Cash Advance App That Works With Cash App
In an era defined by instant gratification and on-demand services, the rise of cash advance apps has been nothing short of meteoric. However, the landscape is fraught with complexities, especially when integrating with platforms like Cash App, raising concerns about transparency, user vulnerability, and the potential for exacerbating financial instability. This article delves into the nuances of cash advance apps that work with Cash App, exploring their functionalities, potential benefits, and the inherent risks they pose to consumers.
This analysis will dissect how these apps operate within the Cash App ecosystem. It will explore the regulatory landscape surrounding them, and offer guidance to users seeking to navigate this increasingly popular, yet potentially perilous financial service. The goal is to provide a balanced perspective, acknowledging the utility these apps can offer in times of need while simultaneously highlighting the critical importance of responsible usage and regulatory oversight.
The Appeal of Instant Access
Cash advance apps have gained traction by promising quick access to funds, often marketed as a solution for bridging the gap between paychecks. Their integration with widely used platforms like Cash App streamlines the process, making it even more convenient for users to obtain small loans. This convenience is particularly appealing to individuals with limited access to traditional banking services or those facing unexpected expenses.
For millions of Americans living paycheck to paycheck, these apps offer a seemingly easy solution to cover immediate needs. The allure of instant financial relief is powerful, and it’s a key driver of the industry’s rapid growth.
How Cash Advance Apps Work with Cash App
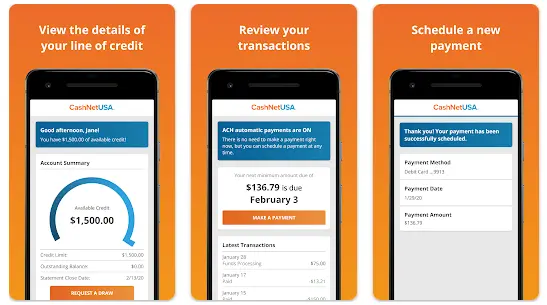
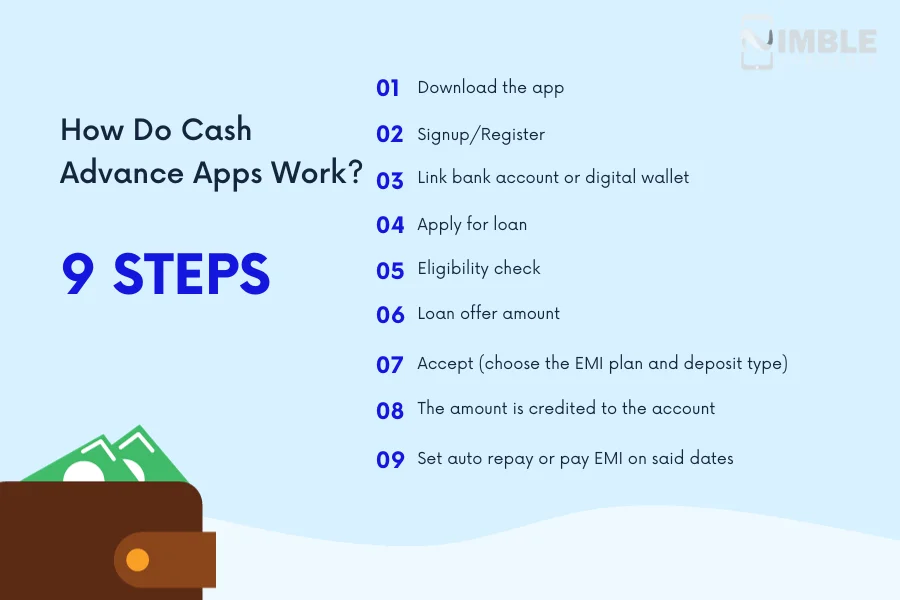
Cash advance apps typically function by analyzing a user’s banking history and transaction data to determine their eligibility for a loan. Once approved, funds are deposited directly into the user's Cash App account, often within minutes.
Repayment is usually automated, with the app withdrawing the owed amount from the user's bank account on their next payday. Some apps may also offer the option to repay through Cash App directly, linking the repayment process to the user's Cash App balance or linked debit card.
Transparency and Fees
One of the major concerns surrounding cash advance apps is the often opaque fee structure. While some apps advertise "no interest" or "zero fees," they often rely on tips or subscription models to generate revenue.
These tips can effectively function as interest, potentially resulting in high annual percentage rates (APRs) if calculated traditionally. Users need to carefully scrutinize the terms and conditions of each app to fully understand the costs involved.
The Role of Cash App
Cash App, developed by Block, Inc., serves as a critical facilitator for these cash advance apps. Its widespread adoption and ease of use make it a natural partner for apps aiming to provide quick access to funds.
However, Cash App itself generally does not offer its own cash advance services. It primarily acts as a platform for transferring funds, adding another layer of complexity when considering the regulatory oversight of these integrated services.
Potential Risks and Concerns
The convenience of cash advance apps comes with significant risks. The ease of borrowing can lead to a cycle of dependence, where users become reliant on these short-term loans to cover recurring expenses.
The high effective APRs, even with seemingly small fees, can quickly escalate the cost of borrowing. Furthermore, the automatic repayment feature can lead to overdraft fees if a user's account doesn't have sufficient funds on the designated repayment date.
Regulatory Scrutiny
The cash advance app industry is facing increased regulatory scrutiny due to concerns about predatory lending practices. The lack of clear regulations and oversight allows some apps to operate in a gray area, potentially exploiting vulnerable consumers.
State and federal regulators are actively exploring ways to address these issues, including implementing stricter disclosure requirements and capping fees. The Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB) is particularly focused on ensuring that consumers are adequately protected from potentially harmful financial products.
Data Privacy Concerns
Cash advance apps require access to sensitive financial information, raising concerns about data privacy and security. Users must carefully consider the privacy policies of each app and understand how their data is being used and protected.
Data breaches and unauthorized access to personal financial information are potential risks that users should be aware of. Choosing reputable apps with robust security measures is crucial.
Navigating the Landscape: Tips for Users
If considering using a cash advance app that works with Cash App, it's essential to exercise caution and conduct thorough research. Read the terms and conditions carefully, paying close attention to the fee structure and repayment terms.
Avoid borrowing more than you can afford to repay on your next payday. Create a budget and assess your financial situation before using these apps. Consider alternative options, such as negotiating with creditors or seeking assistance from nonprofit organizations.
Seek Alternatives
Explore other financial options before resorting to cash advance apps. This includes looking at credit unions or community banks for small personal loans or exploring options for earned wage access through your employer if available.
Building an emergency fund, even a small one, can provide a buffer against unexpected expenses and reduce the need for short-term borrowing.
The Future of Cash Advance Apps
The future of cash advance apps is likely to be shaped by increasing regulatory oversight and evolving consumer expectations. Greater transparency and stricter rules are needed to protect consumers from predatory lending practices.
As awareness of the risks associated with these apps grows, consumers may become more discerning in their choices, opting for more sustainable and responsible financial solutions. The industry will need to adapt to these changes to maintain its relevance and legitimacy.
Ultimately, the key lies in promoting financial literacy and empowering consumers to make informed decisions about their financial well-being. While cash advance apps may offer a temporary solution in times of need, they should not be viewed as a long-term substitute for sound financial planning and responsible budgeting.




![Cash Advance App That Works With Cash App 11 Best Cash Advance Apps That Work with Chime [2025] Updated](https://trybeem.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/Cash-Advance-Apps-That-Work-with-Chime-1024x576.webp)












