Growing Marijuana For Beginners Step By Step
A surge in home cultivation is sweeping the nation as states ease marijuana laws. First-time growers are finding it easier than ever to produce their own cannabis, but navigating the process requires understanding the fundamentals.
This guide provides a step-by-step overview for beginners looking to cultivate marijuana at home, focusing on essential practices for a successful harvest.
Getting Started: Legality and Basic Needs
Before you even think about seeds, verify the marijuana cultivation laws in your state. Many states that have legalized recreational or medical marijuana still have restrictions on the number of plants you can grow. Penalties for violating these laws can be severe, ranging from fines to imprisonment.
Next, gather your basic supplies. You'll need seeds or clones, growing medium (soil, coco coir, or hydroponics), nutrients, grow lights (LEDs are recommended for beginners), containers, and a controlled environment.
A grow tent is a useful way to control light, temperature, and humidity. Proper ventilation is also key to prevent mold and pests.
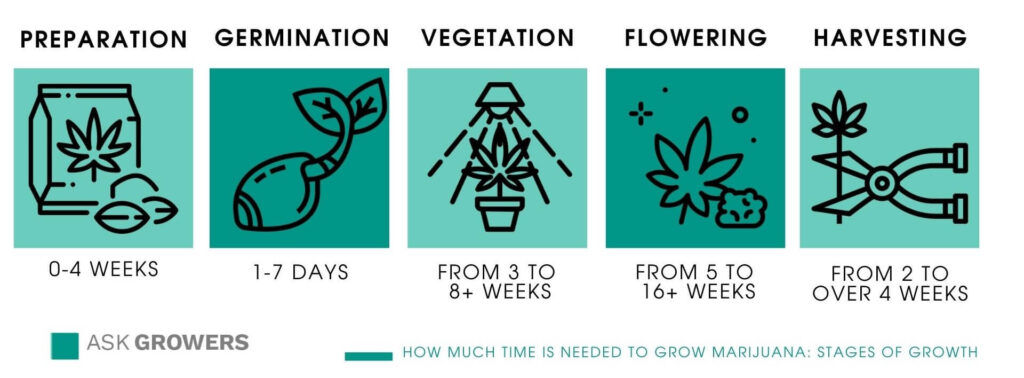
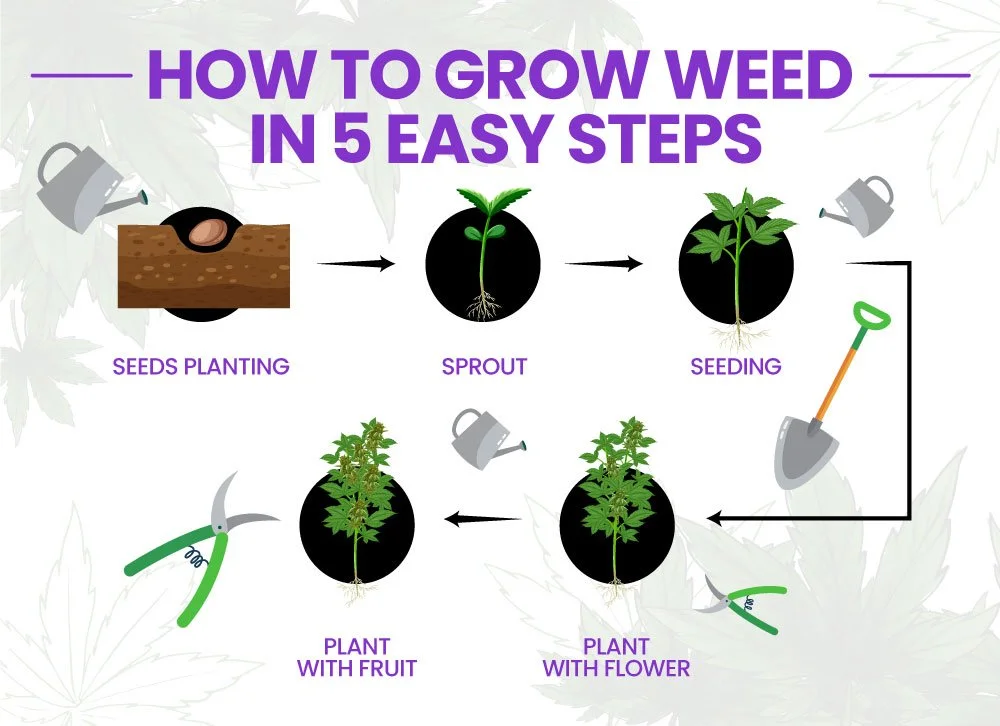
Step 1: Germination
Germination is the process of sprouting your seeds. The paper towel method is a popular and simple approach. Place seeds between moist paper towels on a plate, cover with another plate to create darkness, and keep at room temperature (around 70-80°F or 21-27°C).
Check the seeds daily, keeping the paper towels moist. Within a few days, a small taproot should emerge. Be careful not to damage the taproot during the next step.
Plant the germinated seed, taproot down, in a small container filled with your chosen growing medium. Cover lightly with soil.
Step 2: Seedling Stage
The seedling stage is crucial for establishing a healthy foundation. Provide gentle light (a CFL or low-wattage LED works well) and keep the soil consistently moist, but not waterlogged.
Overwatering is a common mistake that can lead to root rot. Seedlings are fragile and prone to damping off, a fungal disease.
After about 2-3 weeks, the seedling should have developed several sets of true leaves. Now it's time to transplant it into a larger container.
Step 3: Vegetative Stage
During the vegetative stage, your plant focuses on growing taller and producing more leaves. Use a more powerful grow light, such as a higher-wattage LED, and adjust the light cycle to 18 hours of light and 6 hours of darkness (18/6).
Provide your plant with nutrient-rich water according to the manufacturer's instructions. Be careful not to overfeed, which can lead to nutrient burn.
Monitor your plant for pests and diseases. Common pests include spider mites, aphids, and fungus gnats. Address any problems promptly with organic pest control methods if possible.
Step 4: Flowering Stage
The flowering stage is when your plant begins to produce buds. To trigger flowering, change the light cycle to 12 hours of light and 12 hours of darkness (12/12). It is vital that you maintain a consistent 12/12 cycle. Any light leaks during the dark period can cause your plant to revert back to the vegetative stage, or even become a hermaphrodite.
Switch to a flowering-specific nutrient formula. These formulas are typically higher in phosphorus and potassium, which are essential for bud development.
Continue to monitor your plant for pests and diseases. Buds are especially susceptible to mold, so ensure good ventilation and maintain appropriate humidity levels. Bud rot can ruin an entire harvest.
Step 5: Harvesting and Curing
Harvest time depends on the strain and your personal preference. A good indicator is the color of the trichomes (the resin glands on the buds). Use a magnifying glass to examine the trichomes.
When the trichomes are mostly cloudy with some amber, it's time to harvest. Cut the branches and hang them upside down in a dark, well-ventilated room for 7-10 days, or until the stems snap easily.
After drying, trim the buds and place them in airtight jars for curing. Open the jars daily for the first week to burp them and release excess moisture. Curing improves the flavor and potency of your buds. Proper curing is vital for a high-quality product.
Beyond the Basics
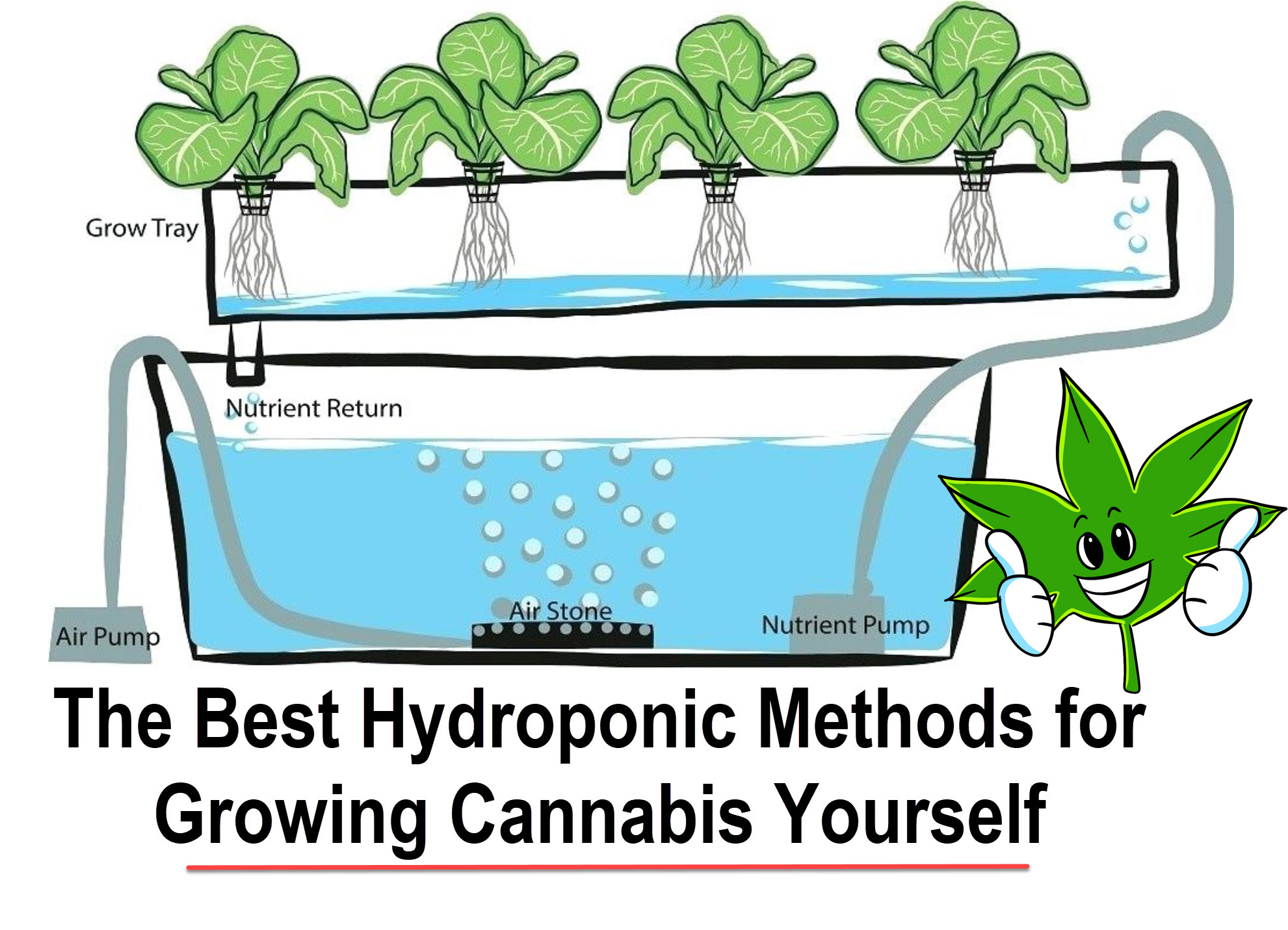
This is a simplified guide, and there's much more to learn about marijuana cultivation. Consider researching different growing techniques, such as hydroponics, sea of green (SOG), and screen of green (SCROG). These methods can increase yields and efficiency.
Join online forums and communities to connect with experienced growers and learn from their expertise. Don't be afraid to experiment and find what works best for you.
As marijuana laws continue to evolve, staying informed about the latest regulations and best practices is crucial for responsible and successful home cultivation. Always prioritize compliance with local laws.











![Growing Marijuana For Beginners Step By Step download book [pdf] 7 steps to grow cannabis: a complete beginner's g](https://www.yumpu.com/en/image/facebook/69005402.jpg)