How Do Aloe Vera Plants Reproduce

Aloe vera, the succulent lauded for its medicinal properties, doesn't just magically appear. Understanding its propagation is crucial for home gardeners and commercial growers alike.
This article delves into the plant's reproductive strategies, uncovering the secrets behind its spread, both sexually and asexually, with emphasis on practical methods for successful cultivation.
Asexual Reproduction: The Primary Pathway
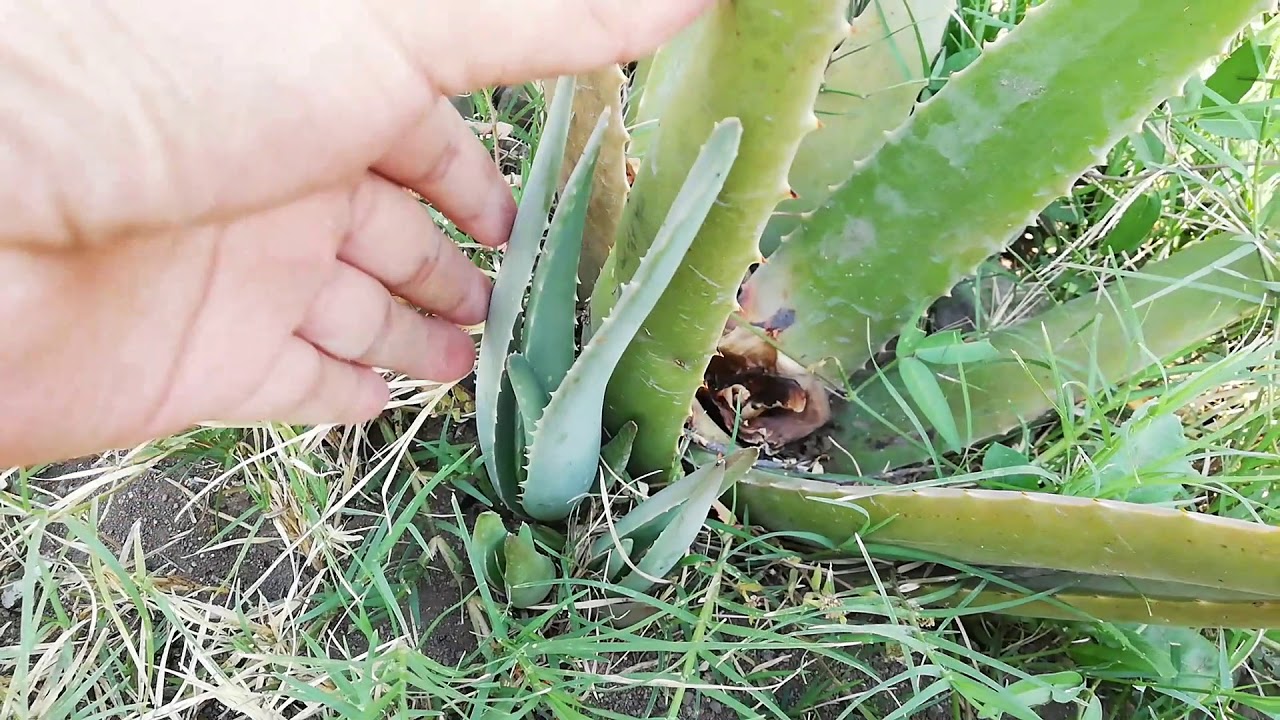
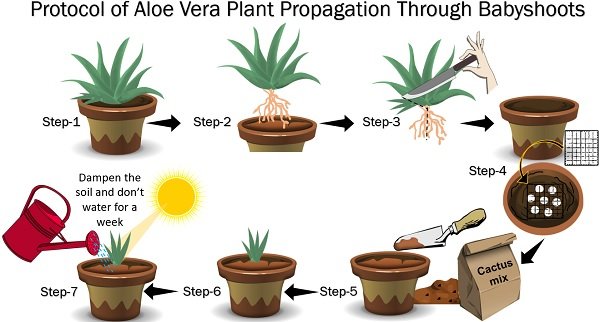
Aloe vera primarily propagates asexually, making it relatively easy to multiply without seeds. This occurs mainly through offsets, also known as "pups".
These are miniature clones of the parent plant that sprout from the base. They develop their own root systems while still attached to the parent, eventually becoming independent plants.
Offsets (Pups): Clonal Expansion
Offsets are the most common and reliable method for aloe vera propagation. These miniature plants emerge from the base of the mother plant, connected by underground stems.
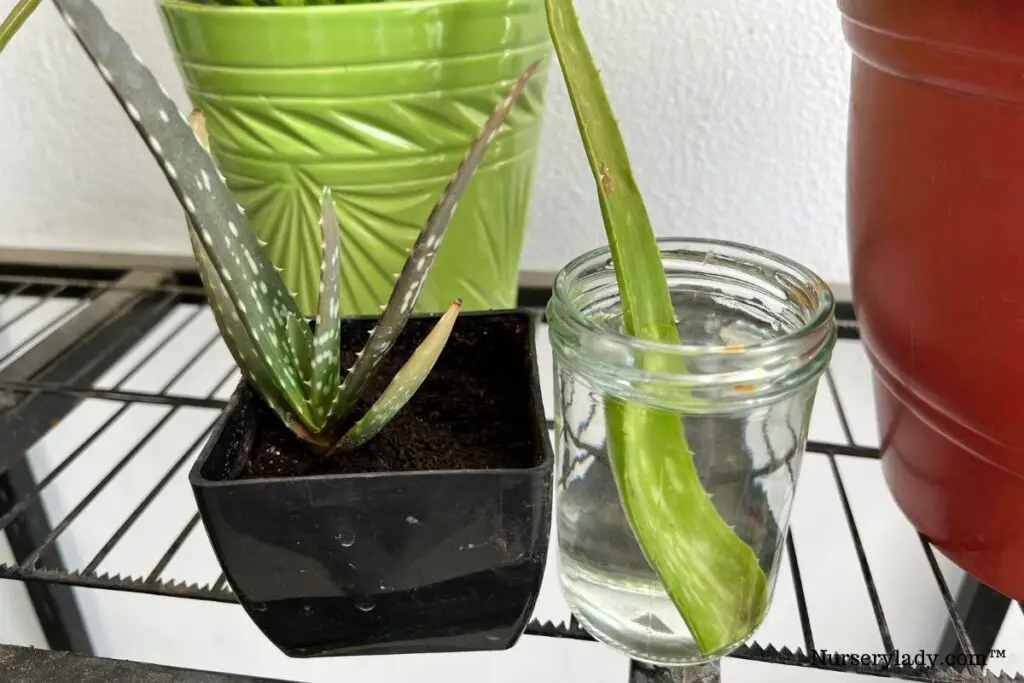
To propagate via offsets, wait until the pups are about one-third the size of the parent plant. Carefully detach them, ensuring they have their own established root system.
Plant the separated offsets in well-draining succulent potting mix. Water sparingly until new growth appears, indicating successful establishment.
Rhizomes: Underground Runners
Aloe vera also spreads through rhizomes, underground stems that send up new shoots. This method is less frequently observed in home gardens but is a natural part of the plant's growth habit.
When repotting an aloe vera plant, you might encounter these rhizomes. Carefully separate sections of the rhizome with attached shoots and plant them in individual pots.
Like offsets, rhizome propagation relies on well-draining soil and careful watering.
Sexual Reproduction: A Less Common Route
While less common in cultivation, aloe vera can reproduce sexually through seeds. This method is more challenging and time-consuming.
However, it's essential for genetic diversity and the development of new aloe varieties. Seed propagation involves pollination, seed collection, and careful germination.
Flowering and Pollination
Aloe vera plants produce flowers on a tall stalk, typically in spring or summer. These flowers can be pollinated by insects or by hand.
Successful pollination leads to the development of seed pods. Allow the seed pods to dry on the plant before harvesting to ensure the seeds are mature.
Cross-pollination between different aloe vera species or varieties can create hybrids with unique characteristics. This is vital for plant breeders looking to create new cultivars.
Seed Germination and Seedling Care
Aloe vera seeds require well-draining soil and a warm environment to germinate. Sow the seeds shallowly in a seed-starting mix.
Keep the soil consistently moist but not waterlogged. Germination can take several weeks. Provide seedlings with bright, indirect light.
Seedlings require more attentive care than offsets. They are vulnerable to fungal diseases and require consistent monitoring.
Factors Influencing Reproduction
Several factors affect aloe vera reproduction, including light, water, and temperature. Optimal conditions promote both asexual and sexual reproduction.
Well-draining soil is critical to prevent root rot, a common killer of aloe vera. Overwatering is a frequent cause of failure in both offset and seed propagation.
Bright, indirect light encourages healthy growth and offset production. Extreme temperatures can hinder reproduction; ideal temperatures range from 65-80°F (18-27°C).
Troubleshooting Propagation Issues
Common problems during aloe vera propagation include root rot, fungal infections, and failure to thrive. Addressing these issues promptly is vital for success.
Ensure proper drainage by using a well-draining potting mix and pots with drainage holes. Apply fungicide if fungal infections are suspected.
If offsets or seedlings fail to thrive, reassess their light, water, and temperature conditions. Adjust these factors as needed to promote healthy growth.
Next Steps
Further research into optimized soil mixtures and watering techniques is ongoing. Plant breeders continue to develop new and improved aloe vera varieties through seed propagation.
Home gardeners can experiment with different propagation methods to find what works best for them. Sharing knowledge and experiences within the gardening community is essential.
Understanding aloe vera reproduction allows for sustainable cultivation and preservation of this valuable plant.