Corporate Social Responsibility Topics

Imagine a world where businesses are about more than just profits. Where boardrooms buzz with discussions about environmental impact, ethical sourcing, and community well-being alongside quarterly earnings. This isn't a utopian dream; it's the evolving landscape of Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR), and its ripple effects are already being felt around the globe.
At its core, CSR represents a company's commitment to operating in an ethical and sustainable manner, considering its impact on society and the environment. It's about going beyond legal obligations to actively contribute to a better world. This article explores the key facets of CSR, its growing importance, and how it's transforming the business world.
The Roots and Rise of CSR
The concept of corporate responsibility isn't new. Throughout history, businesses have engaged in philanthropy and community support. However, the modern CSR movement gained momentum in the latter half of the 20th century, driven by increased awareness of environmental issues and social injustices.
The publication of Rachel Carson's Silent Spring in 1962, for example, sparked widespread concern about the impact of pesticides on the environment. This led to increased pressure on companies to be more environmentally responsible. The term CSR became popularized in the 1970s, with academics and business leaders beginning to explore its potential benefits.
Today, CSR is no longer a niche concept. It's a mainstream expectation. Consumers are increasingly demanding that companies align with their values. Investors are also paying attention. According to a 2023 report by Morgan Stanley, sustainable investing is on the rise, with more investors considering environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors in their investment decisions.
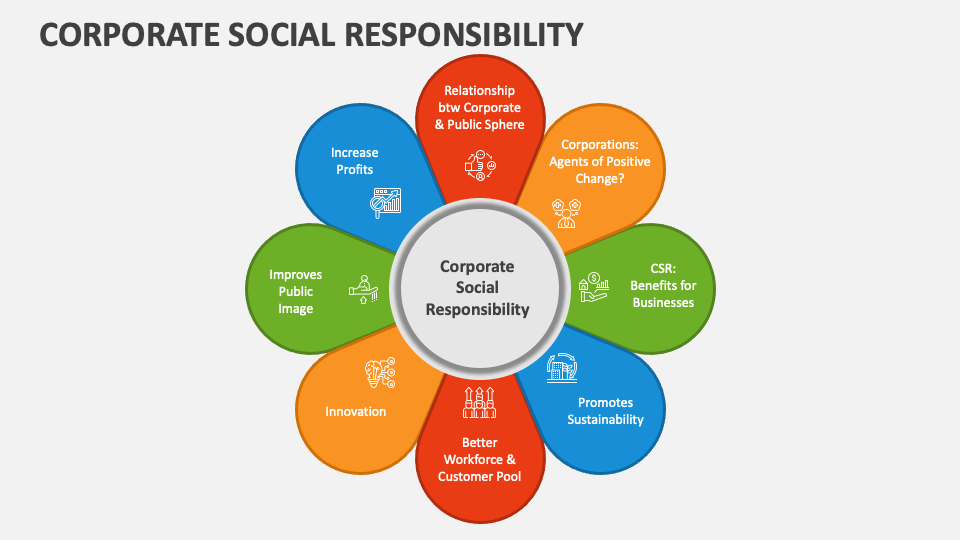
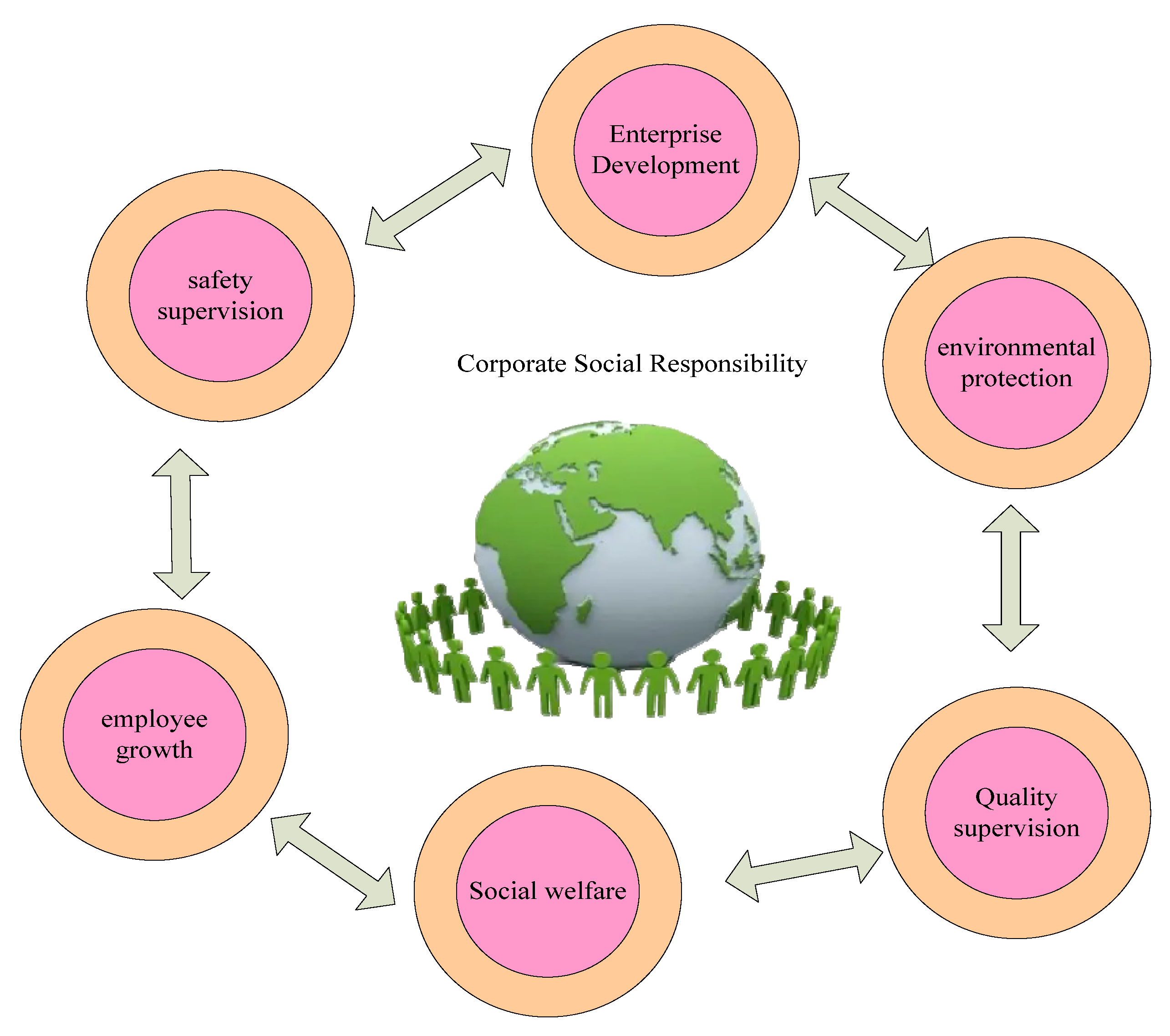
Key Pillars of CSR
CSR encompasses a wide range of activities, typically falling under several key pillars. Each pillar represents a critical aspect of a company's responsibility to stakeholders.
Environmental Sustainability
This pillar focuses on minimizing a company's environmental impact. This includes reducing carbon emissions, conserving resources, and preventing pollution.
Many companies are investing in renewable energy, implementing waste reduction programs, and adopting sustainable sourcing practices. For example, Patagonia, the outdoor clothing company, has long been a leader in environmental sustainability. The company actively works to reduce its environmental footprint and advocates for environmental protection.
Ethical Labor Practices
Ensuring fair wages, safe working conditions, and respect for human rights are central to this pillar. It involves addressing issues such as child labor, forced labor, and discrimination in the workplace.
Companies are increasingly auditing their supply chains to ensure that their suppliers adhere to ethical labor standards. The International Labour Organization (ILO) plays a crucial role in setting international labor standards and promoting decent work.
Community Engagement
This involves contributing to the well-being of the communities in which a company operates. This can include supporting local charities, sponsoring community events, and investing in education and infrastructure.
Many companies have established corporate foundations to support community initiatives. For instance, the Starbucks Foundation invests in programs that empower coffee farmers and their communities.
Ethical Sourcing and Supply Chain Responsibility
This crucial area ensures that companies are sourcing materials and products in a way that is both ethical and sustainable. It focuses on supply chain transparency, preventing exploitation and ensuring responsible resource management.
Fair Trade certifications play a significant role in ensuring farmers and producers in developing countries receive fair prices for their goods, fostering economic empowerment and social justice. Companies are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to ethical practices and sustainable sourcing.
The Business Case for CSR
While CSR is driven by ethical considerations, it also offers significant business benefits. A strong CSR program can enhance a company's reputation, attract and retain talent, and improve its bottom line.
Consumers are more likely to support companies that are perceived as socially responsible. According to a 2022 study by Nielsen, 66% of consumers are willing to pay more for products from companies that are committed to social and environmental responsibility.
Furthermore, CSR can improve employee morale and engagement. Employees are more likely to be proud to work for a company that is making a positive impact on the world. This can lead to increased productivity and reduced employee turnover.
Ultimately, CSR is about creating shared value. It's about finding ways to benefit both the company and society. By embracing CSR, businesses can build a more sustainable and equitable future for all.
"The business of business should not be about money, it should be about responsibility. It should be about public good, not private greed", says Anita Roddick, founder of The Body Shop, highlighting the fundamental shift in perspective required for effective CSR.
As we move forward, the importance of CSR will only continue to grow. Stakeholders are demanding greater accountability from businesses. Companies that embrace CSR will be best positioned to thrive in the long term.
The journey towards a more responsible and sustainable business world is a continuous one. It requires ongoing commitment, innovation, and collaboration. But the rewards – a healthier planet, a more equitable society, and a more prosperous future – are well worth the effort.