Enhanced Barrier Precautions Nursing Care Plan
Hospitals nationwide are urgently implementing enhanced barrier precautions (EBPs) following a surge in multidrug-resistant organism (MDRO) infections. The new protocols aim to curb the spread of these dangerous pathogens and protect vulnerable patients.
The Enhanced Barrier Precautions Nursing Care Plan is a critical strategy to combat rising infection rates, specifically targeting MDROs that pose a significant threat to patient safety and healthcare resources. The implementation focuses on high-risk patients and situations where transmission is most likely.
Who is Affected?
The updated guidelines primarily affect patients at high risk for MDRO colonization or infection. This includes patients with indwelling medical devices, those receiving care in intensive care units (ICUs), and individuals with prolonged hospital stays.
Healthcare workers, including nurses, physicians, and ancillary staff, will also be directly impacted by the new protocols.
Visitors to healthcare facilities will also need to adhere to certain aspects of the enhanced precautions.
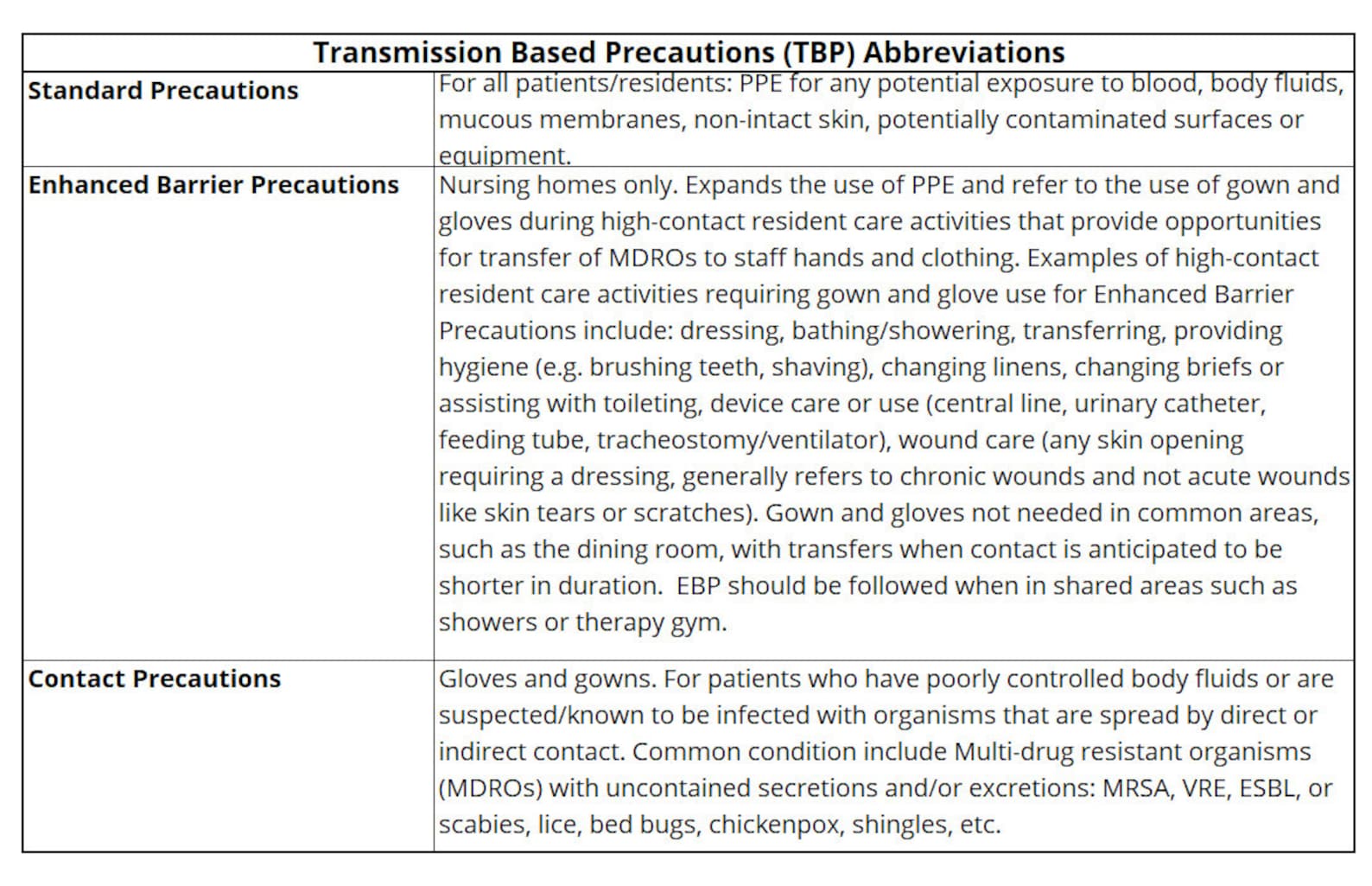
What are the Enhanced Barrier Precautions?
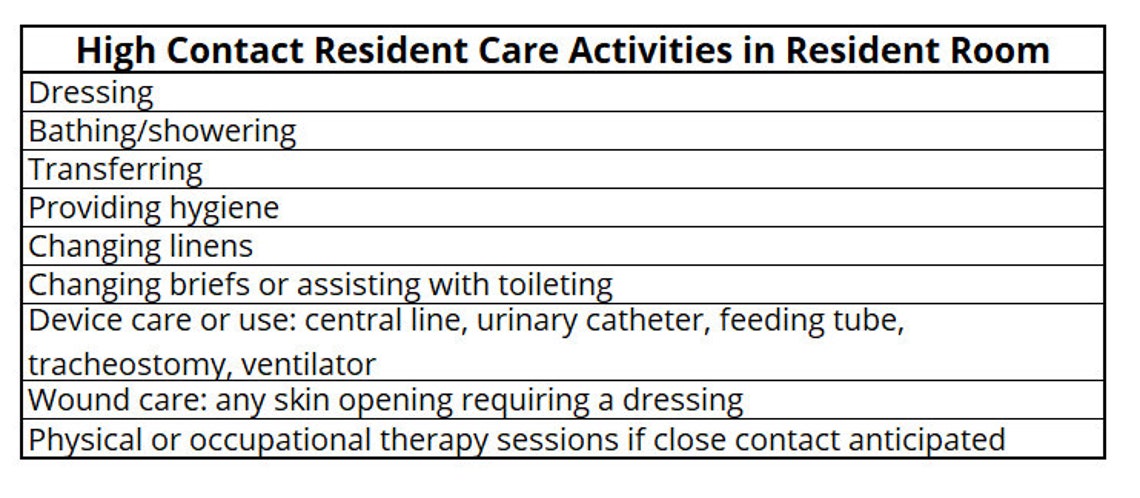
EBPs mandate the use of gowns and gloves for all patient interactions and entry into the patient's room. This expands beyond standard precautions, which typically only require hand hygiene.
The protocol also includes increased emphasis on hand hygiene before and after patient contact. Dedicated equipment should be used for patients on EBPs wherever possible.
Environmental cleaning and disinfection protocols are being intensified to reduce the environmental reservoir of MDROs. This involves more frequent cleaning of high-touch surfaces and equipment.
Where are these Precautions Being Implemented?
These precautions are being rolled out across various healthcare settings, including acute care hospitals, long-term care facilities, and rehabilitation centers. The initial focus is on areas with the highest MDRO prevalence, such as ICUs and oncology units.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is recommending nationwide adoption of EBPs to standardize infection control practices.
When Did This Start?
Implementation of EBPs began in response to a noticeable increase in MDRO infections reported throughout 2023 and early 2024. Several hospitals started piloting programs earlier this year before widespread adoption.
A nationwide advisory was issued by the CDC in July, prompting hospitals to swiftly adapt their existing protocols.
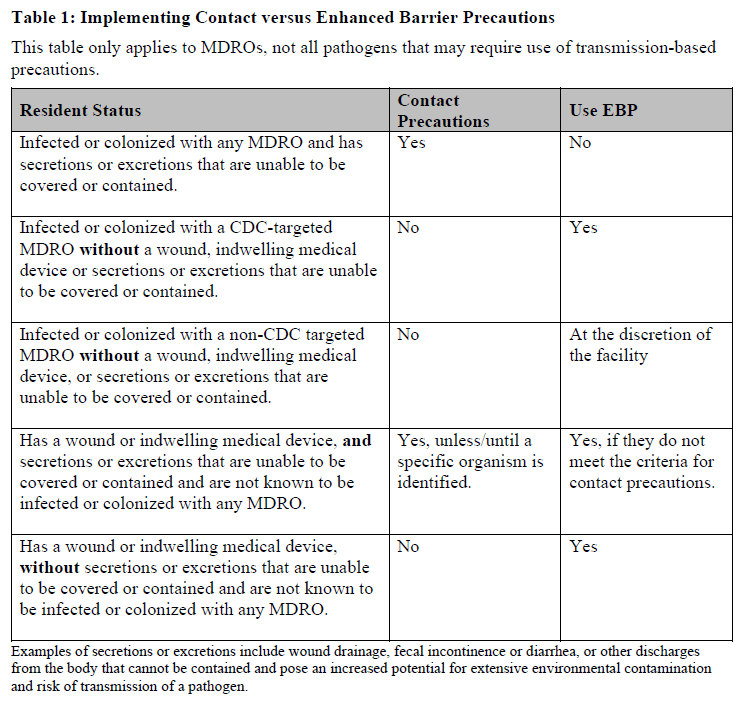
How are these Precautions Different?
Unlike standard precautions, EBPs require gown and glove use for *all* patient interactions, regardless of anticipated contact with body fluids. This proactive approach aims to prevent transmission from asymptomatic carriers of MDROs.
The previous guidelines were often based on perceived risk, but EBPs eliminate ambiguity by mandating barrier protection for all encounters.
Enhanced environmental cleaning further reduces the risk of environmental transmission.
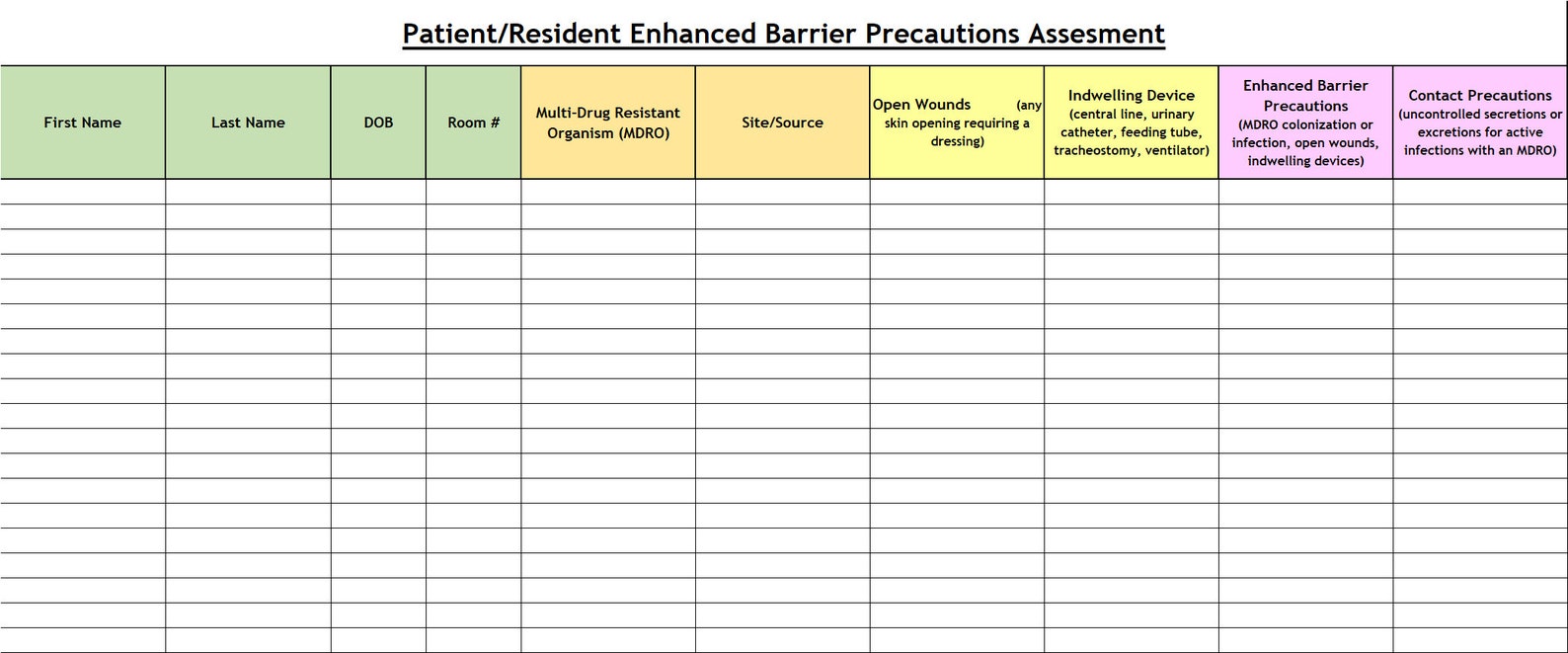
Impact on Nursing Care Plans
The new precautions necessitate significant revisions to existing nursing care plans. Nurses must now factor in additional time for donning and doffing personal protective equipment (PPE) before and after each patient interaction.
Patient education is also a crucial component of the revised care plans. Nurses need to explain the rationale behind EBPs to patients and their families.
Communication among healthcare team members must be enhanced to ensure consistent adherence to the protocols. Dedicated team huddles can help reinforce best practices.
Challenges and Solutions
One of the main challenges is ensuring consistent adherence to EBPs across all shifts and staff members. Ongoing training and education are essential to address this issue.
PPE supply chain management is another critical concern. Hospitals must ensure adequate stock of gowns and gloves to support the increased usage.
Some patients may experience isolation or anxiety due to the enhanced precautions. Providing emotional support and clear communication can help mitigate these concerns.
Data and Outcomes
Early data from hospitals that have implemented EBPs show a promising trend toward reduced MDRO transmission rates. Preliminary reports indicate a significant decrease in Clostridioides difficile infections (CDI) and carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae (CRE) infections.
The CDC is closely monitoring the impact of EBPs on infection rates nationwide. Further data analysis will be conducted to refine the guidelines and optimize their effectiveness.
Next Steps and Ongoing Developments
Hospitals are continuing to refine their EBP implementation strategies based on ongoing data and feedback from healthcare workers. Further research is being conducted to identify the most effective strategies for environmental cleaning and disinfection.
The CDC plans to update its guidelines periodically to reflect the latest scientific evidence. Healthcare facilities should stay informed about these updates and adapt their protocols accordingly.
The success of EBPs hinges on consistent adherence and ongoing vigilance. Continued collaboration among healthcare providers, researchers, and public health agencies is essential to combat the threat of MDROs.