Can You Take Nr And Nmn Together

The burgeoning field of longevity research is facing a critical question: Is combining Nicotinamide Riboside (NR) and Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN) safe and effective? Early adopters experimenting with these supplements must understand the limited research before combining these potent compounds.
This article dissects the current scientific understanding of combining NR and NMN, addressing safety concerns and highlighting the gaps in research that demand caution.
Understanding NR and NMN
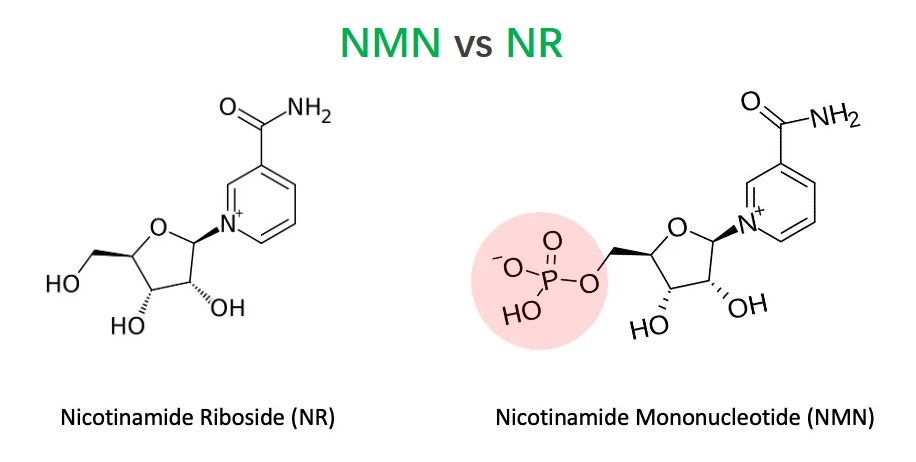
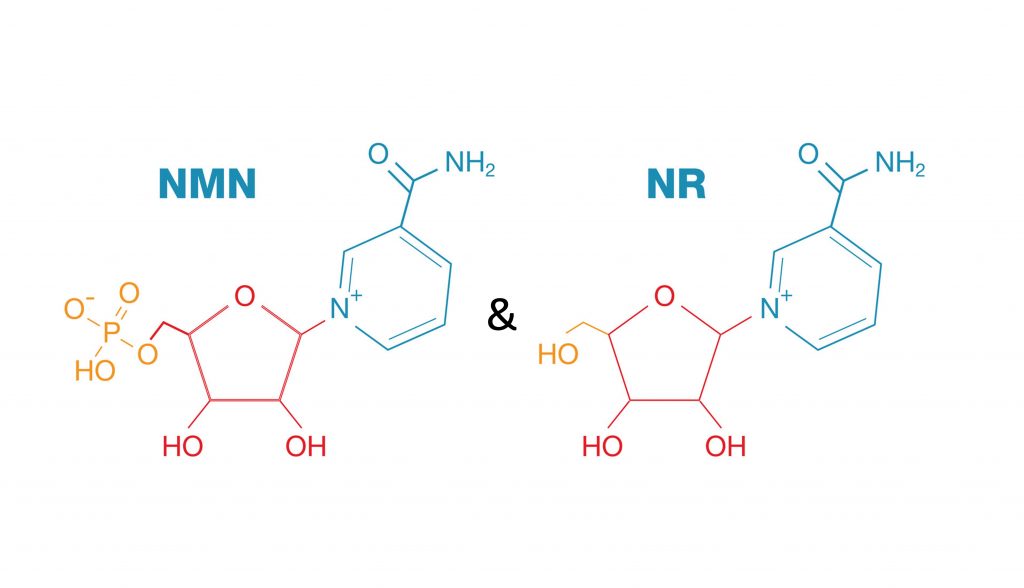
NR and NMN are precursors to Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD+), a crucial coenzyme involved in numerous cellular processes. NAD+ levels decline with age, prompting interest in NR and NMN as potential anti-aging interventions.
NR is a form of vitamin B3, while NMN is a nucleotide derived from ribose and nicotinamide. Both are marketed as dietary supplements to boost NAD+ levels.
The Rationale Behind Combination
The idea behind combining NR and NMN stems from the hypothesis that they might work synergistically to elevate NAD+ levels more effectively than either alone. Some believe that using both addresses different pathways or bottlenecks in NAD+ synthesis.
The precise mechanism is still debated. Some theories suggest NR is more efficiently absorbed into some tissues, while NMN might be better in others.
Current Scientific Evidence: Limited and Inconclusive
Human studies directly investigating the combined effects of NR and NMN are currently scarce. Most research has focused on each compound individually.
Several studies have shown that NR and NMN supplementation can increase NAD+ levels in humans. However, comparing results is difficult due to varied dosages, study durations, and participant demographics.
A lack of controlled trials specifically assessing the combined effects of NR and NMN makes definitive conclusions impossible.
Safety Concerns and Potential Risks
While both NR and NMN are generally considered safe at commonly used dosages, the safety profile of their combined use is less clear.
Potential risks could include unforeseen interactions, amplified side effects, or imbalances in metabolic pathways. Gastrointestinal distress is a common side effect reported in some studies of NR and NMN individually.
Long-term effects of both supplements, either alone or in combination, remain largely unknown. This is an important consideration.
Expert Opinions and Recommendations
Most experts recommend caution when considering combining NR and NMN. They emphasize the need for more research to understand the potential benefits and risks.
Dr. [Hypothetical Name], a leading researcher in aging, advises against combining the supplements without consulting a healthcare professional. "The long-term effects are simply not known, and individual responses can vary significantly," they stated.
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) stresses the importance of relying on evidence-based recommendations regarding dietary supplements.
Dosage Considerations
Since there are no established guidelines for combining NR and NMN, determining appropriate dosages is challenging. Individuals combining them typically use dosages similar to those used when taking each supplement alone. This is not a safe practice and should be avoided.
Dosages of NR often range from 300mg to 1000mg per day. NMN dosages vary widely, from 125mg to over 1000mg per day.
The potential for exceeding safe upper limits when combining these compounds should be carefully considered.
Future Research Directions
Future research should focus on conducting randomized, controlled trials to evaluate the combined effects of NR and NMN. These trials need to assess both efficacy and safety.
Studies should also investigate the optimal ratios and dosages of NR and NMN for different populations. This is key to better understanding.
Longitudinal studies are needed to determine the long-term effects of combining these supplements on health and longevity.
The Bottom Line
Currently, there is insufficient evidence to support the widespread use of combined NR and NMN supplementation. The lack of data means the potential benefits do not outweigh the unknown risks.
Until more robust research is available, individuals should exercise caution and consult with healthcare professionals before combining these supplements.
Ongoing research is critical to determine the true potential of these compounds for promoting healthy aging. Stay informed as the science evolves.