Constant Need To Urinate After Ejaculation

A persistent urge to urinate immediately after ejaculation, medically termed post-ejaculatory micturition, is a concern that affects a significant, albeit underreported, number of men. While often dismissed as a minor inconvenience, this symptom can be a source of considerable anxiety and may, in some instances, point to underlying health issues that require medical attention.
Understanding the causes, potential complications, and available treatments for this condition is crucial for both those experiencing it and the healthcare professionals who treat them.
This article delves into the complexities of post-ejaculatory micturition, exploring its potential causes, associated risk factors, diagnostic approaches, and management strategies, based on the latest medical research and expert opinions.
What is Post-Ejaculatory Micturition?
The sensation of needing to urinate shortly after ejaculation is not uncommon, but when it becomes a frequent and distressing occurrence, it warrants investigation. The condition, though not formally classified as a specific disease, often falls under the umbrella of lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) and can significantly impact quality of life.
It's essential to distinguish between the occasional urge to urinate after sex and a consistent, almost immediate, and sometimes painful, need to void.
The latter is what raises a red flag and should prompt a medical consultation.
Possible Causes and Contributing Factors
The etiology of post-ejaculatory micturition is multifactorial and can involve a complex interplay of neurological, hormonal, and anatomical factors.
Several potential causes have been identified, including:
1. Prostatitis and Prostatic Inflammation
Inflammation of the prostate gland, known as prostatitis, is a leading cause. This inflammation can irritate the bladder and urethra, leading to increased urinary frequency and urgency.
Chronic prostatitis, in particular, is often associated with a persistent feeling of needing to urinate, even after voiding.
The National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK) recognizes prostatitis as a common condition affecting men of all ages.
2. Overactive Bladder (OAB)
Overactive bladder is another potential culprit, characterized by a sudden, uncontrollable urge to urinate. Ejaculation can sometimes trigger or exacerbate OAB symptoms.
This is possibly due to nerve stimulation during sexual activity.
OAB is diagnosed through a combination of symptom evaluation, physical examination, and potentially, bladder function tests.
3. Pelvic Floor Dysfunction
Weak or dysfunctional pelvic floor muscles can contribute to urinary urgency and frequency.
These muscles play a crucial role in supporting the bladder and urethra, and when they are not functioning properly, it can lead to issues with bladder control.
Pelvic floor dysfunction can be addressed with targeted exercises and physical therapy.
4. Urethral Strictures
A narrowing of the urethra, called a urethral stricture, can obstruct the flow of urine and lead to urinary retention. This can then create a feeling of urgency after ejaculation.
Strictures can result from injury, infection, or inflammation.
Treatment often involves dilation or surgical repair of the urethra.
5. Psychological Factors
In some cases, anxiety or stress related to sexual performance or other life stressors can manifest as urinary symptoms.
The mind-body connection can play a significant role in bladder function.
Therapy and stress management techniques may be beneficial in addressing these psychological components.
Diagnosis and Evaluation
A thorough medical evaluation is essential to determine the underlying cause of post-ejaculatory micturition.
This typically involves a detailed medical history, physical examination, and various diagnostic tests.
Some common diagnostic procedures include:
- Urine analysis: To check for infection or other abnormalities.
- Prostate exam: To assess the size and consistency of the prostate gland.
- Uroflowmetry: To measure the rate and volume of urine flow.
- Post-void residual (PVR) measurement: To determine how much urine remains in the bladder after urination.
- Cystoscopy: A procedure that uses a thin, flexible tube with a camera to visualize the inside of the bladder and urethra.
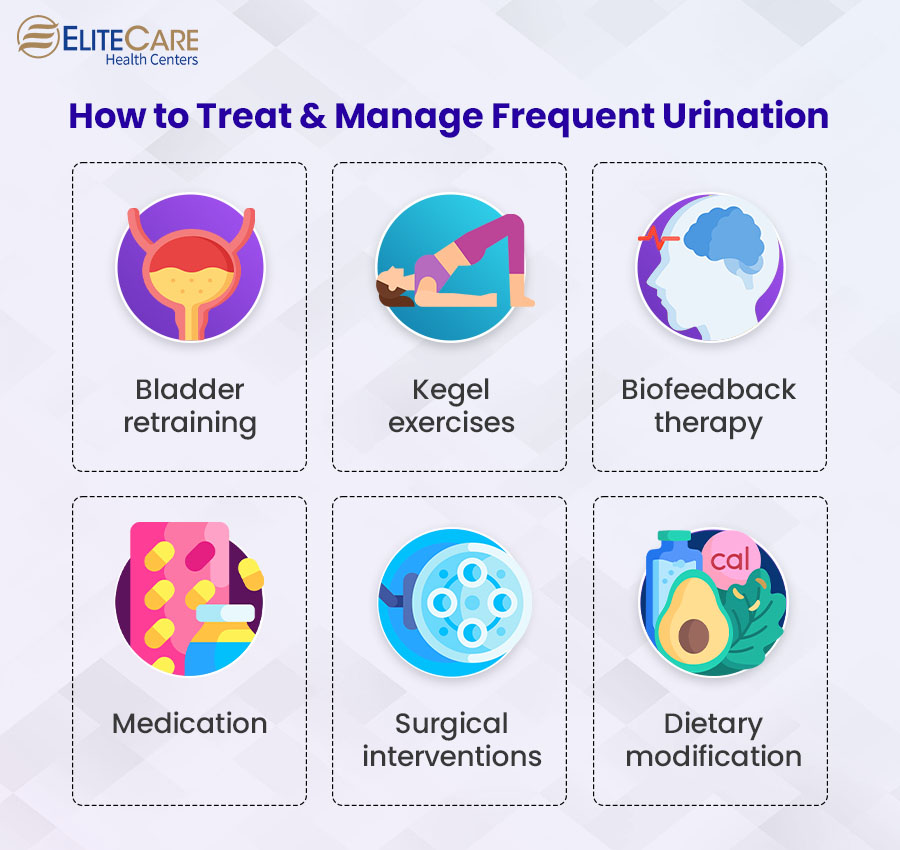
Treatment Options
The treatment approach for post-ejaculatory micturition depends on the underlying cause.
Options may include:
- Antibiotics: For bacterial prostatitis.
- Alpha-blockers: To relax the muscles in the prostate and bladder neck, improving urine flow.
- 5-alpha reductase inhibitors: To shrink the prostate gland in cases of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).
- Anticholinergics or beta-3 agonists: For overactive bladder.
- Pelvic floor physical therapy: To strengthen and rehabilitate pelvic floor muscles.
- Urethral dilation or surgery: For urethral strictures.
- Stress management techniques or therapy: For psychologically driven symptoms.
Living with Post-Ejaculatory Micturition
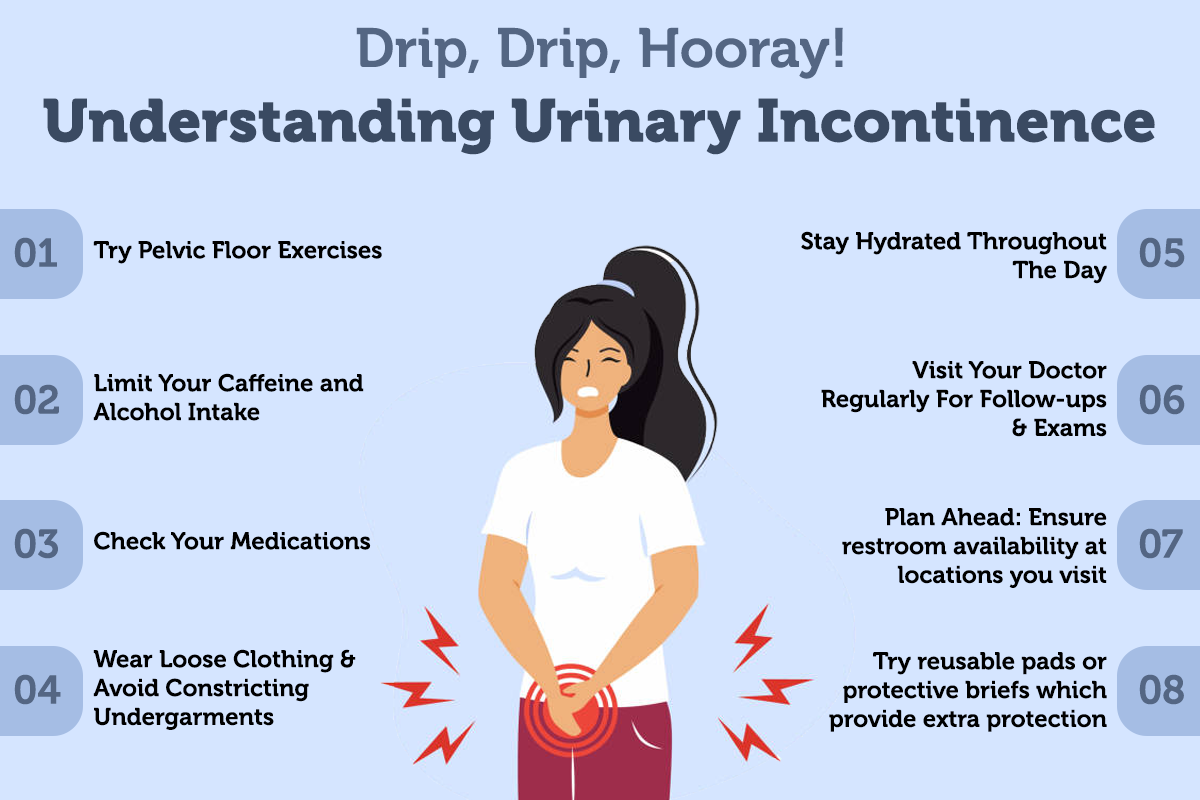
Managing post-ejaculatory micturition involves not only medical treatment but also lifestyle adjustments.
These adjustments may include limiting caffeine and alcohol intake, practicing bladder retraining techniques, and maintaining a healthy weight.
Open communication with a healthcare provider is crucial for developing an effective management plan and addressing any anxieties or concerns.
The Future of Research
Further research is needed to better understand the underlying mechanisms and develop more targeted therapies for post-ejaculatory micturition.
Studies focusing on the neurological and hormonal aspects of this condition are particularly important.
Increased awareness and open discussion will encourage more men to seek help, leading to improved diagnosis and management.
By fostering a greater understanding of this often-overlooked issue, we can improve the quality of life for countless men.




:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/frequent-urination-at-night-nocturia-3300107_V22-73a81516f53a4d088e28c74ec09f22d1.png)


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/urethralpainfnal-01-5c6332b946e0fb0001f255a7-feb3d6c689a446ffb72064e1443cf305.png)