Explain Some Of The Benefits Of Biotechnology.
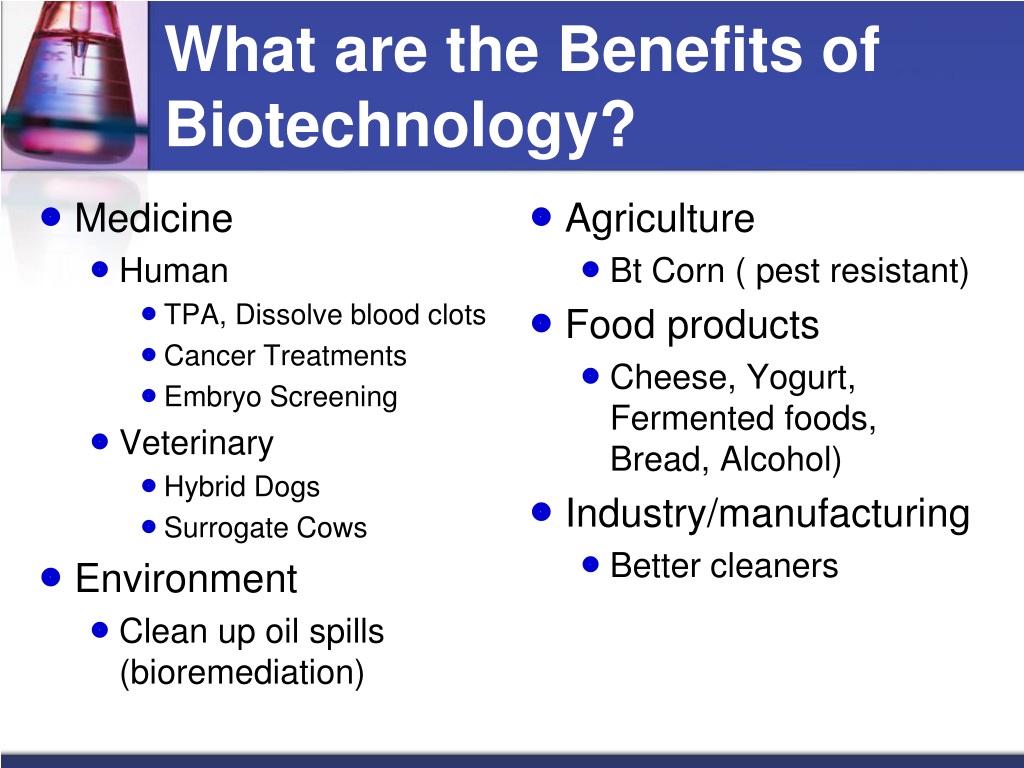
The looming threat of climate change, coupled with a rapidly expanding global population, demands innovative solutions across all sectors. Biotechnology, the application of biological processes for industrial and other purposes, is increasingly recognized as a powerful tool in addressing these urgent challenges. From revolutionizing healthcare to transforming agriculture, biotechnology offers a diverse range of benefits with the potential to reshape our world for the better.
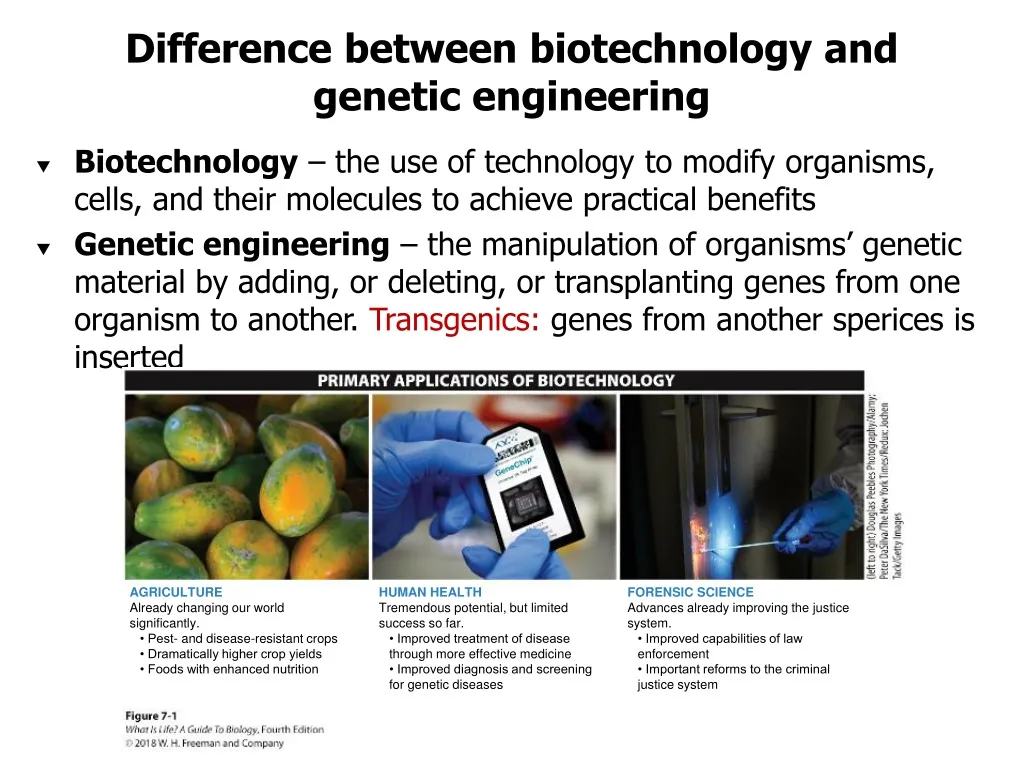
At its core, biotechnology uses living organisms or their components to develop products and processes that improve human health, food security, and environmental sustainability. This article delves into some of the most significant benefits of biotechnology, exploring its impact on medicine, agriculture, and industry, while also acknowledging some concerns surrounding its development and deployment.
Biotechnology in Healthcare: A New Era of Medicine
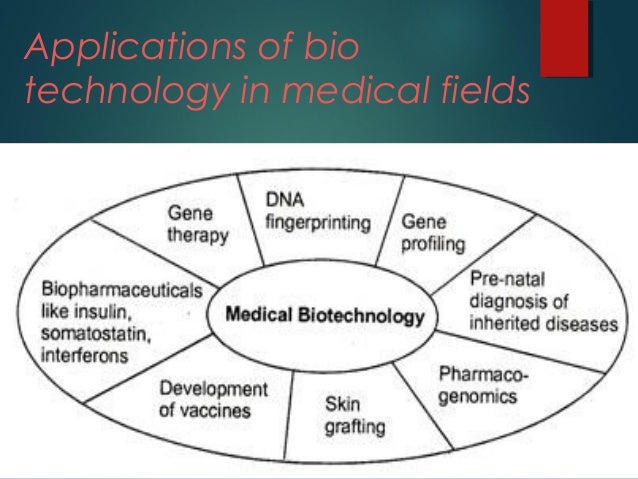
Perhaps the most widely recognized benefit of biotechnology lies in its transformative impact on healthcare. Biopharmaceutical advancements have led to the development of life-saving treatments and diagnostic tools for a wide range of diseases.
Monoclonal antibodies, for example, are now commonly used in cancer therapy, targeting specific cancer cells with unprecedented precision. Genetic engineering has also enabled the production of recombinant proteins, such as insulin for diabetes and growth hormone for growth disorders.
Gene therapy, a more recent advancement, holds immense promise for treating genetic diseases by correcting or replacing faulty genes. According to the National Institutes of Health (NIH), gene therapy has shown remarkable success in treating certain forms of inherited blindness, spinal muscular atrophy, and other debilitating conditions.
Personalized Medicine: Tailoring Treatments to the Individual
Biotechnology is also paving the way for personalized medicine, an approach that tailors medical treatments to the individual characteristics of each patient. Pharmacogenomics, the study of how genes affect a person's response to drugs, allows doctors to predict which medications are most likely to be effective and safe for a given patient.
Genetic testing can also identify individuals at risk for developing certain diseases, enabling them to take preventive measures or undergo early screening. This proactive approach to healthcare has the potential to improve patient outcomes and reduce healthcare costs.
Biotechnology in Agriculture: Enhancing Food Security
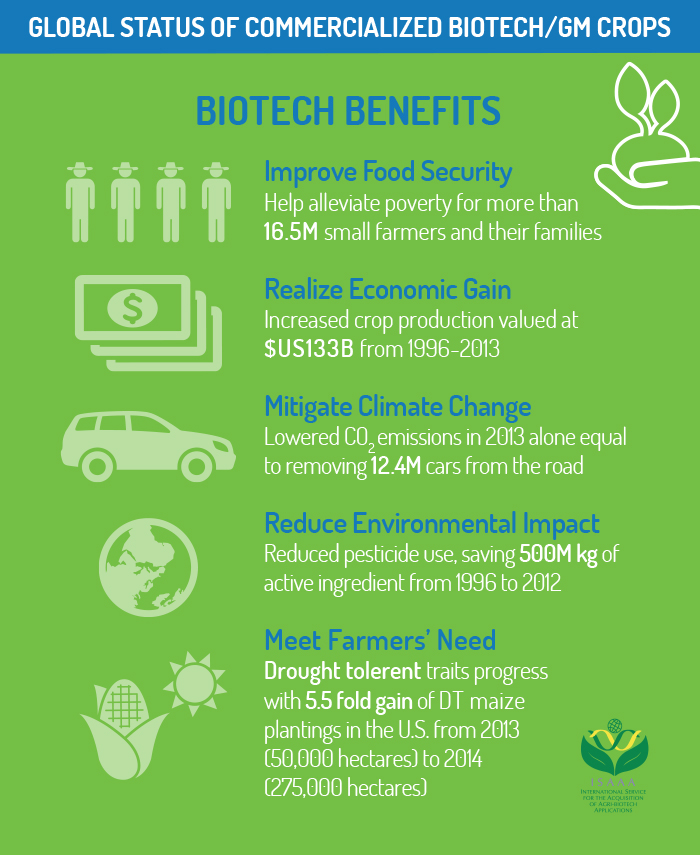
With the global population projected to reach nearly 10 billion by 2050, ensuring food security is a major challenge. Biotechnology offers a range of tools to improve crop yields, enhance nutritional content, and reduce the environmental impact of agriculture.
Genetically modified (GM) crops, also known as biotech crops, have been engineered to possess desirable traits such as insect resistance, herbicide tolerance, and drought tolerance. Studies conducted by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) have shown that GM crops can significantly increase yields and reduce the need for pesticides, leading to increased farm incomes and reduced environmental pollution.
However, the use of GM crops remains a subject of debate, with concerns raised about potential health risks, environmental impacts, and the control of seed production by large corporations.
Beyond GM Crops: Sustainable Agricultural Practices
Biotechnology is also contributing to more sustainable agricultural practices beyond GM crops. Microbial inoculants, for example, can improve soil fertility and reduce the need for synthetic fertilizers. Biopesticides, derived from natural sources, offer a more environmentally friendly alternative to conventional pesticides.
Furthermore, biotechnology is being used to develop crops that are more resilient to climate change, such as drought-resistant varieties and crops that can tolerate higher temperatures. These advancements are crucial for ensuring food security in the face of a changing climate.
Biotechnology in Industry: A Greener Future
Biotechnology is not limited to healthcare and agriculture; it also has a significant role to play in transforming industrial processes and creating a more sustainable future. Biomanufacturing, the use of biological systems to produce materials and chemicals, offers a greener alternative to traditional manufacturing methods.
Bioplastics, for example, are derived from renewable resources such as corn starch and sugarcane, offering a biodegradable alternative to petroleum-based plastics. Biofuels, produced from biomass, can reduce our dependence on fossil fuels and lower greenhouse gas emissions.
Enzyme technology is also being used to improve the efficiency and reduce the environmental impact of various industrial processes, such as textile manufacturing and paper production.
Addressing Concerns and Ensuring Responsible Development
While the benefits of biotechnology are undeniable, it is crucial to address potential risks and ensure responsible development. Ethical considerations surrounding gene editing, the potential for unintended consequences of GM crops, and the equitable access to biotechnological innovations are all important issues that need to be carefully considered.
Robust regulatory frameworks, transparent communication, and ongoing research are essential for mitigating risks and fostering public trust. International collaborations are also crucial for ensuring that the benefits of biotechnology are shared equitably across the globe.
The World Health Organization (WHO) emphasizes the need for rigorous safety assessments and ethical guidelines to ensure that biotechnology is used responsibly and for the benefit of all.
The Future of Biotechnology: A World of Possibilities
Biotechnology is a rapidly evolving field with the potential to address some of the world's most pressing challenges. From developing new cures for diseases to creating more sustainable agricultural practices and transforming industrial processes, biotechnology offers a world of possibilities.
Continued investment in research and development, coupled with responsible regulation and ethical considerations, is essential for unlocking the full potential of biotechnology and creating a healthier, more sustainable future for all. The advancements in areas like CRISPR gene editing and synthetic biology promise even more revolutionary changes in the years to come, highlighting the critical importance of ongoing dialogue and careful management of this powerful technology.