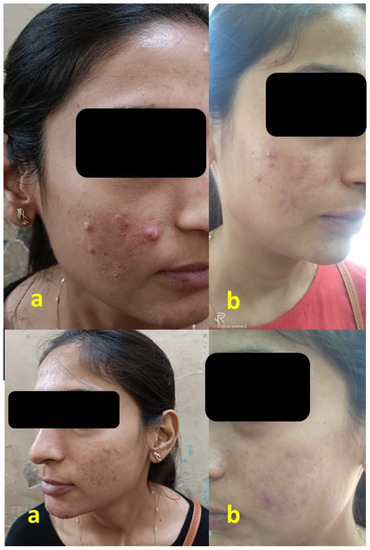
Before And After Clindamycin Phosphate Gel

Acne sufferers are reporting significant improvements following treatment with clindamycin phosphate gel, but dermatologists are urging caution regarding overuse. The topical antibiotic offers a potent solution for inflammatory acne but carries the risk of antibiotic resistance and other side effects, making informed use crucial.
Clindamycin phosphate gel is a topical antibiotic primarily used to treat acne vulgaris, particularly inflammatory lesions like papules and pustules. It works by inhibiting the growth of acne-causing bacteria, Cutibacterium acnes, and reducing inflammation. However, widespread and improper use has raised concerns among medical professionals.
The Visible Impact: Before and After
Clinical studies and patient testimonials showcase the potential effectiveness of clindamycin phosphate gel. Before treatment, individuals often present with moderate to severe acne characterized by red, inflamed pimples and potential scarring.
After consistent and proper application, many users experience a noticeable reduction in the number of acne lesions and inflammation. Skin texture can also improve, although results vary depending on the severity of the initial condition and adherence to treatment guidelines.
A study published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology demonstrated that clindamycin phosphate gel significantly reduced inflammatory lesions compared to a placebo. The study involved 150 participants with mild to moderate acne, tracked over a 12-week period.
Who Benefits Most?
Clindamycin phosphate gel is most effective for individuals with inflammatory acne. It's generally not recommended as a first-line treatment for mild comedonal acne (blackheads and whiteheads).
Dermatologists often prescribe it in combination with other acne treatments, such as benzoyl peroxide or retinoids, to enhance its effectiveness and minimize the risk of antibiotic resistance. This combination approach targets different aspects of acne development.
Real Patient Experiences
"I struggled with acne for years, and clindamycin gel really helped calm the inflammation," says Sarah M., a 28-year-old patient. "My skin is much clearer now, but I make sure to use it exactly as my doctor prescribed."
However, not all experiences are positive. "I saw some improvement initially, but then my acne came back worse than before," reports David L., 35. "My dermatologist said I might have developed antibiotic resistance."
The Risk of Resistance: A Growing Concern
The overuse of topical antibiotics like clindamycin phosphate gel contributes to the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria. This is a significant public health concern, as it can make acne more difficult to treat in the long run.
Cutibacterium acnes can develop resistance to clindamycin through various mechanisms, including genetic mutations. Resistant bacteria can then proliferate, leading to treatment failure.
The American Academy of Dermatology recommends limiting the use of topical clindamycin and combining it with benzoyl peroxide to reduce the risk of resistance. This dual approach helps kill bacteria through different mechanisms.
Proper Usage: How to Maximize Benefits and Minimize Risks
Clindamycin phosphate gel should only be used under the guidance of a dermatologist. They can assess your skin condition and determine the most appropriate treatment plan.
Apply a thin layer of the gel to the affected areas once or twice daily, as directed by your doctor. Avoid contact with eyes, mouth, and mucous membranes.
It's crucial to follow your dermatologist's instructions carefully and to report any side effects, such as redness, dryness, or irritation. Discontinue use if severe reactions occur.
Where and When is it Available?
Clindamycin phosphate gel is available by prescription from pharmacies nationwide. Its availability and pricing may vary depending on the specific formulation and insurance coverage.
The medication is typically prescribed for a limited duration, usually 12 weeks, to minimize the risk of antibiotic resistance. Longer-term use requires careful monitoring by a dermatologist.
It's important to note that generics are widely available, offering a more affordable option for patients. Discuss the cost and potential alternatives with your doctor and pharmacist.
Next Steps: Monitoring and Future Developments
Dermatologists are actively researching new acne treatments that minimize the risk of antibiotic resistance. Alternative therapies, such as topical retinoids and other non-antibiotic options, are being explored.
Ongoing surveillance of antibiotic resistance patterns in Cutibacterium acnes is crucial for informing treatment guidelines. This helps ensure that acne is treated effectively and responsibly.
Patients experiencing acne should consult with a dermatologist to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses their specific needs and minimizes potential risks. Early intervention is key to preventing long-term scarring and improving skin health.