Financial Management Involves Decisions About Which Of The Following
Savvy financial management is a cornerstone of success for individuals and organizations alike, requiring careful consideration of various interconnected factors. Neglecting core principles can lead to instability and missed opportunities, underscoring the need for informed decision-making.
This article delves into the key areas encompassed by financial management, exploring the decisions that shape financial outcomes. These choices impact resource allocation, risk mitigation, and the overall achievement of financial goals.
Core Decisions in Financial Management
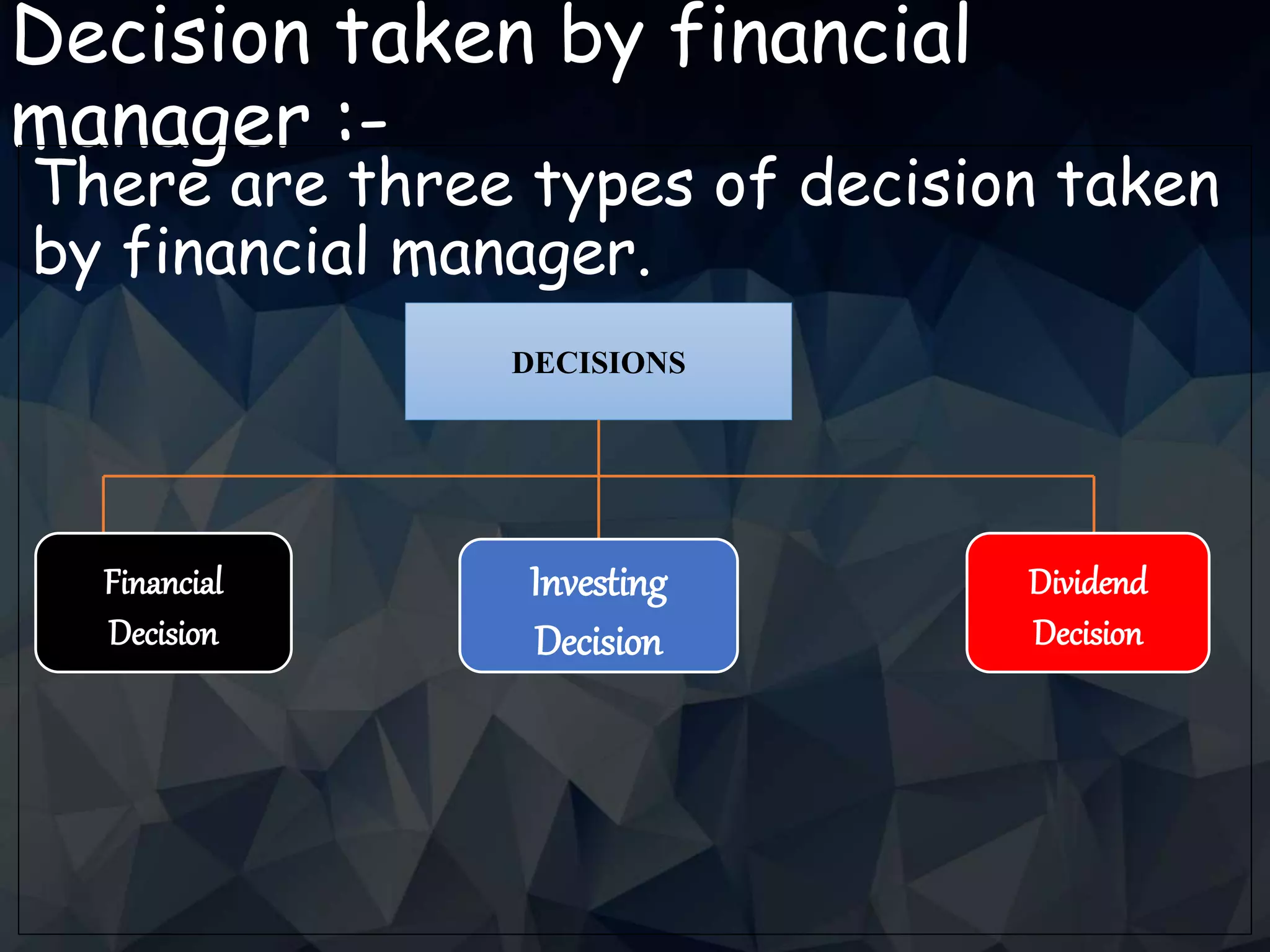
Financial management, at its heart, involves strategically navigating a complex web of choices.
These decisions dictate how resources are acquired, allocated, and utilized to maximize value and minimize risk.
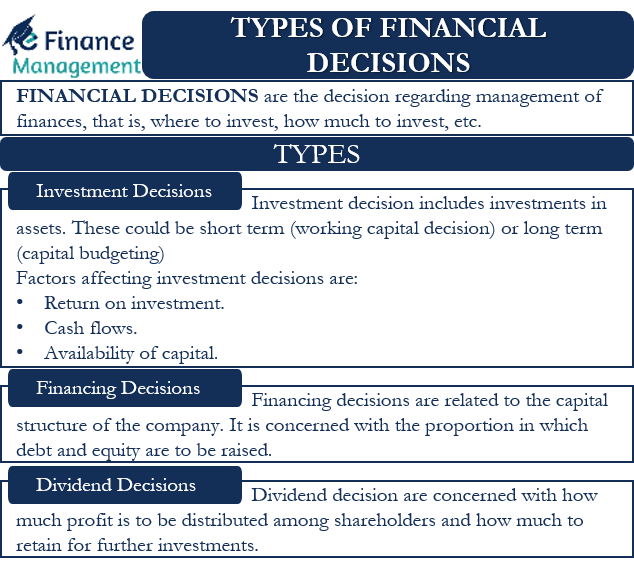
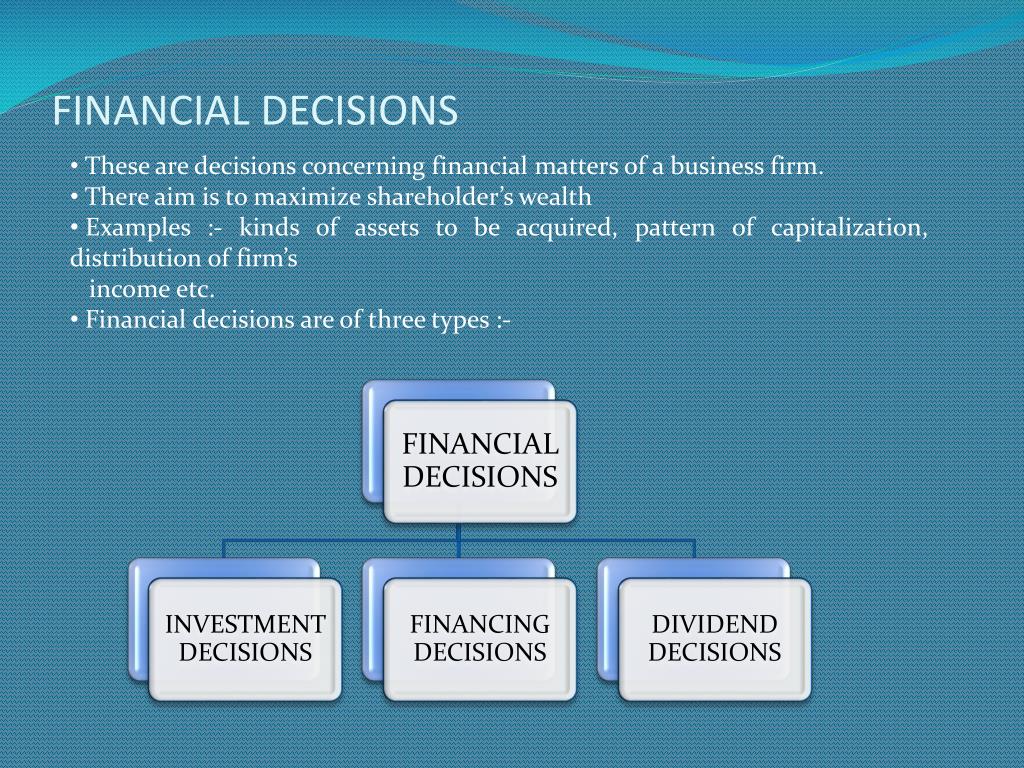
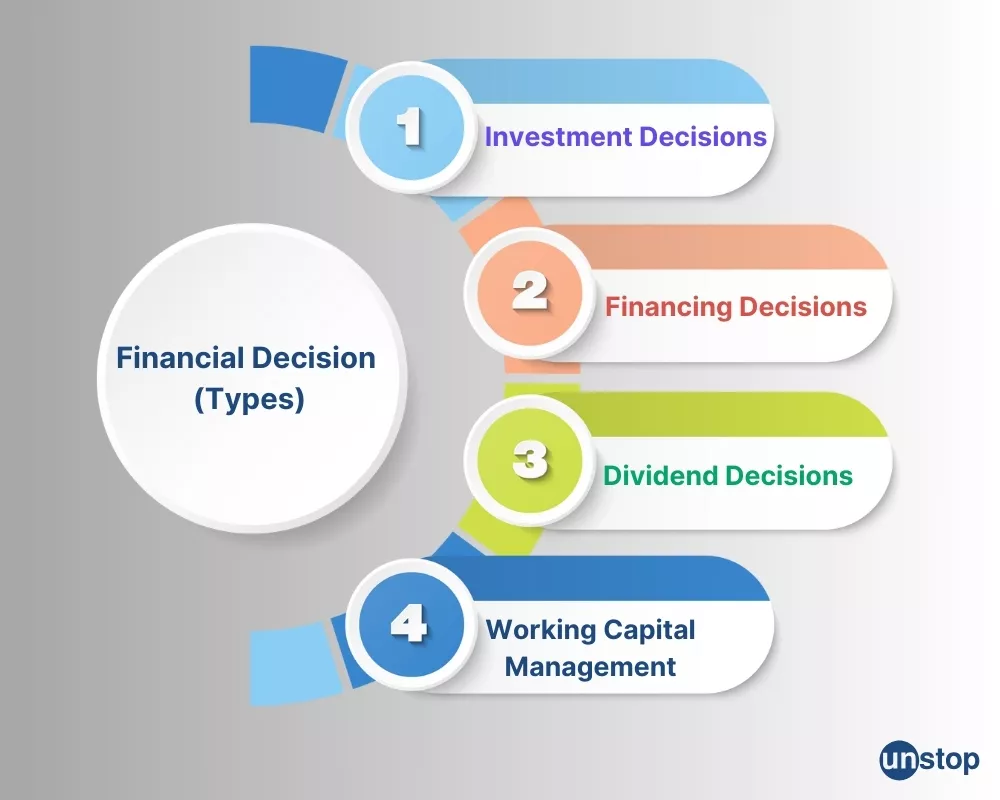
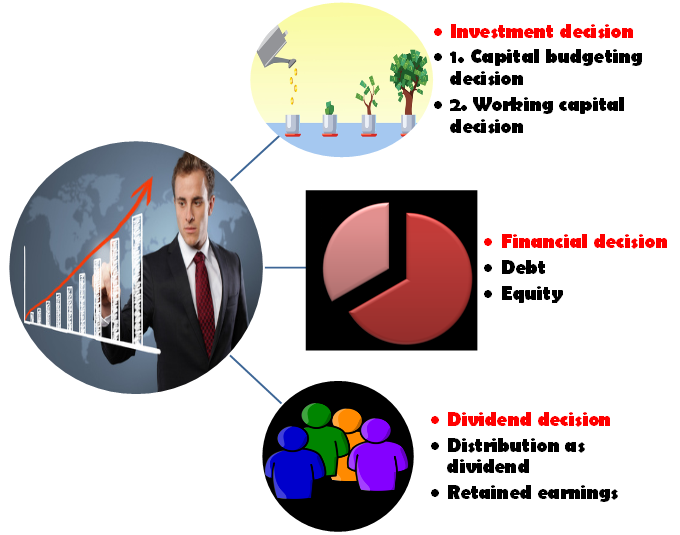
Investment Decisions
Perhaps the most visible aspect of financial management is investment. This encompasses decisions about where to allocate capital to generate future returns.
This includes everything from purchasing stocks and bonds to investing in real estate or new business ventures. These decisions are guided by factors like risk tolerance, time horizon, and projected returns.
Investment decisions are not just about maximizing profit; they also consider the liquidity and security of the investment.
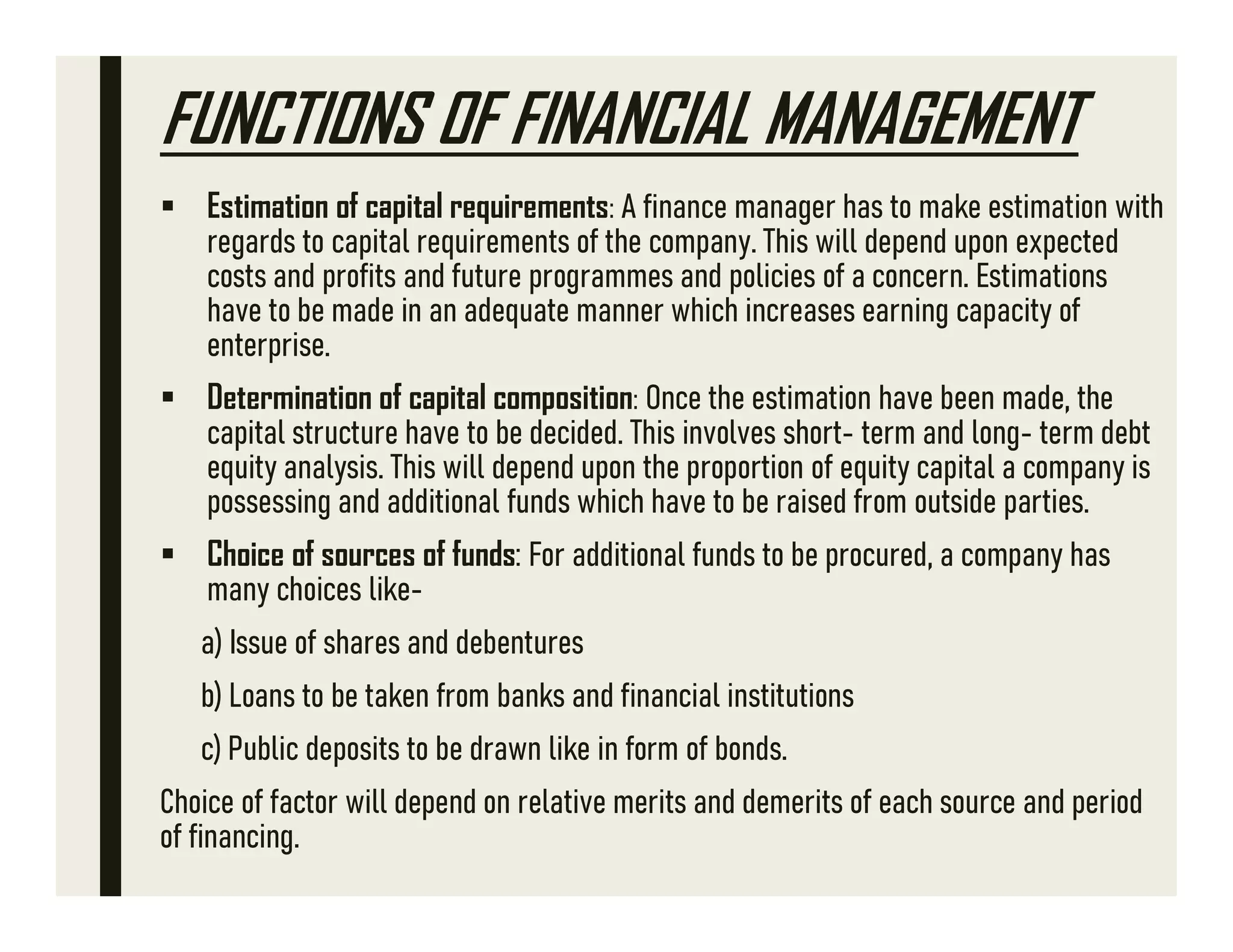
Financing Decisions
Securing the necessary capital to fund operations and investments is crucial. Financing decisions address how a company or individual obtains these funds.
Options range from taking on debt (loans, bonds) to raising equity (selling stock). Each financing method has its own cost and risk profile, influencing the overall financial health of the entity.
The optimal mix of debt and equity, also known as the capital structure, is a key consideration for financial managers.
Working Capital Management Decisions
Working capital management focuses on the day-to-day financial operations of a business. It involves managing current assets and liabilities.
Effective management of working capital ensures the company has enough cash on hand to meet its short-term obligations. This includes managing inventory, accounts receivable, and accounts payable.
Inefficient working capital management can lead to cash flow problems, even if the company is profitable on paper.
Dividend Decisions
For publicly traded companies, dividend decisions are an important part of financial management. These decisions involve determining how much of the company's profits to distribute to shareholders as dividends versus reinvesting back into the business.
A high dividend payout may attract investors seeking income, but it can also limit the company's ability to fund future growth. Striking the right balance is crucial.
These decisions signal the company's financial health and future prospects to the market.
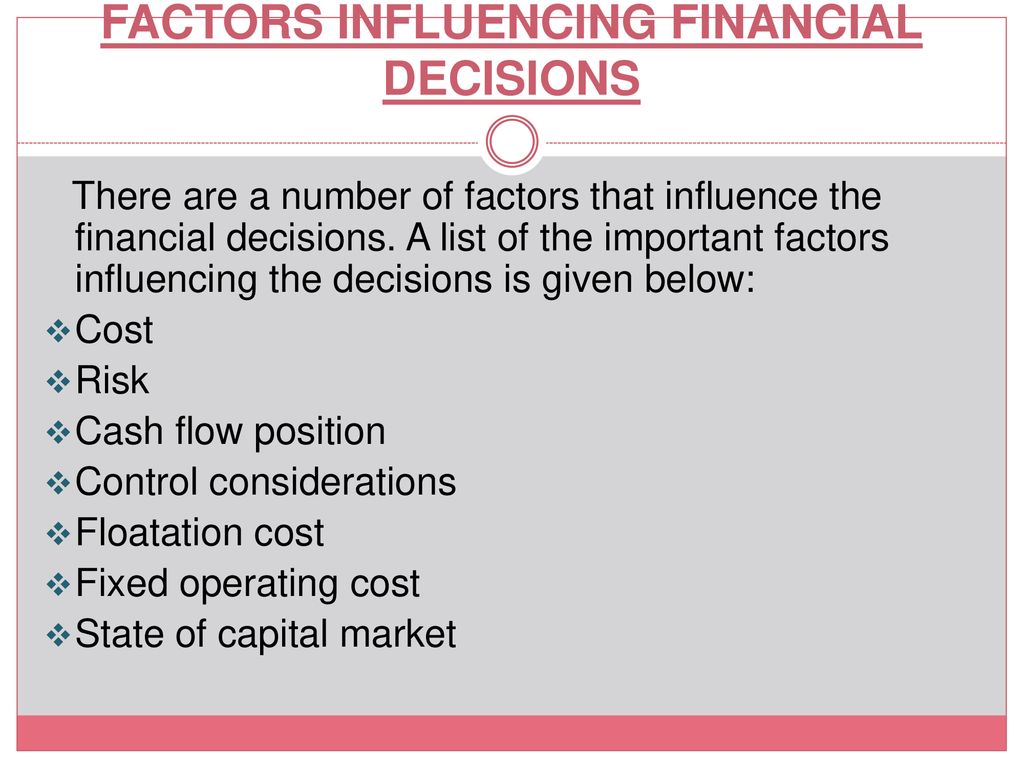
Risk Management Decisions
All financial decisions carry some degree of risk. Risk management decisions involve identifying, assessing, and mitigating these risks.
This may include purchasing insurance, hedging against currency fluctuations, or diversifying investments. Effective risk management protects against potential losses and ensures the long-term stability of the organization.
Risk mitigation strategies are vital for navigating uncertain economic climates.
The Interconnectedness of Financial Decisions
It's important to note that these areas are not mutually exclusive. They are interconnected and interdependent. A decision in one area can have significant ripple effects in others.
For example, a decision to take on more debt to finance a new project (financing decision) will impact the company's financial risk profile (risk management decision) and its ability to pay dividends (dividend decision).
Successful financial management requires a holistic perspective and a deep understanding of how these various decisions interact.
The Significance of Informed Financial Management
Informed financial management is crucial for the success of any organization, regardless of size or industry.
Poor financial decisions can lead to financial distress, bankruptcy, and lost opportunities. On the other hand, effective financial management can drive growth, increase profitability, and create long-term value.
Individuals also benefit greatly from sound financial planning, enabling them to achieve financial security and realize their life goals.
"Financial literacy is the cornerstone of economic empowerment,"noted Jane Doe, a financial advisor at Acme Financial Services.
Conclusion
Financial management is a multifaceted discipline that demands a thorough understanding of investment, financing, working capital, dividend, and risk management decisions. These elements work together to shape financial outcomes.
By carefully considering these factors and making informed choices, individuals and organizations can improve their financial well-being and achieve long-term success. Continuous learning and adaptation are essential in the ever-changing financial landscape.
Ultimately, mastering these financial decisions translates to greater control over one's financial destiny and the ability to navigate both opportunities and challenges with confidence.