Energy Transformations In Organisms Are Always Associated With

Imagine a lush green forest, sunlight dappling through the leaves, fueling an unseen symphony of life. From the towering trees reaching for the sky to the smallest fungi decomposing matter on the forest floor, every organism is a bustling hub of energy transformation, a continuous dance of breaking down and building up. But this dance, this fundamental aspect of existence, always comes with a partner, an inseparable companion.
The essential truth we're exploring is this: Energy transformations in organisms are always associated with heat. This isn't just a scientific fact; it's a cornerstone of biology, impacting everything from the way we fuel our bodies to the intricate workings of entire ecosystems.
Understanding this association is crucial for comprehending the limits of efficiency in biological systems, the flow of energy through food webs, and even the impact of our own activities on the planet. We'll delve into the science, explore its implications, and uncover why this constant release of heat is not just a byproduct, but a fundamental law of life.
The First Law of Thermodynamics: The Foundation
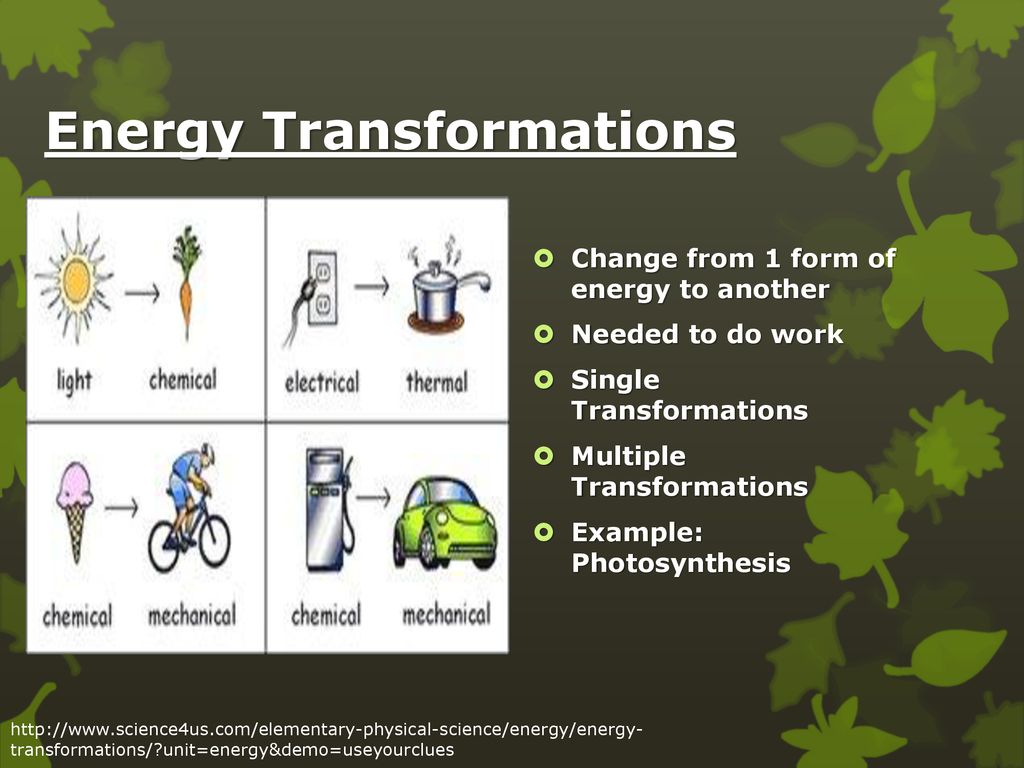
To understand why energy transformations always involve heat, we need to touch upon the bedrock of physics: the First Law of Thermodynamics. This law, in essence, states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed from one form to another.
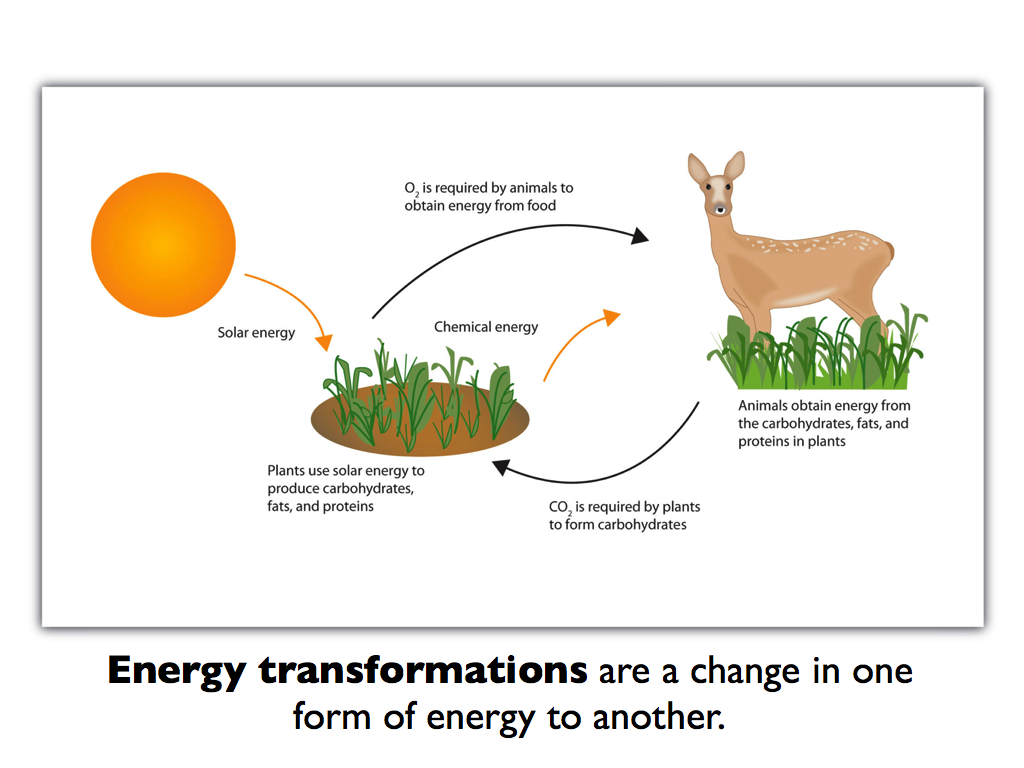
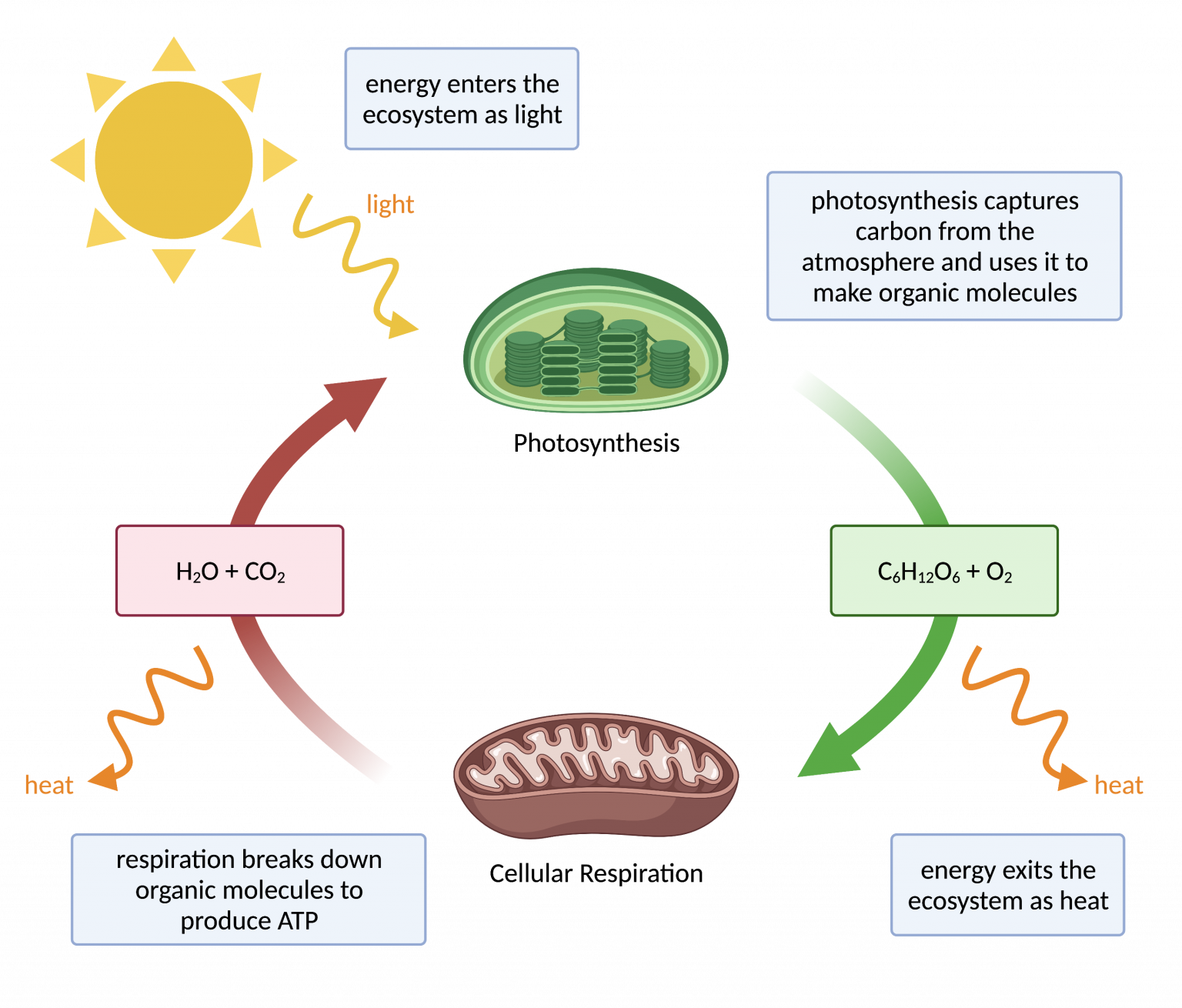
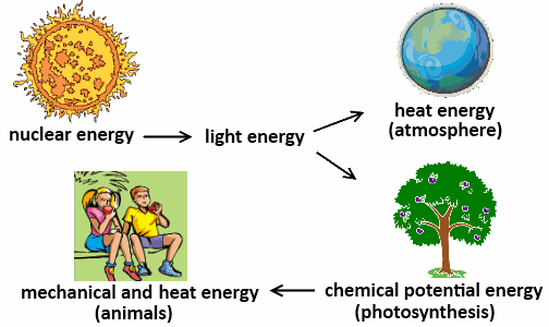
Think of a plant performing photosynthesis. It captures light energy from the sun and converts it into chemical energy in the form of sugars.
But this transformation isn't perfectly efficient. Some of the light energy is inevitably lost as heat during the intricate biochemical reactions involved.
The Inevitable Loss: Entropy and Heat
This loss of energy as heat is intimately linked to the concept of entropy. Entropy, in simple terms, refers to the degree of disorder or randomness in a system.
The Second Law of Thermodynamics dictates that entropy tends to increase over time in a closed system. This means that any energy transformation will inherently lead to a greater degree of disorder.
Heat, being the random motion of molecules, is a direct manifestation of this increased disorder. Therefore, every time energy is converted, some of it inevitably dissipates as heat, increasing the overall entropy of the system.
Cellular Respiration: Fueling Life, Generating Heat
Now, let's zoom in on a specific example: cellular respiration. This process, which occurs in nearly all living organisms, is how we extract energy from the food we eat.
We break down glucose, a simple sugar, and use that energy to create ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the cell's primary energy currency. This process also produces carbon dioxide and water.
However, not all the energy stored in glucose is transferred to ATP. A significant portion is lost as heat, which is why our bodies maintain a relatively constant temperature.
The Human Body: A Warm-Blooded Example
Humans, being warm-blooded or endothermic, rely heavily on this heat generation to maintain our internal temperature.
Our metabolic processes, from muscle contraction to brain activity, constantly produce heat. This allows us to function optimally regardless of the external environment.
Shivering, for instance, is a rapid muscle contraction designed to generate heat when we are cold. The shivering is not an efficient use of energy, but it is a means to maintain the core temperature.
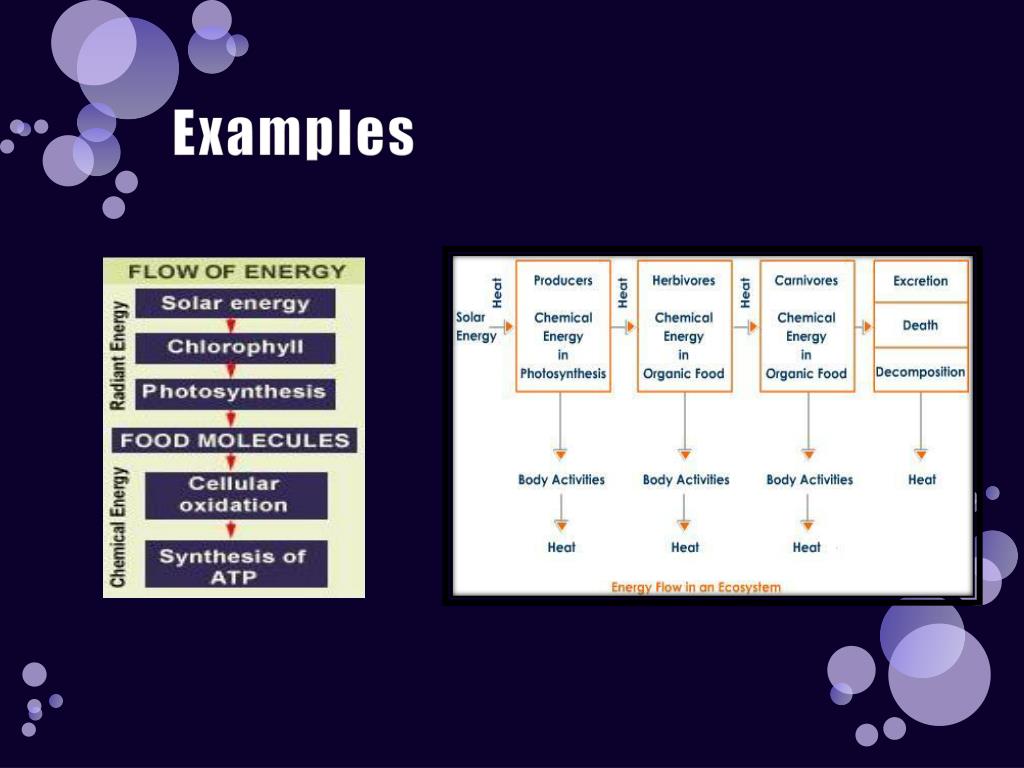
Ecosystems: Energy Flow and Heat Loss
The principle of heat loss during energy transformations extends beyond individual organisms to entire ecosystems. Think of a food chain: plants capturing sunlight, herbivores eating the plants, and carnivores eating the herbivores.
At each level of this chain, energy is transferred, but also lost as heat. This is why there is less energy available at higher trophic levels.
A large amount of energy trapped by the plants is dissipated as heat during the herbivores' digestive process. The carnivores in turn will not receive the full amount of energy from the herbivores.
The Ten Percent Rule: A Consequence of Heat Loss
This loss of energy at each trophic level is often summarized by the "ten percent rule." This rule states that, on average, only about 10% of the energy stored in one trophic level is converted into biomass in the next trophic level.
The remaining 90% is used for metabolic processes, including respiration, and ultimately lost as heat. This highlights the crucial role of heat in limiting the length and complexity of food chains.
This is why a pyramid of energy exists in any ecological system. The base, consisting of the primary producers, hold the most amount of energy, while each proceeding level above it has less energy available to it.
Implications and Applications
Understanding the link between energy transformations and heat has numerous practical implications. In agriculture, it informs our understanding of energy efficiency in crop production and livestock farming.
In medicine, it helps us understand metabolic disorders and develop strategies to manage body temperature. And in environmental science, it's crucial for assessing the impact of human activities on global energy balance.
For example, understanding the energy flow of agricultural crops and livestock can help find ways to make agriculture more efficient by introducing crops that are optimized for their environment and do not need as much energy to grow.
The Constant Hum of Life
The constant release of heat during energy transformations is a fundamental constraint on life, but it's also what allows life to exist. It's the constant hum of activity that drives all biological processes, from the smallest cell to the largest ecosystem.
It reminds us that the universe operates under certain laws, and understanding these laws is essential for navigating our world and making informed decisions about our future.
So, the next time you feel the warmth of the sun on your skin or the heat generated by your own body, remember the intricate dance of energy transformation happening all around you, a dance that always, inevitably, involves the release of heat.