Can You Take Melatonin And Magnesium Glycinate Together

The amber glow of the bedside lamp casts long shadows across the room. Outside, the crickets chirp their nightly symphony, a sound that usually lulls you to sleep. Tonight, however, your mind is racing, replaying the day's events on an endless loop. You reach for the familiar supplements on your nightstand – melatonin and magnesium glycinate – and a question pops into your head: Are these two sleep aids safe to take together?
This is a question many grapple with as they navigate the world of sleep supplements. While both melatonin and magnesium glycinate are individually known for their sleep-promoting properties, combining them raises valid concerns. The general answer from experts is that, for most individuals, taking melatonin and magnesium glycinate together is generally considered safe, and could potentially offer enhanced sleep benefits.
Understanding Melatonin and Magnesium Glycinate
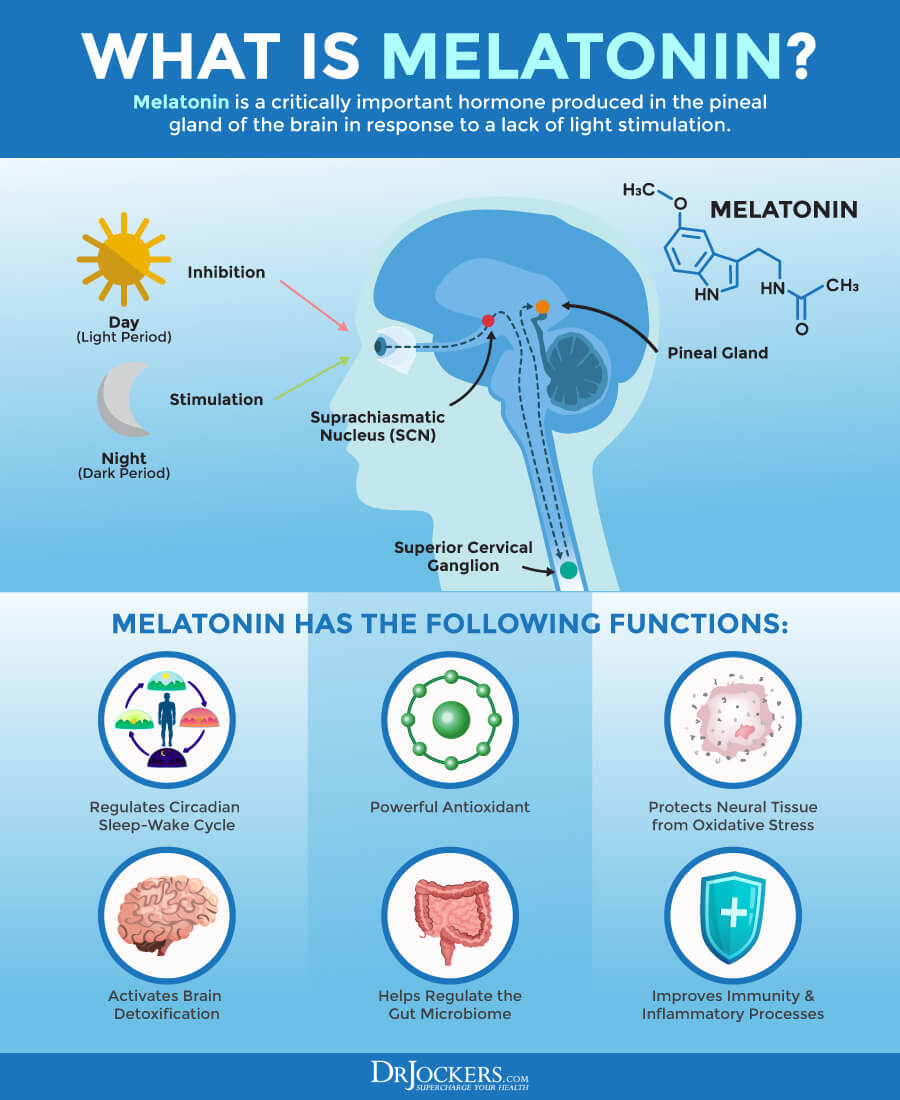
Melatonin is a naturally occurring hormone produced by the pineal gland in the brain. It plays a crucial role in regulating the sleep-wake cycle, often referred to as the circadian rhythm. Melatonin levels typically rise in the evening, signaling to the body that it's time to sleep, and decrease in the morning to promote wakefulness.
Supplemental melatonin can be helpful for individuals experiencing jet lag, shift work sleep disorder, or other conditions that disrupt their sleep patterns. It essentially acts as a signal, helping to nudge the body's internal clock back on track.
Magnesium, on the other hand, is an essential mineral involved in hundreds of bodily functions. These functions include muscle and nerve function, blood sugar control, and blood pressure regulation. Different forms of magnesium exist, with magnesium glycinate being particularly well-regarded for its bioavailability and gentle effect on the digestive system.
Magnesium glycinate, in particular, is known for its calming and relaxing properties. It can help to reduce anxiety and muscle tension, making it easier to fall asleep and stay asleep.
The Potential Benefits of Combining Them
The synergistic effect is the most compelling argument for combining melatonin and magnesium glycinate. Melatonin helps to regulate the sleep-wake cycle. Meanwhile, magnesium promotes relaxation. Together, they address sleep from different angles.
Some studies suggest that magnesium deficiency can disrupt melatonin production. Supplementing with magnesium glycinate may indirectly support healthy melatonin levels. This, in turn, can lead to better sleep quality.
Many individuals report experiencing improved sleep latency (the time it takes to fall asleep). They also report increased sleep duration and overall sleep quality when taking both supplements. These reports, while anecdotal, are common and highlight the potential benefits of this combination.
Potential Risks and Side Effects
While generally safe, it's important to be aware of potential side effects when taking melatonin and magnesium glycinate together. Side effects are generally mild when taken within the recommended dosage.
Common side effects of melatonin include drowsiness, headache, dizziness, and nausea. Some individuals may experience vivid dreams or nightmares.
Magnesium glycinate can sometimes cause digestive issues, such as diarrhea or stomach cramps, especially at higher doses. Starting with a low dose and gradually increasing it can help minimize these effects.
In rare cases, both supplements can interact with certain medications. It's crucial to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen, especially if you have underlying health conditions or are taking prescription drugs.
Dosage and Timing
Determining the right dosage of melatonin and magnesium glycinate depends on individual factors. These factors include age, weight, health status, and sensitivity to the supplements.
A typical dose of melatonin for sleep is between 0.3 mg and 5 mg, taken 30-60 minutes before bedtime. It's generally recommended to start with the lowest effective dose and gradually increase it as needed.
For magnesium glycinate, a common dosage range is between 200 mg and 400 mg, taken in the evening. Again, starting with a lower dose and gradually increasing it is advisable.
The timing of supplementation is also important. Taking melatonin too early in the evening can disrupt your natural sleep-wake cycle. Similarly, taking magnesium glycinate too close to a meal can interfere with its absorption.
Consulting with a Healthcare Professional
The information provided here is for general knowledge and informational purposes only, and does not constitute medical advice. It is essential to consult with a qualified healthcare professional before taking any new supplements, including melatonin and magnesium glycinate.
A healthcare provider can assess your individual needs, review your medical history, and identify any potential risks or interactions with medications you may be taking. They can also provide personalized recommendations on dosage and timing.
Self-treating sleep disorders can be risky, and it's important to rule out any underlying medical conditions that may be contributing to your sleep problems. A healthcare professional can help you identify the root cause of your sleep issues and develop a comprehensive treatment plan.
The Bottom Line
Combining melatonin and magnesium glycinate can potentially offer enhanced sleep benefits for many individuals. However, it's essential to approach this combination with caution and awareness.
Start with low doses, monitor your body's response, and consult with a healthcare professional to ensure safety and effectiveness. Remember that sleep is a complex process, and there is no one-size-fits-all solution.
Ultimately, the best approach is to prioritize good sleep hygiene practices, such as maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, creating a relaxing bedtime routine, and optimizing your sleep environment. Melatonin and magnesium glycinate can be helpful tools, but they are most effective when used in conjunction with healthy sleep habits.