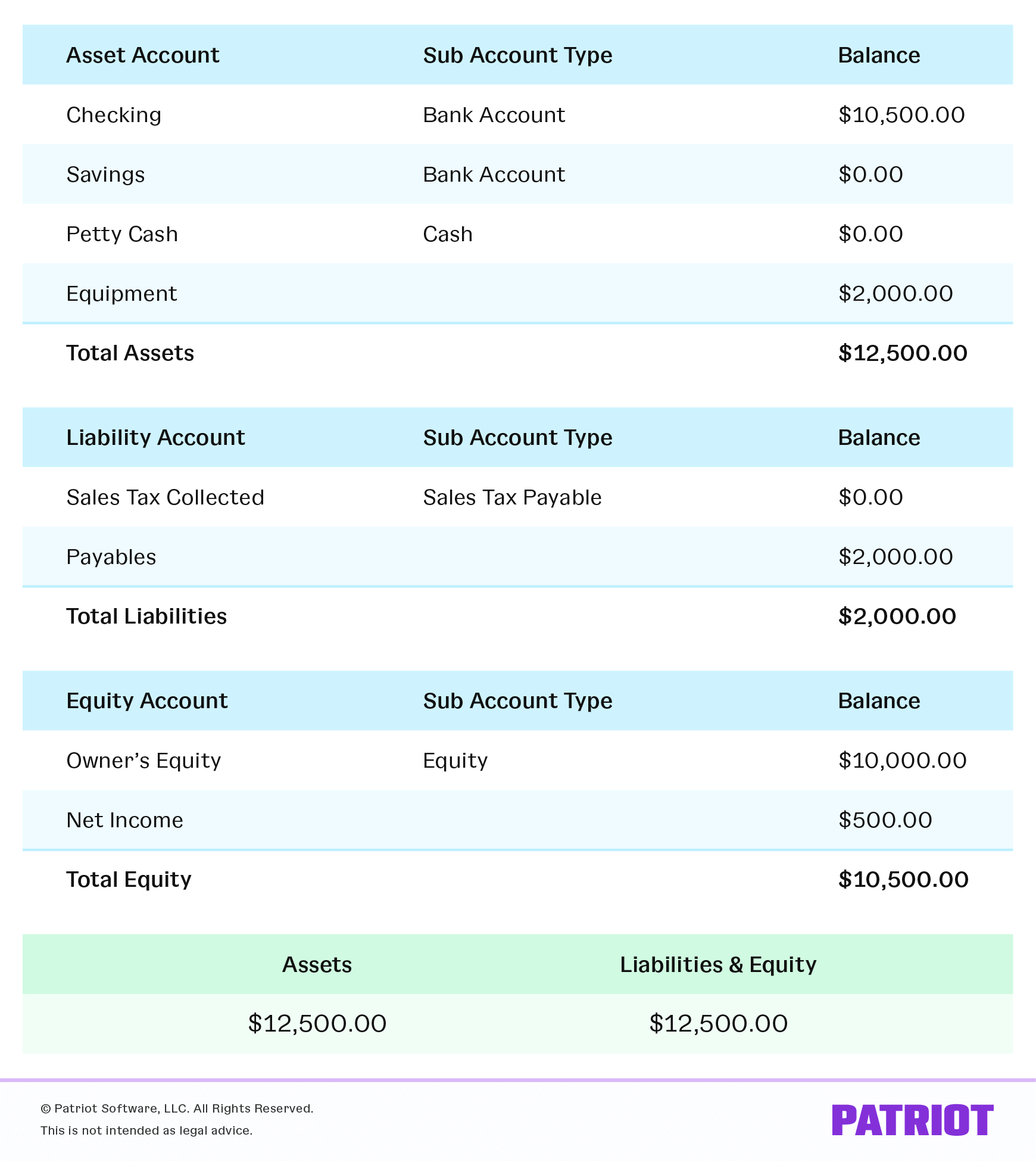
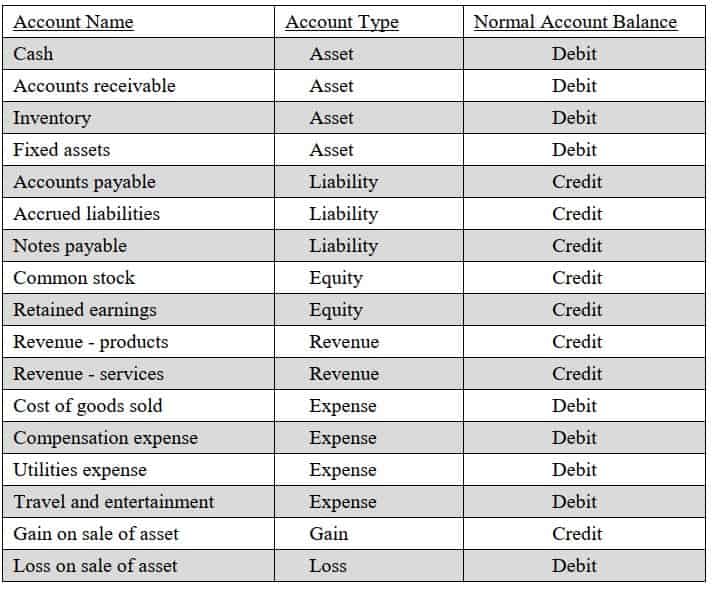
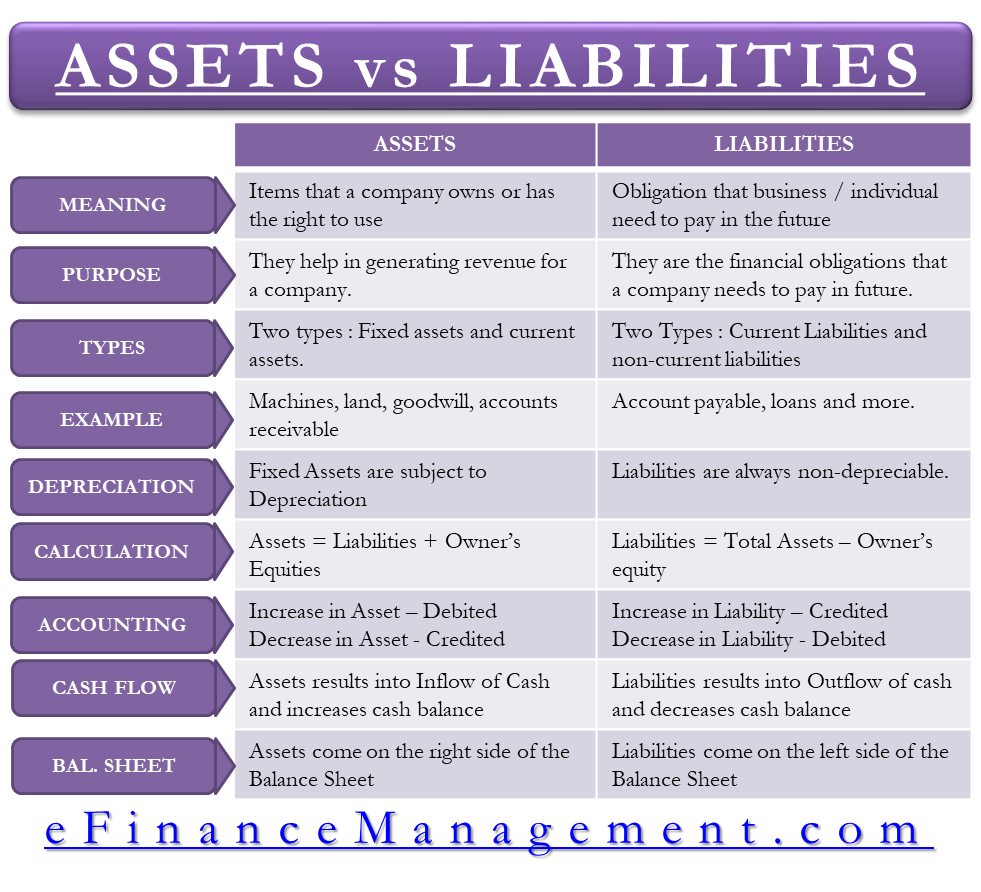
Assets are a company's resources that hold economic value.
These resources are expected to provide future benefit.
Examples include cash, accounts receivable (money owed by customers), inventory, equipment, and property.
Examples of Assets:
Cash: The most liquid asset, used for immediate transactions.
Accounts Receivable: Money due from customers for goods or services already provided.
Inventory: Goods available for sale to customers.
Equipment: Machinery, vehicles, and other tools used in operations.
Property: Land and buildings owned by the company.
Understanding Liabilities
Liabilities represent a company's obligations to others.
These are debts or amounts owed to creditors, suppliers, or lenders.
Common liabilities include accounts payable, salaries payable, and loans.
Examples of Liabilities:
Accounts Payable: Money owed to suppliers for goods or services received.
Salaries Payable: Wages owed to employees for work performed.
Loans Payable: The outstanding balance of borrowed money from banks or other lenders.
Equity: The Owner's Stake
Equity represents the owner's stake in the company's assets after liabilities are deducted.
It is often referred to as net worth or shareholders' equity.
Equity can increase through profits and additional investments.
Examples Affecting Equity:
Common Stock: Represents ownership shares in the company.
Retained Earnings: Accumulated profits that have not been distributed to owners.
Revenue: The Top Line
Revenue is the income generated from a company's primary business activities.
It's the total amount of money received from selling goods or services.
Revenue is often referred to as sales or turnover.
Examples of Revenue:
Sales Revenue: Income from selling products to customers.
Service Revenue: Income from providing services to clients.
Expenses: Costs of Doing Business
Expenses are the costs incurred by a company to generate revenue.
These are the costs associated with operating the business.
Examples include salaries, rent, utilities, and cost of goods sold.
Examples of Expenses:
Salaries Expense: Wages paid to employees.
Rent Expense: Cost of renting office or retail space.
Utilities Expense: Costs for electricity, water, and gas.
Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): The direct costs of producing goods sold by a company.
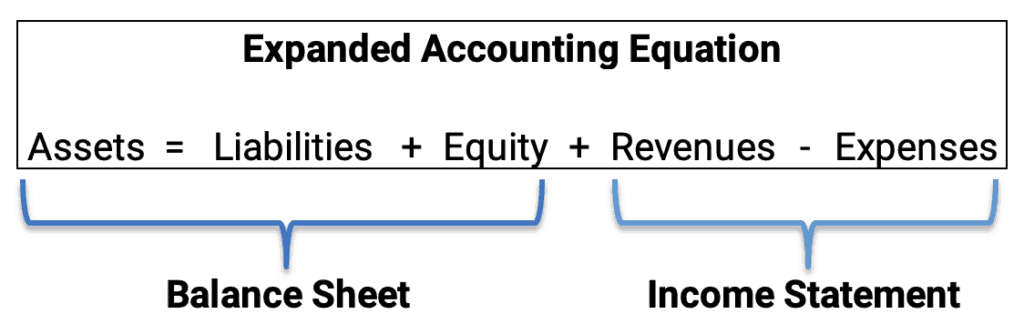
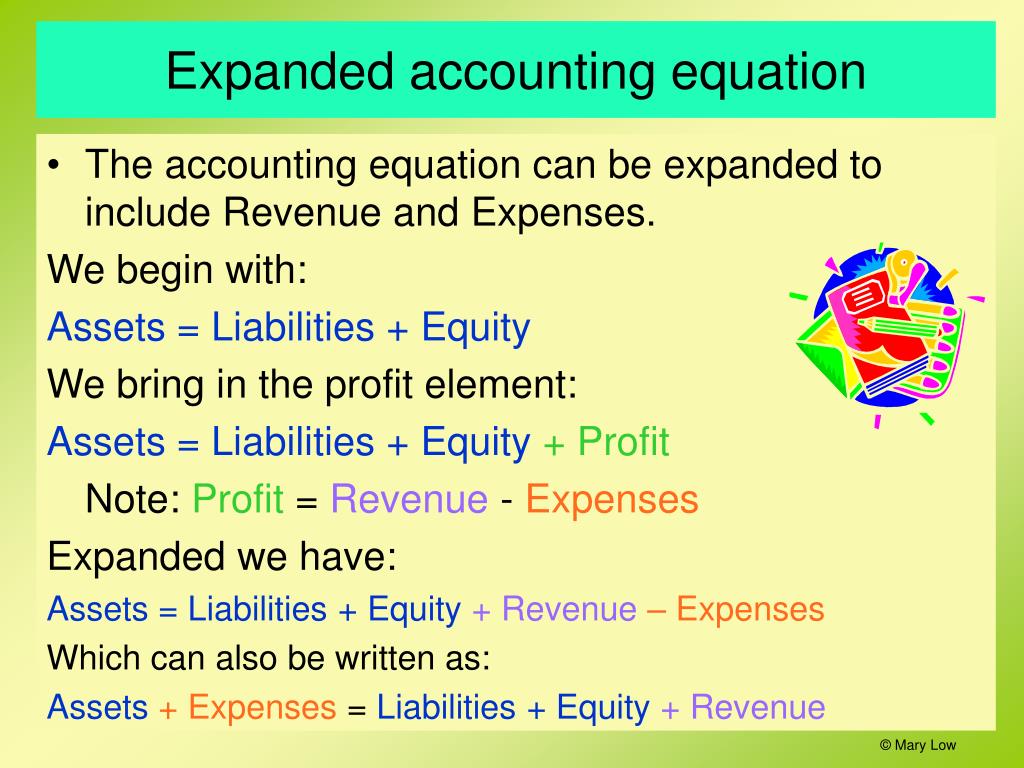
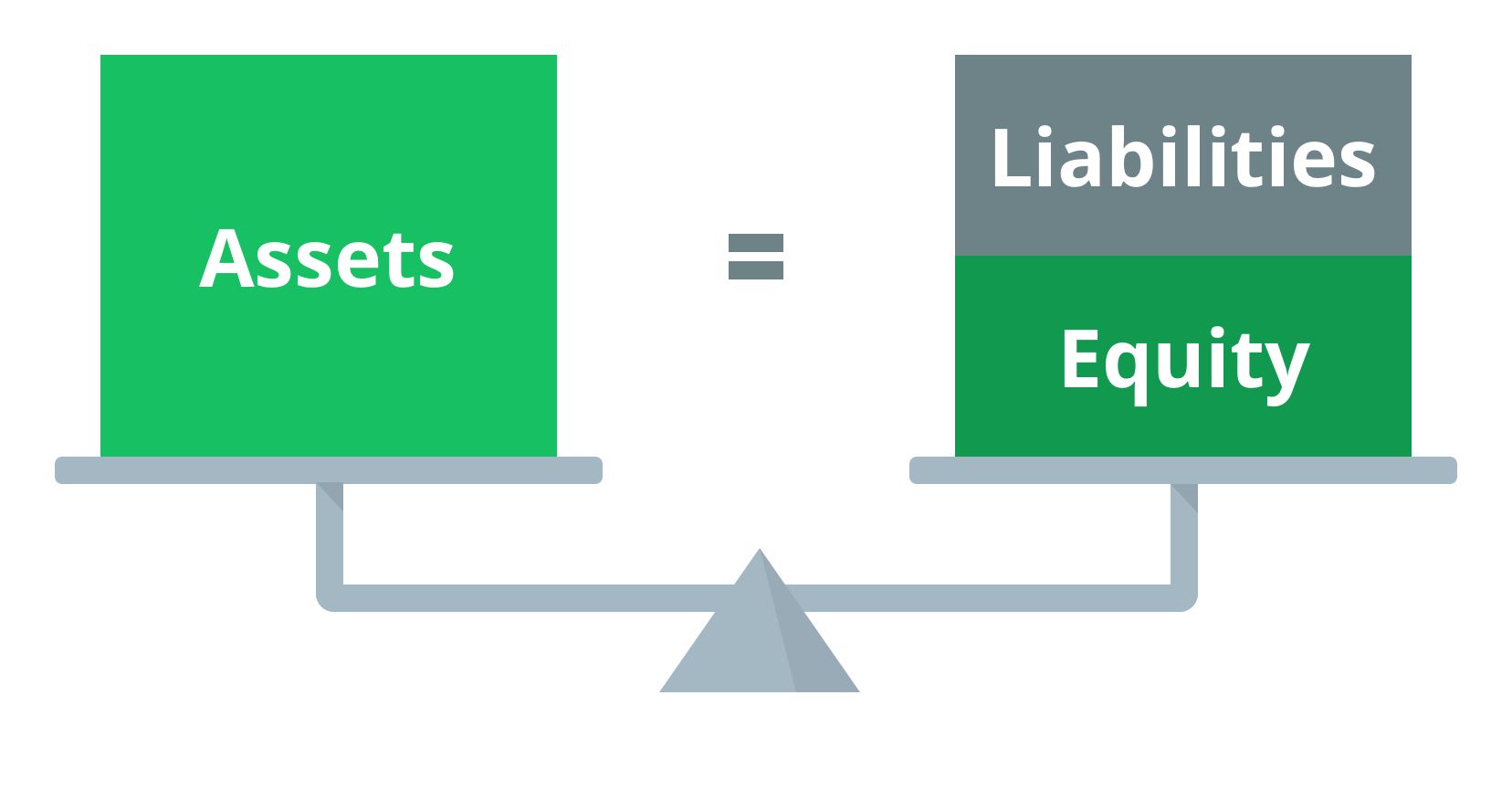
The Accounting Equation: The Foundation
The accounting equation is the fundamental principle underlying all accounting.
It states that Assets = Liabilities + Equity.
This equation demonstrates that a company's assets are financed by either liabilities (debts) or equity (owner's investment).
Real-World Application: A Quick Case Study
Imagine a small bakery. Its assets include cash ($5,000), baking equipment ($10,000), and inventory of ingredients ($2,000).
The bakery has liabilities in the form of a small business loan ($8,000) and amounts owed to suppliers ($1,000).
Therefore, the bakery's equity is $8,000 ($5,000 + $10,000 + $2,000 - $8,000 - $1,000 = $8,000).
Why This Matters Now
In today's volatile economic climate, understanding these financial concepts is paramount.
Businesses must accurately track their assets and liabilities to ensure solvency and make informed investment decisions.
Furthermore, monitoring revenue and expenses is crucial for profitability and sustainable growth.
Moving Forward: Next Steps
Business owners should immediately review their financial statements, consult with financial advisors, and implement robust accounting practices.
Ongoing developments in accounting standards and regulations require constant vigilance.
Ignoring these fundamentals could have dire consequences. Act now.