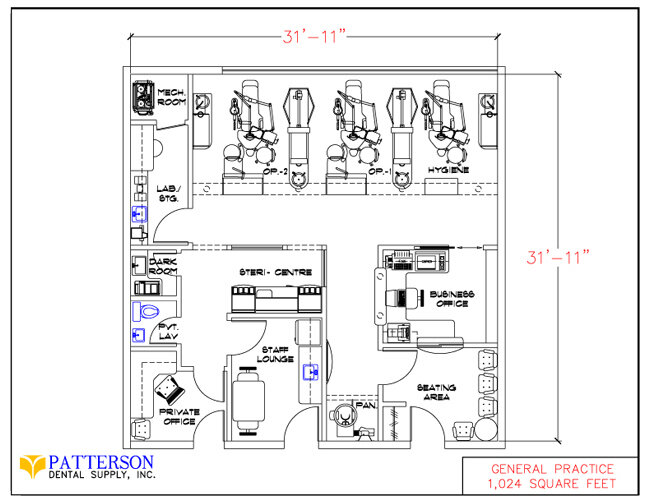
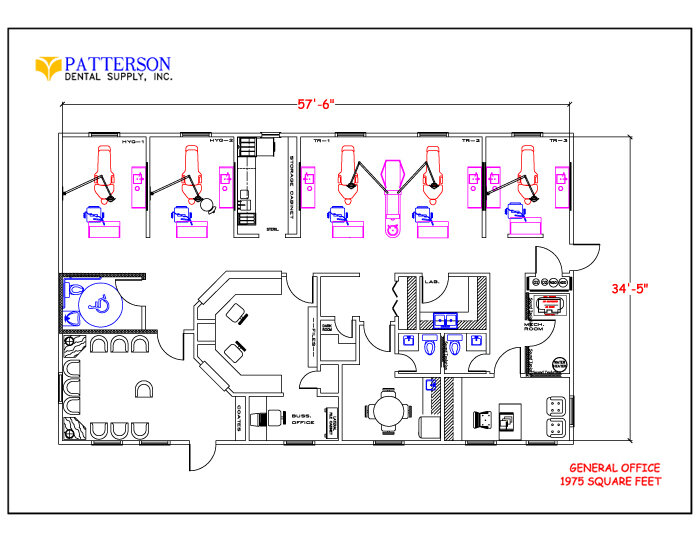
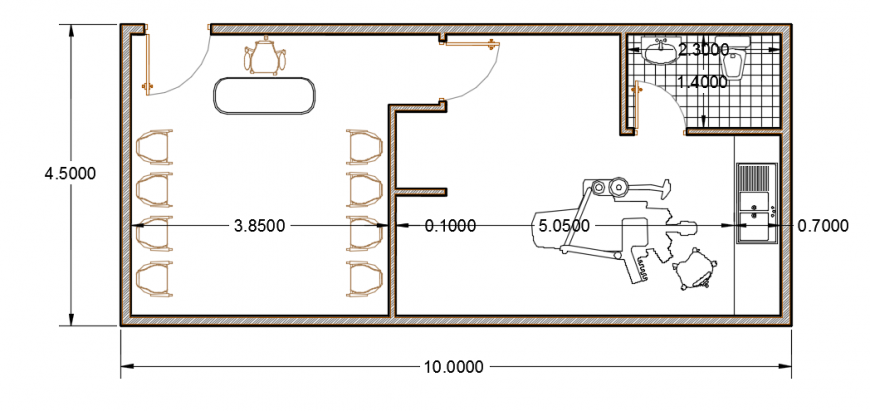
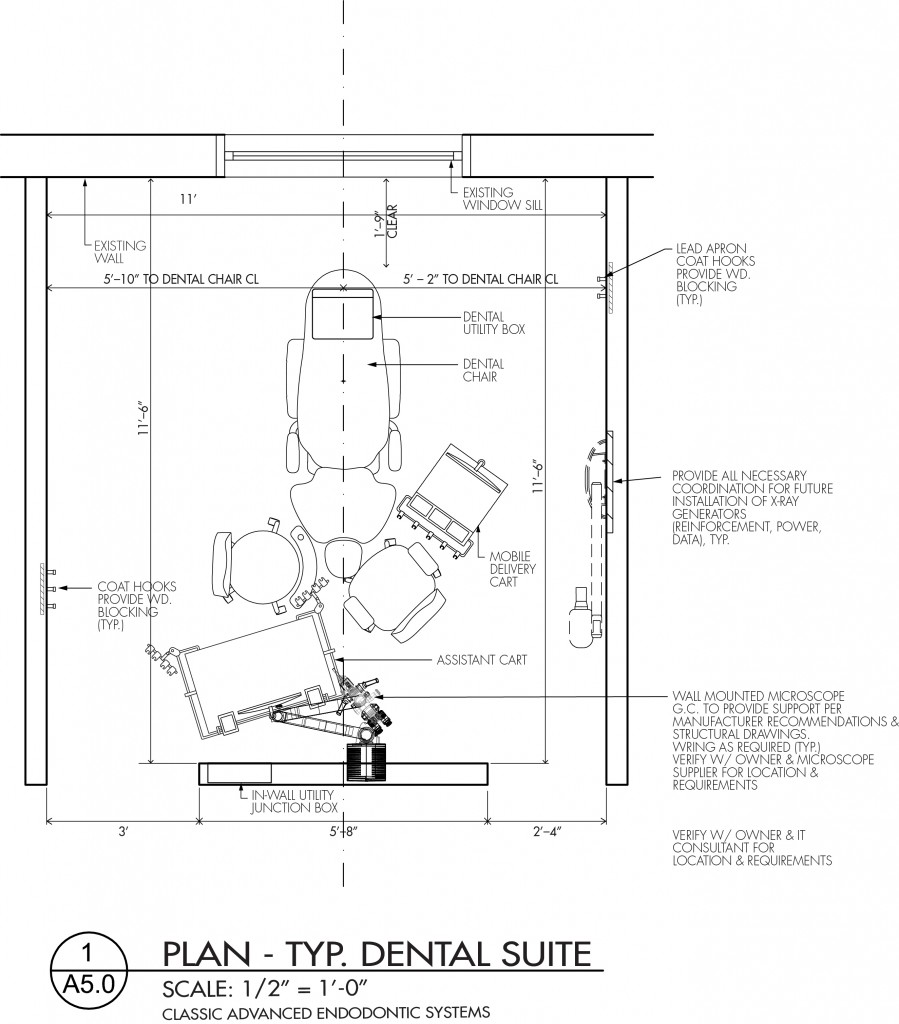
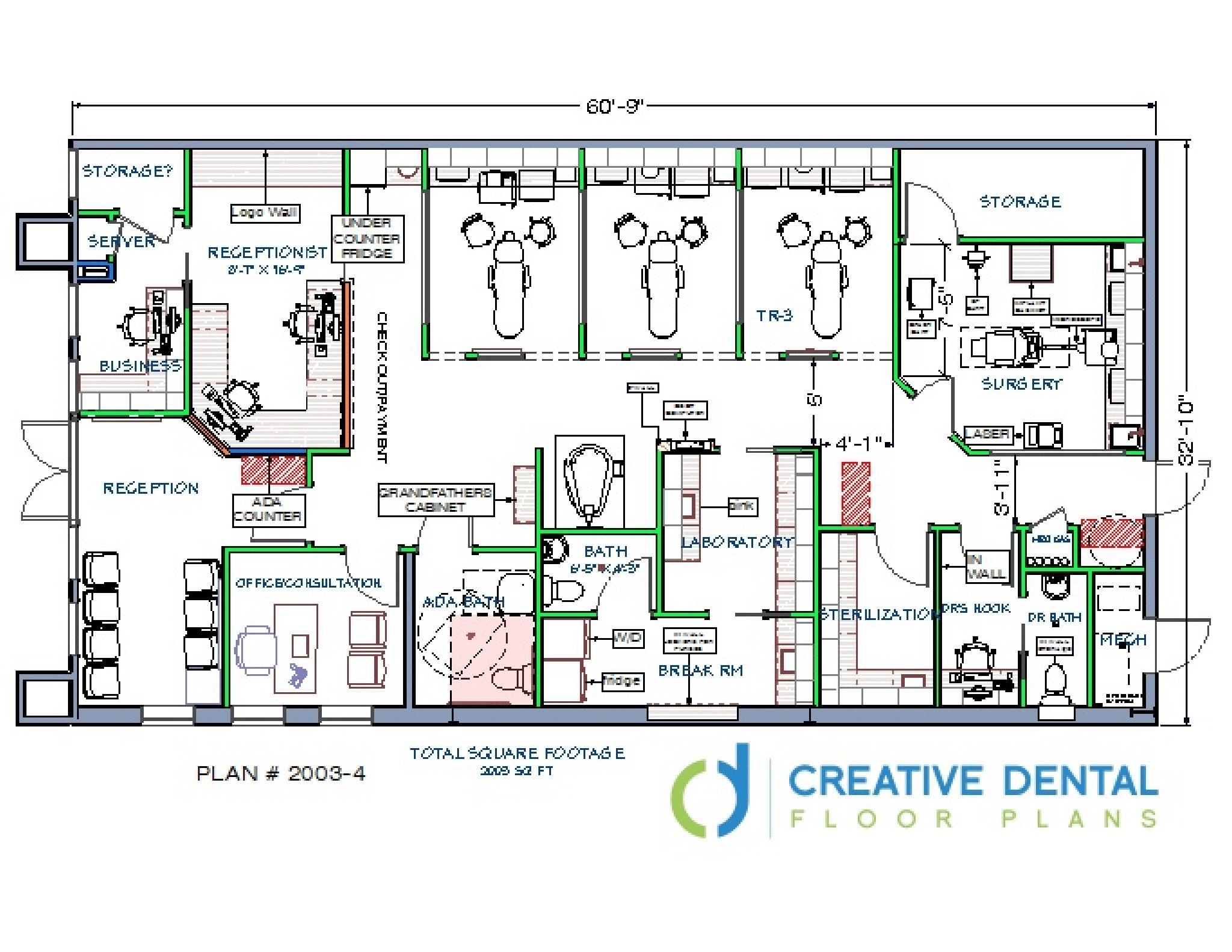
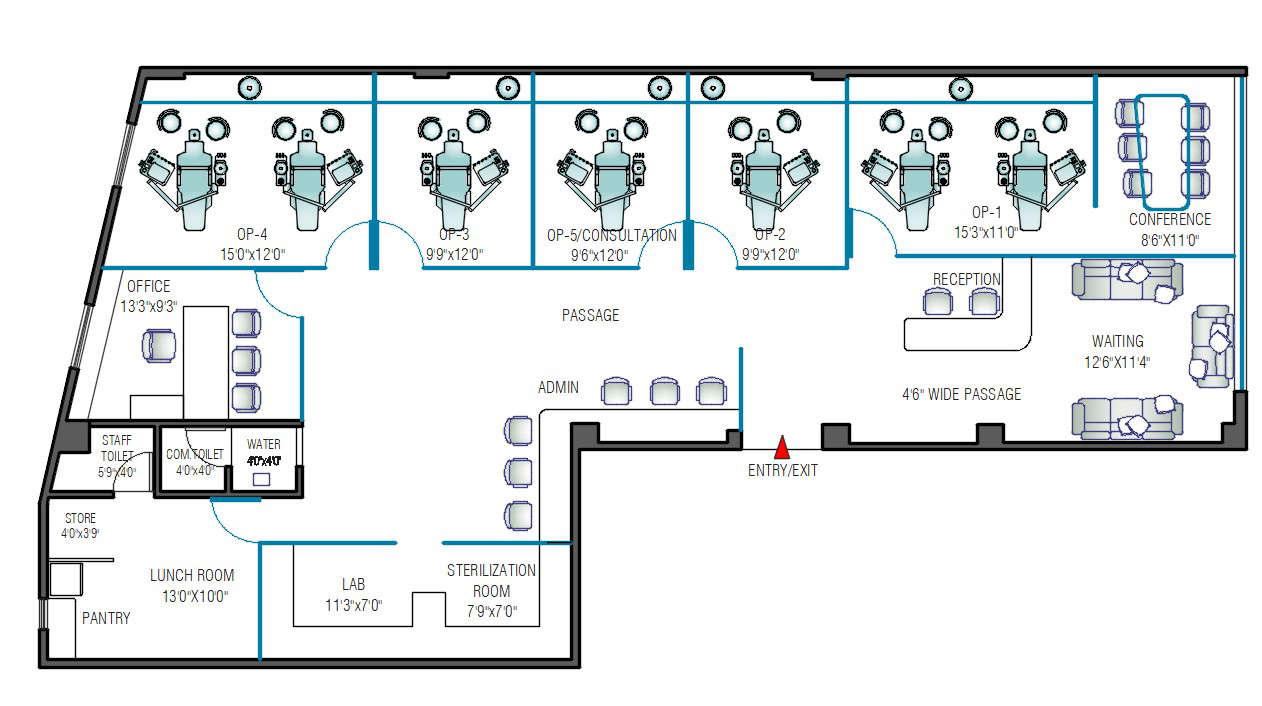
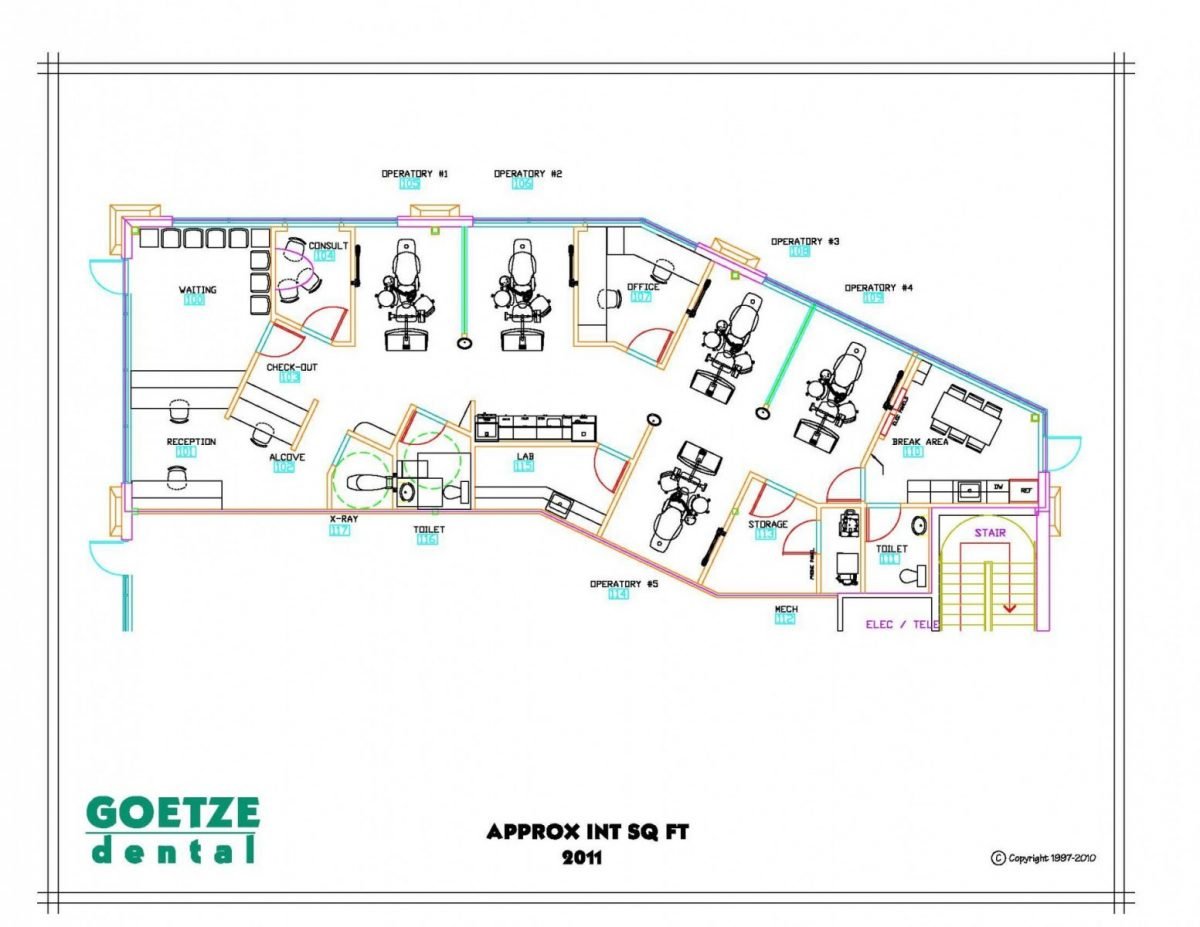
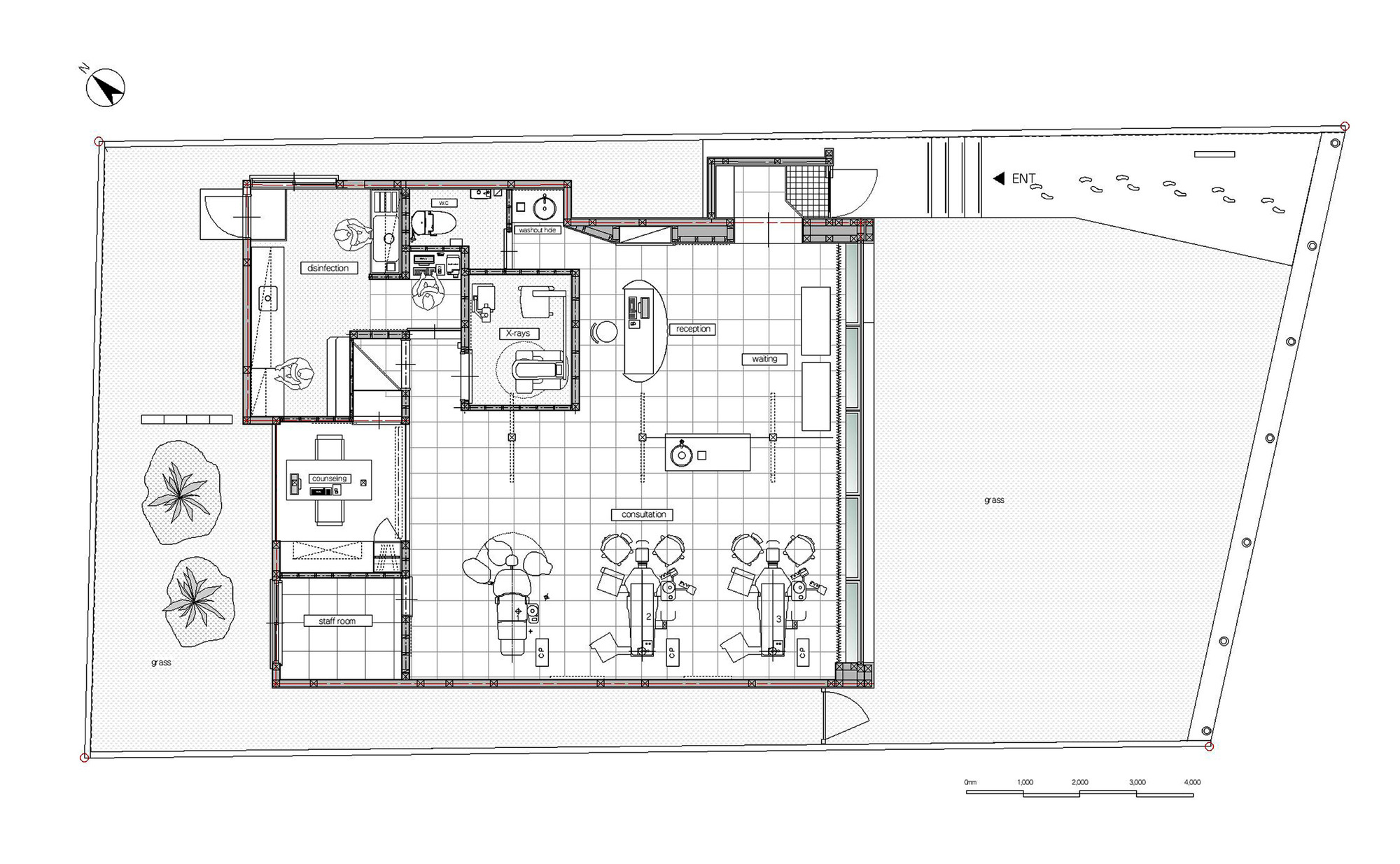
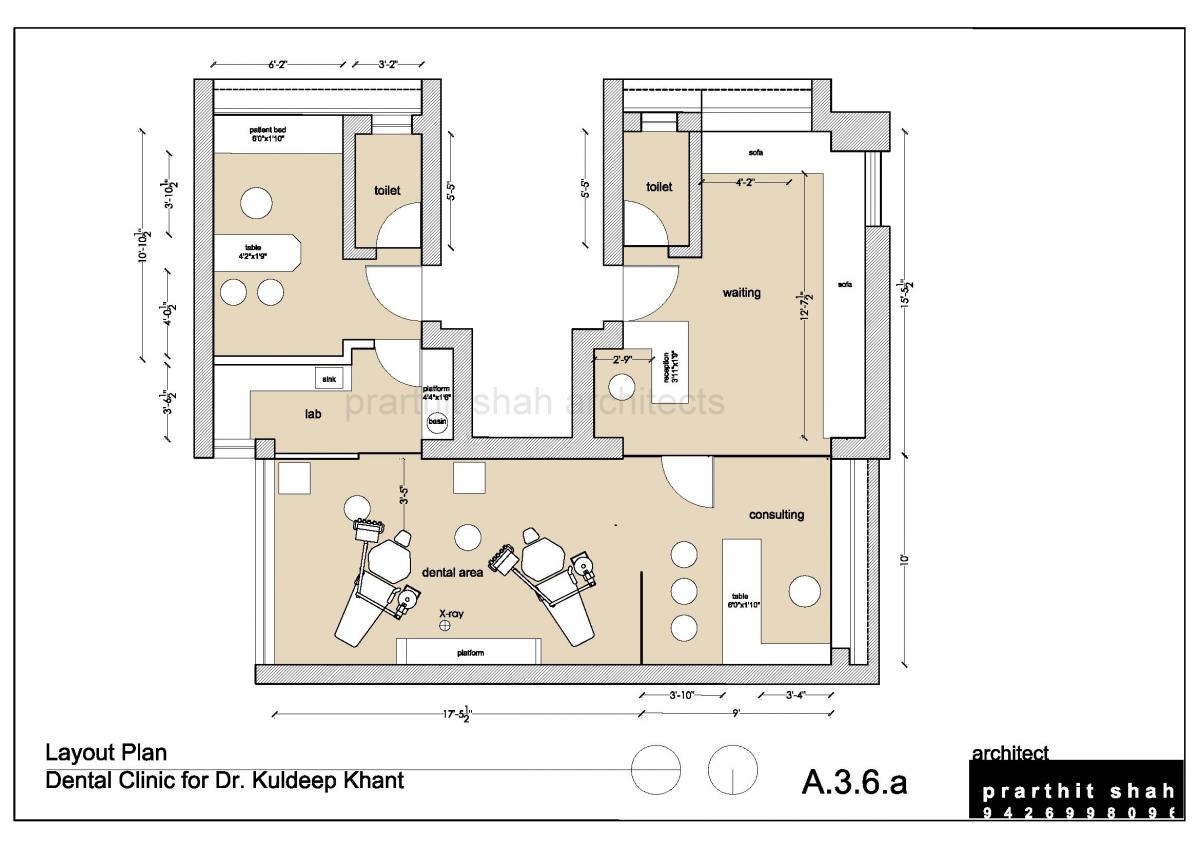
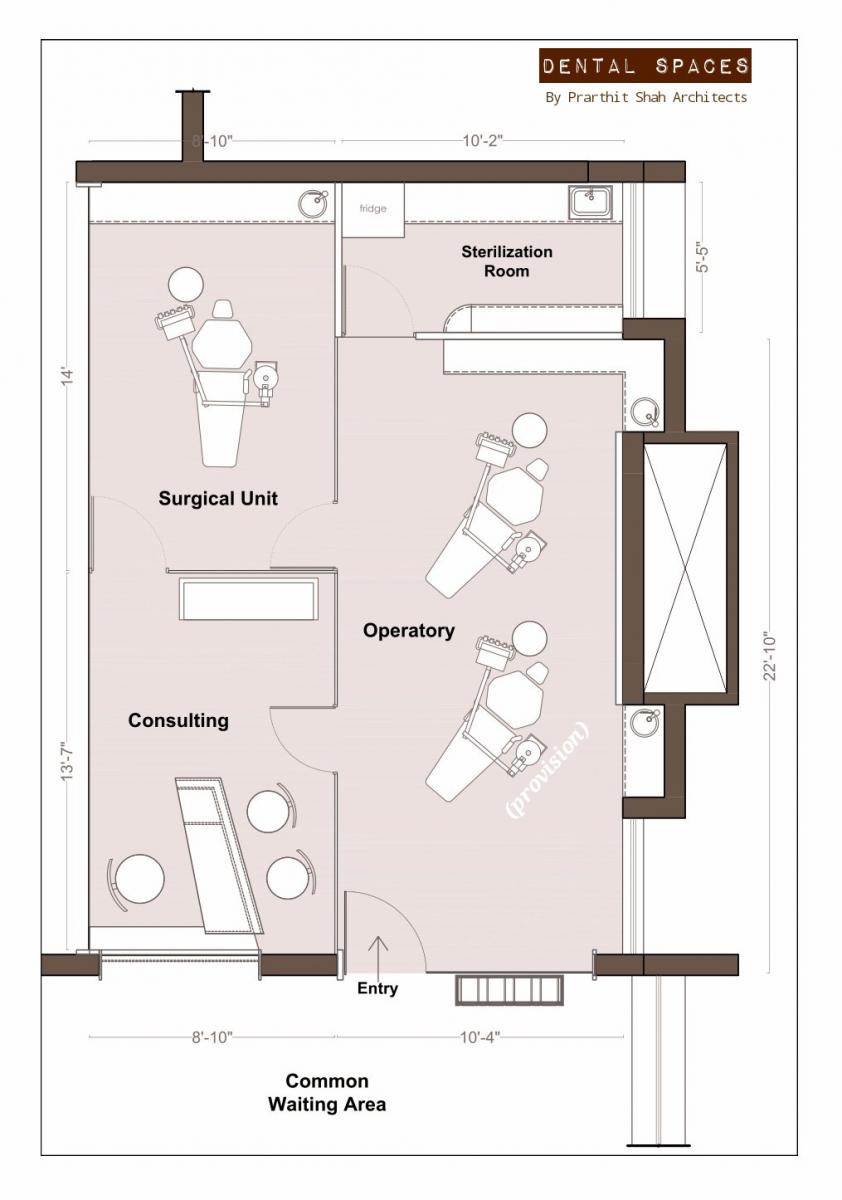
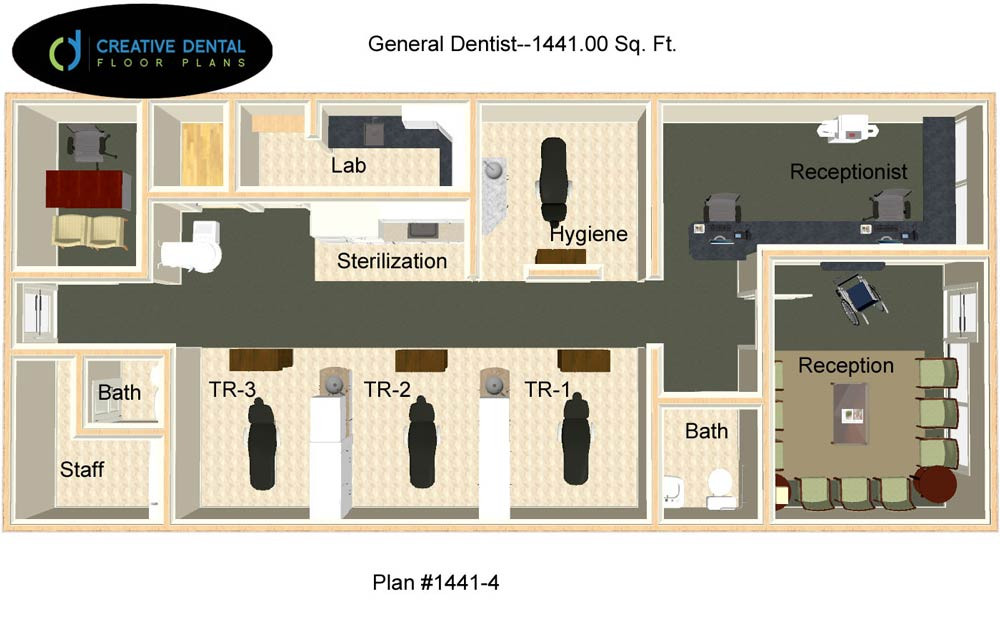
Dental Clinic Floor Plan With Dimensions

Designing a dental clinic involves meticulous planning, and the floor plan is arguably the most critical element. It dictates workflow, patient experience, and overall efficiency. Understanding the standard dimensions and layout considerations is essential for anyone involved in building or renovating a dental practice.
This article explores the key aspects of dental clinic floor plans, highlighting typical dimensions and design principles. We aim to provide a comprehensive overview for architects, dentists, and anyone interested in creating a functional and aesthetically pleasing dental space.
Key Considerations for Dental Clinic Floor Plans
The floor plan of a dental clinic isn’t just about fitting rooms; it's about creating a space that facilitates efficient workflows. It needs to ensure patient comfort and maximizes the productivity of dental professionals. Several crucial elements must be taken into account when drafting a dental clinic floor plan.
Reception and Waiting Area
The reception area is the first point of contact for patients. A comfortable and welcoming waiting area is critical for setting a positive tone.
Typical dimensions for the reception area range from 150 to 300 square feet, depending on the size of the clinic and anticipated patient volume. Seating should be ample and arranged to allow for easy movement and accessibility.
Treatment Rooms (Operatories)
Operatories, or treatment rooms, are the core of the dental clinic. These spaces require careful planning to accommodate dental equipment, staff, and patients comfortably.
A standard operatory typically measures around 100 to 120 square feet. According to the American Dental Association (ADA), this provides sufficient space for the dental chair, assistant's seating, equipment carts, and storage.
Sterilization Area
The sterilization area is a crucial space for maintaining hygiene standards. It must be separated from patient areas to prevent cross-contamination.
A dedicated sterilization area should ideally be at least 60 to 80 square feet. This area requires ample counter space for processing instruments and dedicated zones for clean and contaminated items.
X-Ray Room
The x-ray room requires specific shielding to protect patients and staff from radiation. This often includes lead-lined walls and doors.
The dimensions of an x-ray room typically range from 70 to 100 square feet. The exact size depends on the type of x-ray equipment used, such as panoramic or cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) machines.
Office and Consultation Room
A private office is essential for administrative tasks and patient consultations. This space should offer privacy and a professional atmosphere.
An office or consultation room typically measures between 100 and 150 square feet. This space should accommodate a desk, chairs, and storage for patient records.
Restrooms and Staff Areas
Adequate restroom facilities are essential for both patients and staff. A separate staff lounge or break room can contribute to employee well-being.
Restroom dimensions should comply with local building codes and ADA accessibility guidelines. Staff areas can range from 80 to 120 square feet depending on the number of employees.
Accessibility and Workflow
Accessibility is a critical consideration in dental clinic design. All areas of the clinic must be accessible to patients with disabilities, complying with ADA standards.
Hallways should be wide enough to accommodate wheelchairs, typically at least 36 inches wide. Doorways should also meet accessibility requirements.
Effective workflow is crucial for maximizing efficiency. The floor plan should facilitate a smooth flow of patients and staff, minimizing bottlenecks and unnecessary movement. Consideration should be given to the proximity of the sterilization area to the operatories and the reception area's visibility to the treatment rooms.
Dr. Emily Carter, a practicing dentist, emphasizes the importance of a well-designed floor plan: "A thoughtfully designed layout not only enhances efficiency but also improves the patient experience. It's an investment that pays off in the long run."
Technology Integration
Modern dental clinics rely heavily on technology. The floor plan should accommodate the necessary wiring and infrastructure for computers, digital x-ray systems, and other equipment.
Adequate power outlets and data ports should be strategically placed throughout the clinic. Consider the future needs of the practice and plan for potential technology upgrades.
The use of digital systems also impacts storage needs. While digital records reduce paper storage, space is still needed for computer servers and backup systems.
Conclusion
Designing a dental clinic floor plan is a complex process that requires careful consideration of numerous factors. From the dimensions of individual rooms to the overall workflow and accessibility, every detail plays a crucial role in creating a functional and patient-friendly environment.
By understanding the key principles and standard dimensions outlined in this article, architects, dentists, and other stakeholders can create dental spaces that meet the needs of both patients and dental professionals. A well-designed floor plan is not just about aesthetics; it's about creating a space that promotes efficiency, comfort, and ultimately, better patient care. Remember to consult with experienced professionals like architects specializing in dental office design and contractors familiar with dental equipment requirements.