California Common Core State Standards Ela

Imagine a classroom buzzing with collaboration, students poring over historical documents, dissecting the nuances of a poem, and passionately debating the merits of different solutions to complex problems. This isn't just a scene from a Hollywood movie; it's a glimpse into classrooms across California where the Common Core State Standards (CCSS) for English Language Arts (ELA) are shaping the future of education.
The California Common Core State Standards for ELA aim to equip students with the critical thinking, reading, writing, and communication skills necessary to succeed in college, careers, and life. These standards, adopted by California in 2010, represent a shift toward deeper learning and a focus on applying knowledge in meaningful contexts.
The Genesis of Common Core ELA in California
The story of Common Core in California begins with a nationwide movement to create consistent educational standards across states. In the early 2000s, policymakers and educators recognized the need for greater coherence and rigor in K-12 education to ensure that all students, regardless of their zip code, were prepared for the demands of the 21st century.
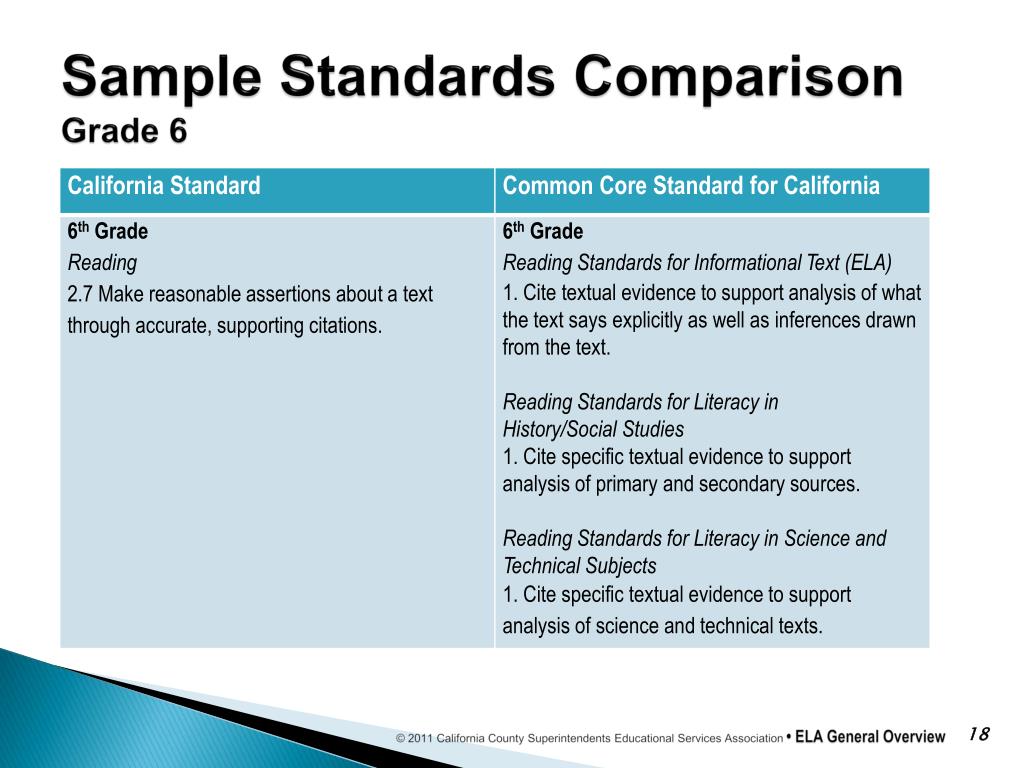
California, like many other states, joined the Common Core initiative, seeing it as an opportunity to raise academic expectations and improve student outcomes. The state adopted the CCSS for ELA and mathematics, but with some important modifications. These were branded as the California Common Core State Standards.
The state’s adaptation involved incorporating existing California standards and adding new content specific to the state's history, culture, and unique needs. The goal was to maintain the rigor of the Common Core while ensuring that the standards were relevant and meaningful to California's diverse student population.
Key Shifts in ELA Instruction
The CCSS for ELA represent a significant departure from traditional, skills-based instruction. They emphasize critical thinking, analysis, and the ability to apply knowledge in real-world contexts.
One key shift is the focus on informational texts. Students are expected to read and analyze a wider range of non-fiction materials, including historical documents, scientific articles, and technical manuals.
Another important change is the emphasis on evidence-based writing. Students are taught to support their arguments with evidence from texts and to cite sources appropriately. This helps develop strong analytical and argumentative skills.
The standards also promote collaborative discussions, where students learn to listen actively, share their ideas, and respectfully engage with different perspectives. These discussions help students deepen their understanding of complex topics and develop strong communication skills.
Impact and Implementation
The implementation of the California Common Core State Standards for ELA has been a complex and multifaceted process. It has required significant investment in teacher training, curriculum development, and assessment reform.
Teachers have been at the forefront of this effort, adapting their teaching practices to align with the new standards. They've embraced project-based learning, inquiry-based activities, and other innovative approaches to engage students and promote deeper learning.
The California Department of Education has provided resources and support to help teachers navigate the transition. This includes professional development workshops, online resources, and model curricula.
However, the implementation hasn't been without its challenges. Some teachers have struggled to adapt their teaching practices, and some parents have raised concerns about the rigor of the standards and the new assessment methods.
The Smarter Balanced Assessment Consortium (SBAC), a standardized test aligned with the Common Core, has been used to measure student progress. However, concerns about over-testing and the validity of standardized tests have led to ongoing debates about assessment practices.
Success Stories and Challenges
Despite the challenges, there are many examples of schools and districts in California that have successfully implemented the Common Core ELA standards. These schools have seen improvements in student engagement, critical thinking skills, and academic outcomes.
For example, some schools have adopted project-based learning models where students work collaboratively on real-world problems, applying their ELA skills to research, analyze, and present their findings. These projects not only help students develop their academic skills but also foster creativity, problem-solving abilities, and a sense of civic responsibility.
However, there are still significant achievement gaps among different student groups. Low-income students, students of color, and English learners continue to face systemic barriers to academic success. Addressing these inequities requires a comprehensive approach that includes targeted interventions, culturally responsive teaching, and increased investment in schools and communities.
Looking Ahead: The Future of ELA Education in California
The California Common Core State Standards for ELA are not static; they are constantly evolving to meet the changing needs of students and society. Educators and policymakers are continually reflecting on the successes and challenges of implementation and making adjustments as needed.
The focus is increasingly on providing personalized learning experiences that cater to the individual needs and interests of each student. Technology is playing an increasingly important role in this effort, providing access to a wealth of resources and tools that can support differentiated instruction.
Efforts are also underway to promote equity and ensure that all students have access to high-quality ELA instruction. This includes addressing issues such as teacher shortages, funding disparities, and the achievement gap.
According to the California Department of Education, ongoing professional development remains a key component, focusing on refining instructional practices, supporting diverse learners, and integrating technology effectively. The goal is to ensure that educators are equipped with the knowledge and skills they need to help all students succeed.
A Brighter Future Through Language
The journey to implement the California Common Core State Standards for ELA has been a long and winding one, filled with challenges and triumphs. But through it all, the goal has remained constant: to empower students with the language skills they need to navigate the complexities of the 21st century.
By fostering critical thinking, communication, and collaboration, the Common Core ELA standards are helping to prepare students for success in college, careers, and life. And as students continue to engage with challenging texts, express their ideas clearly, and work together to solve problems, they are building a foundation for a brighter future for themselves and for California.
The standards are more than just a set of guidelines; they represent a commitment to ensuring that all students have the opportunity to reach their full potential. This is not just about raising test scores; it's about cultivating a lifelong love of learning and empowering students to become informed, engaged, and responsible citizens.