Can Peripheral Neuropathy Be Caused By Stress
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/nerve-tingling-is-it-a-stroke-3145943-HL-d52bb6e327544076a9a422579024d94e.png)
Imagine a relentless buzzing in your feet, a pins-and-needles sensation that just won't quit, or a numbness that creeps up your legs, making each step feel precarious. For many, this is the reality of peripheral neuropathy, a condition affecting millions worldwide, leaving them searching for answers and relief.
The prevailing wisdom points to diabetes, injuries, infections, and certain medications as the primary culprits behind this nerve damage. But what if the invisible weight of chronic stress, the kind that gnaws at you day in and day out, could also play a role? This article explores the potential link between chronic stress and the development or exacerbation of peripheral neuropathy, offering insights into this complex relationship and potential avenues for managing both conditions.
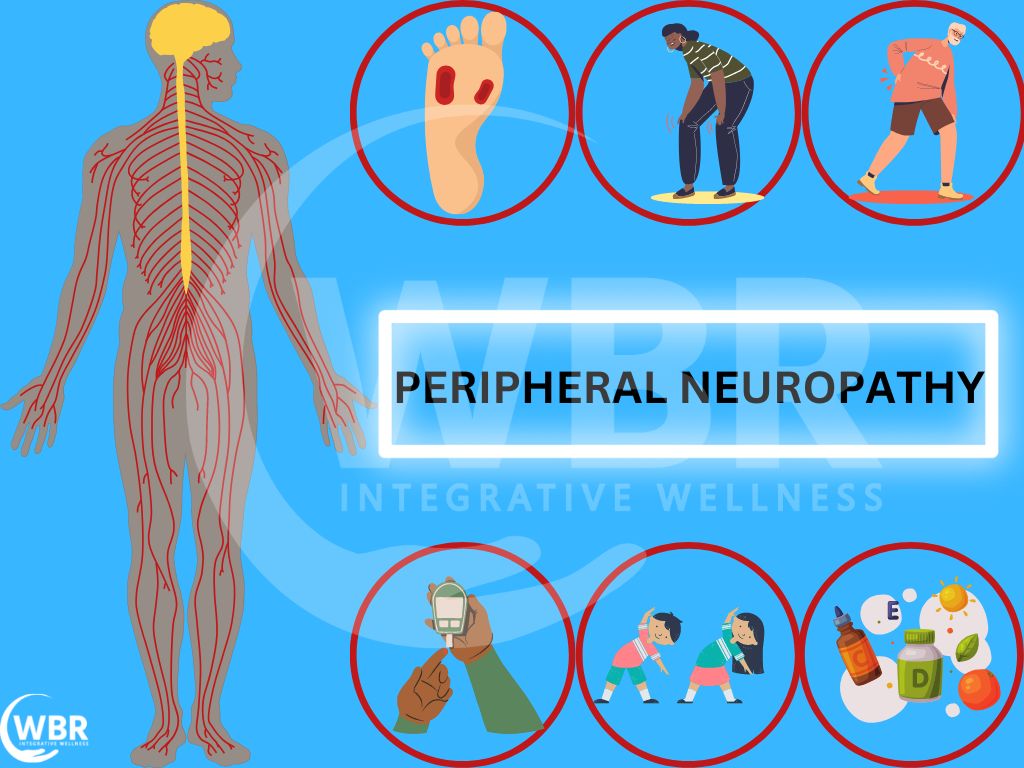
Understanding Peripheral Neuropathy
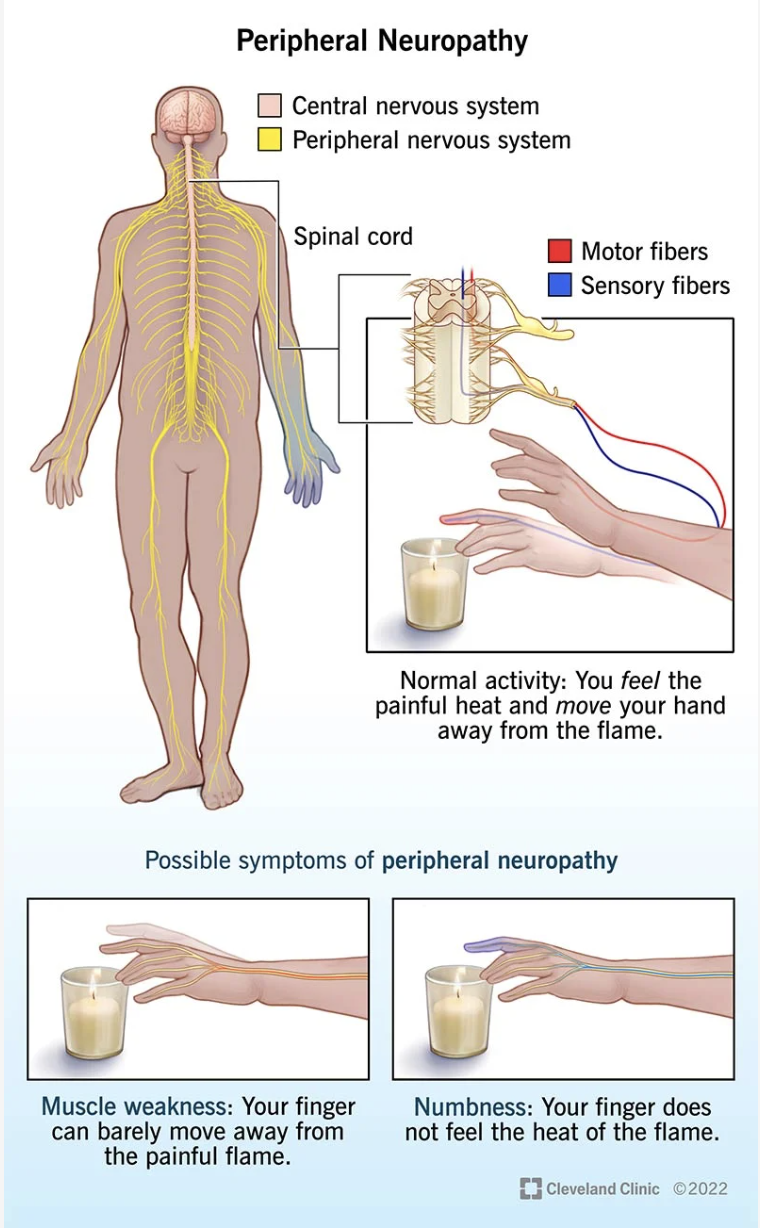
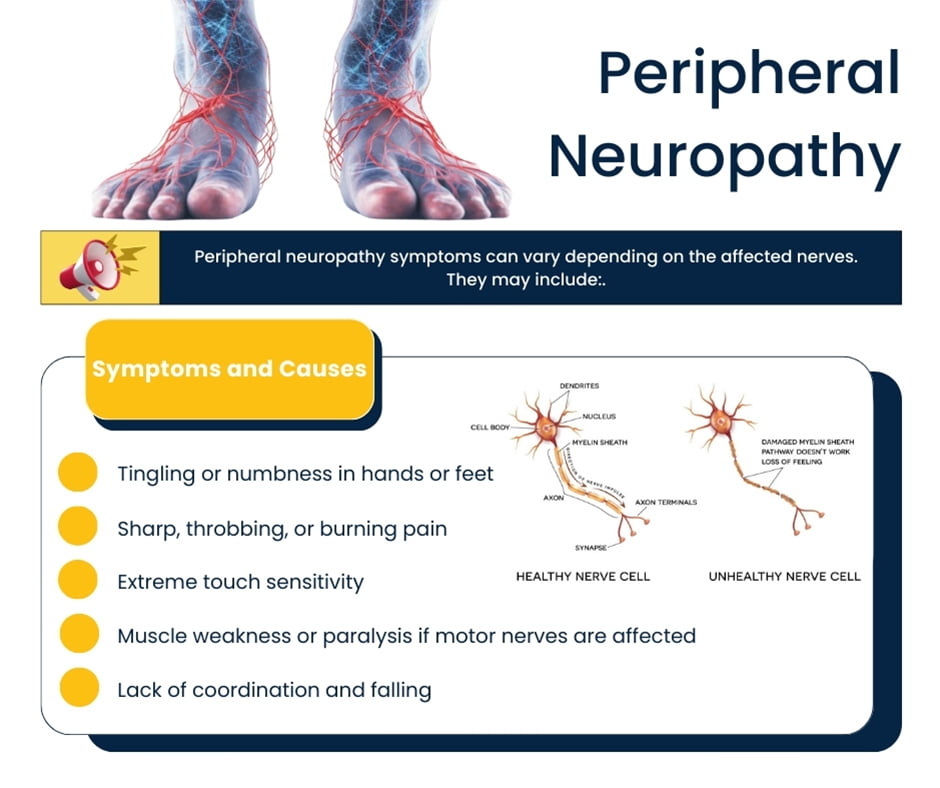
Peripheral neuropathy occurs when the nerves outside of the brain and spinal cord (the peripheral nerves) become damaged. These nerves are responsible for transmitting information between the central nervous system and the rest of the body.
Damage to these nerves can disrupt this communication, leading to a variety of symptoms, ranging from mild discomfort to debilitating pain.
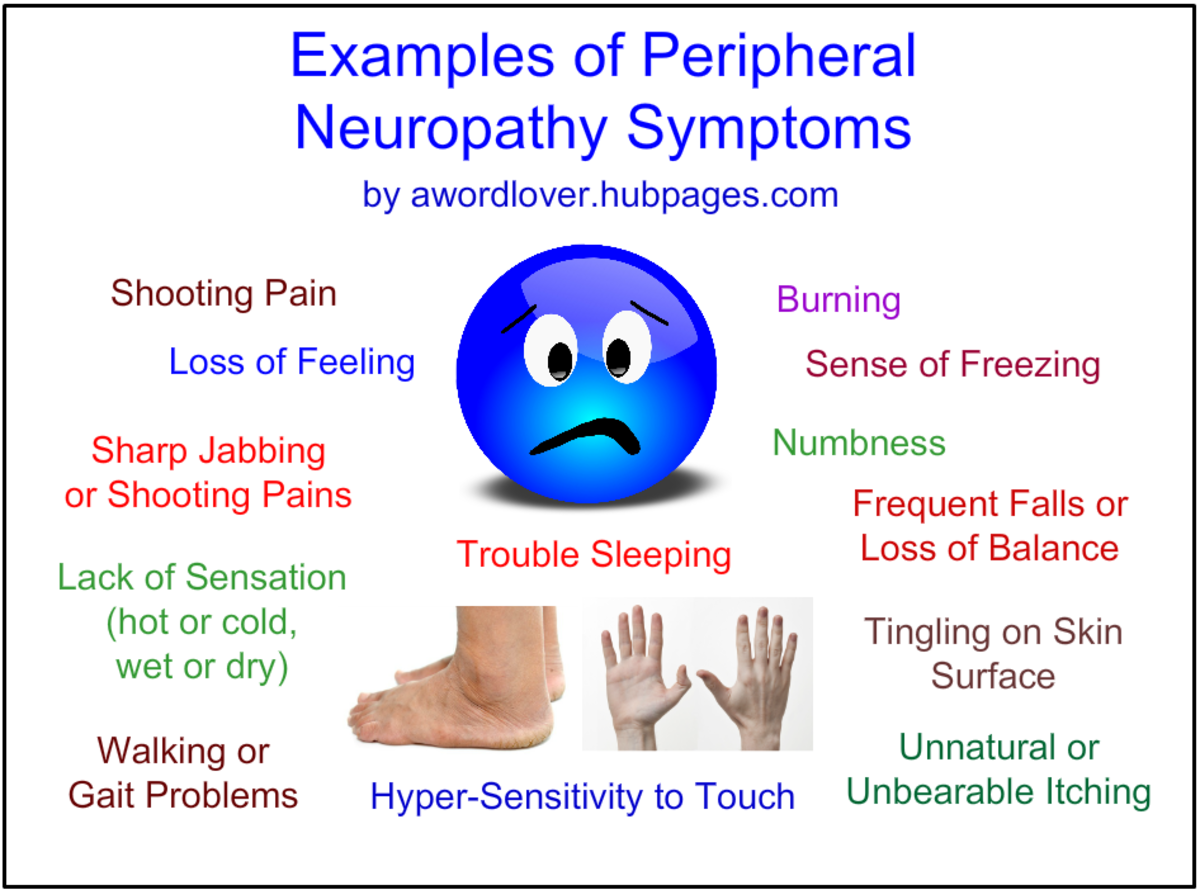
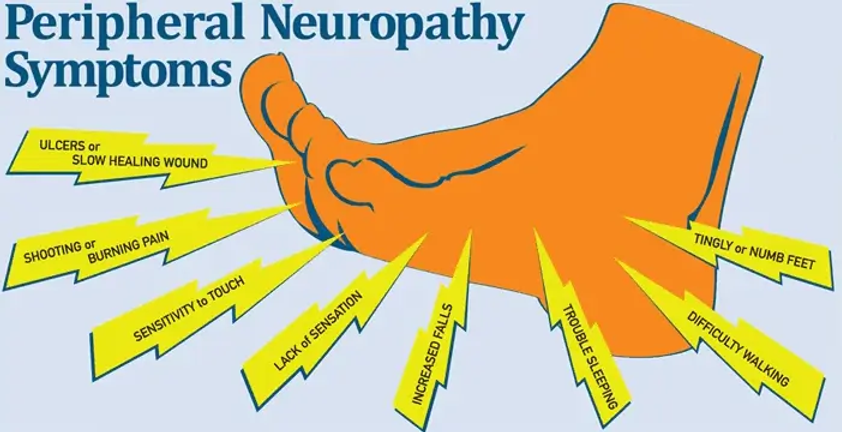
Common symptoms include:
- Numbness and tingling in the hands and feet
- Sharp, throbbing, or burning pain
- Increased sensitivity to touch
- Muscle weakness
- Loss of coordination
- Difficulty walking
Traditional Causes of Peripheral Neuropathy
While the connection to stress is being investigated, numerous established causes of peripheral neuropathy are well-documented. Diabetes is a leading cause, with high blood sugar levels damaging nerves over time.
Physical trauma, such as injuries from accidents or repetitive motions, can also directly damage nerves. Certain infections, like shingles and Lyme disease, can lead to nerve inflammation and damage.
Furthermore, some medications, particularly those used in chemotherapy, have neurotoxic effects and can cause peripheral neuropathy as a side effect. Autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis and lupus can also contribute to nerve damage.
The Stress Connection: A Growing Area of Research
Emerging research suggests a compelling, albeit complex, relationship between chronic stress and peripheral neuropathy. The human body's response to stress involves the activation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, leading to the release of stress hormones like cortisol.
While cortisol is essential for managing acute stress, prolonged exposure to elevated levels can have detrimental effects on the body, including the nervous system.
One potential mechanism through which stress might contribute to peripheral neuropathy is by exacerbating inflammation. Chronic stress is known to promote systemic inflammation, which can damage nerve cells and impair their function.
Inflammation can disrupt the protective myelin sheath that surrounds nerve fibers, further contributing to nerve damage. Additionally, chronic stress can impair blood flow to the peripheral nerves, depriving them of oxygen and nutrients and hindering their ability to function properly.
Studies have shown that chronic stress can lead to changes in nerve growth factors, which are essential for nerve survival and regeneration. Reduced levels of these factors can make nerves more vulnerable to damage and slow down the healing process.
While direct causation is difficult to establish, the evidence suggests that chronic stress can significantly worsen the symptoms and progression of peripheral neuropathy, particularly in individuals already predisposed to the condition.
Expert Opinions and Ongoing Studies
Dr. Anya Sharma, a neurologist specializing in peripheral neuropathy, explains, "We're seeing increasing evidence that chronic stress can act as a significant aggravating factor for patients with peripheral neuropathy. While it might not be the sole cause in many cases, it can certainly amplify symptoms and hinder recovery."
She emphasizes the importance of addressing stress as part of a comprehensive treatment plan. "Managing stress through techniques like mindfulness, exercise, and therapy can be incredibly beneficial in improving patients' quality of life and overall outcomes," Dr. Sharma adds.
Researchers are actively investigating the specific pathways through which stress impacts peripheral nerve function. Ongoing studies are exploring the role of specific stress hormones, inflammatory markers, and nerve growth factors in the development and progression of neuropathy. These studies aim to identify potential targets for interventions that can mitigate the effects of stress on the nervous system.
Managing Stress to Mitigate Neuropathy Symptoms
Given the potential link between stress and peripheral neuropathy, incorporating stress management techniques into a treatment plan can be highly beneficial. A holistic approach that addresses both the physical and psychological aspects of the condition is often the most effective.
Here are some strategies that can help manage stress and potentially alleviate neuropathy symptoms:
- Mindfulness and Meditation: Practicing mindfulness and meditation can help reduce stress hormones and promote relaxation. Regular meditation can train the mind to focus on the present moment, reducing anxiety and improving overall well-being.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity is a powerful stress reliever and can also improve circulation and nerve function. Low-impact exercises like walking, swimming, or yoga are often recommended for individuals with peripheral neuropathy.
- Healthy Diet: Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can provide the nutrients needed for nerve health and overall well-being. Avoiding processed foods, excessive sugar, and alcohol can also help reduce inflammation.
- Adequate Sleep: Getting enough sleep is crucial for managing stress and allowing the body to repair itself. Aim for 7-8 hours of quality sleep each night.
- Therapy and Counseling: Talking to a therapist or counselor can provide valuable support and coping strategies for managing chronic stress and its impact on health. Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is particularly effective in helping individuals change negative thought patterns and behaviors.
- Support Groups: Connecting with others who have peripheral neuropathy can provide a sense of community and shared understanding. Support groups offer a safe space to share experiences, learn coping strategies, and receive emotional support.
It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses your specific needs and circumstances. Managing underlying conditions, such as diabetes, is also crucial for preventing further nerve damage.
Looking Ahead: Hope and Empowerment
While living with peripheral neuropathy and chronic stress can be challenging, it's important to remember that there is hope. By understanding the potential link between these conditions and taking proactive steps to manage stress, individuals can significantly improve their quality of life.
The journey toward managing peripheral neuropathy and stress is often a marathon, not a sprint. It requires patience, persistence, and a willingness to experiment with different strategies to find what works best.
Empowerment comes from knowledge and action. By educating yourself about peripheral neuropathy, understanding the role of stress, and taking control of your health, you can pave the way for a brighter, more comfortable future. Remember, you are not alone, and with the right support and resources, you can navigate this journey with resilience and grace.



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/peripheral-neuropathy-explained-1901092-5c8fc07346e0fb00017700e6.png)





.jpg)


