How Do You Compact And Repair A Database In Access
Access database performance grinding to a halt? Data corruption looming? Immediate action is needed to compact and repair your database, preventing potential data loss and system downtime.
This guide provides a critical, step-by-step approach to maintaining database health, ensuring data integrity, and restoring operational efficiency, acting as an essential tool for both novice and experienced users facing database issues.
Understanding Compact and Repair
The Compact and Repair Database utility optimizes database performance by defragmenting files and reclaiming wasted space. It also attempts to fix corruption issues that can lead to errors and data loss.
Think of it like defragging a hard drive – it reorganizes the database for quicker access and stability.
Manual Compact and Repair
Here’s how to manually trigger the compact and repair process within Microsoft Access.
Access 2010 and Later Versions
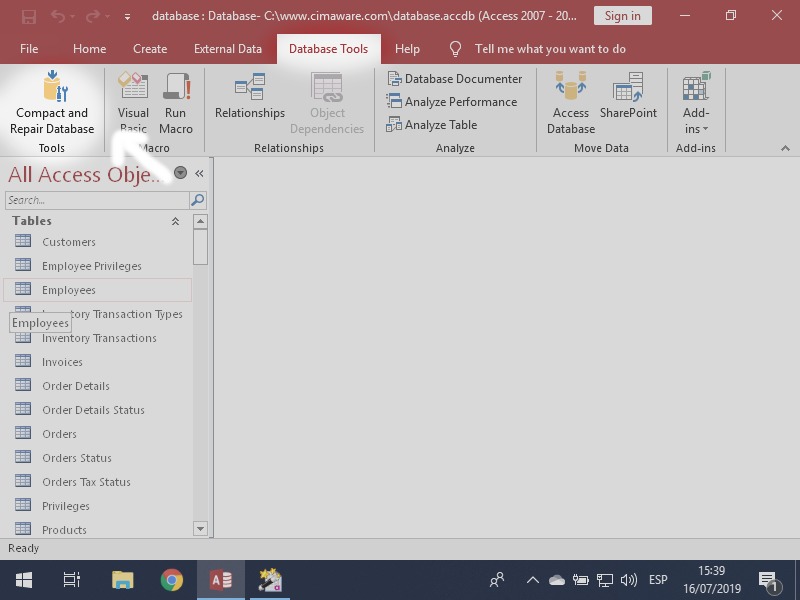
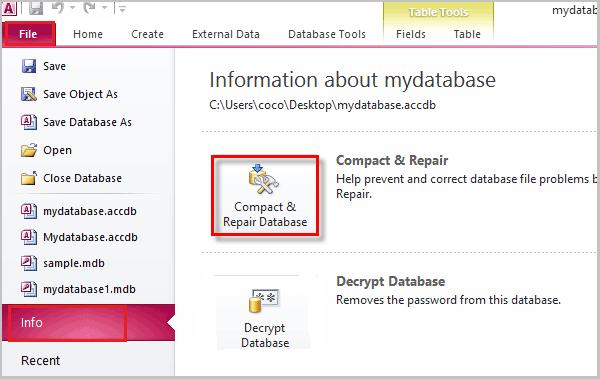
First, close the database you wish to compact and repair. Then, launch Access. Do not open the database directly.
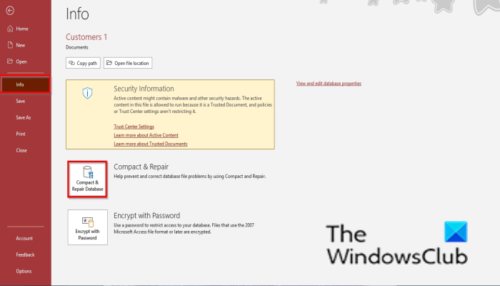
Navigate to File > Info > Compact & Repair Database. Access will then compact and repair the database, creating a temporary backup in case of failure.
If the database is open, you will not see the *Compact & Repair Database* option.
Access 2007
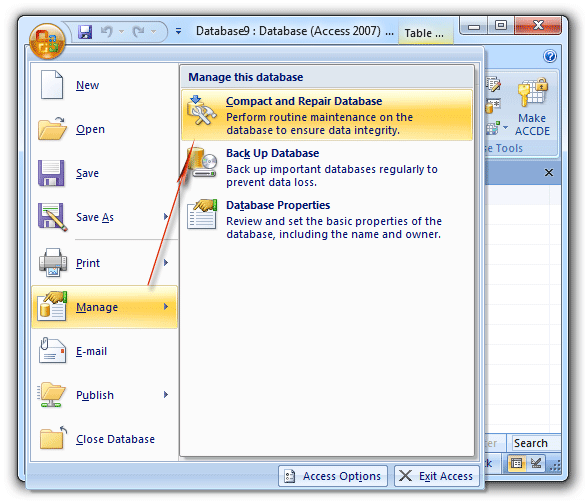
Close the target database. Open Access, but without opening the database directly.
Click the Microsoft Office Button in the top-left corner. Select Manage > Compact and Repair Database. Access will then begin the process.
This version functions similarly to later versions, ensuring a clean and optimized database.
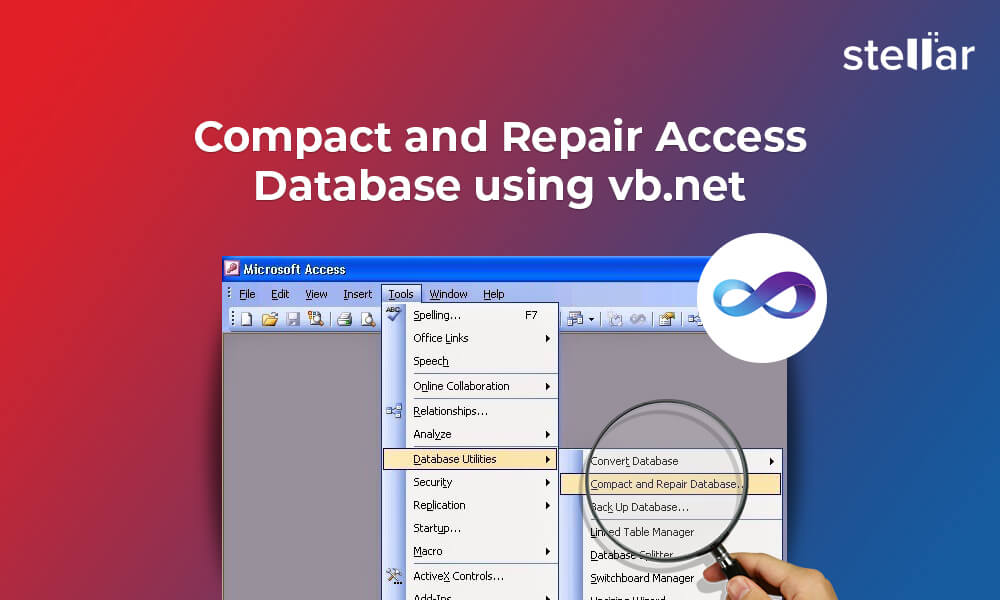
Access 2003 and Earlier Versions
Close the database needing repair. In Access, navigate to Tools > Database Utilities > Compact and Repair Database.
A dialog box will appear; select the database file and click "Compact". A backup will be created, and the database will be repaired.
This method is the legacy approach but remains effective for older Access files.
Compact and Repair on Close
Configure Access to automatically compact and repair the database each time it closes.
This proactive approach helps prevent corruption and maintain optimal performance.
Steps to Enable Compact on Close
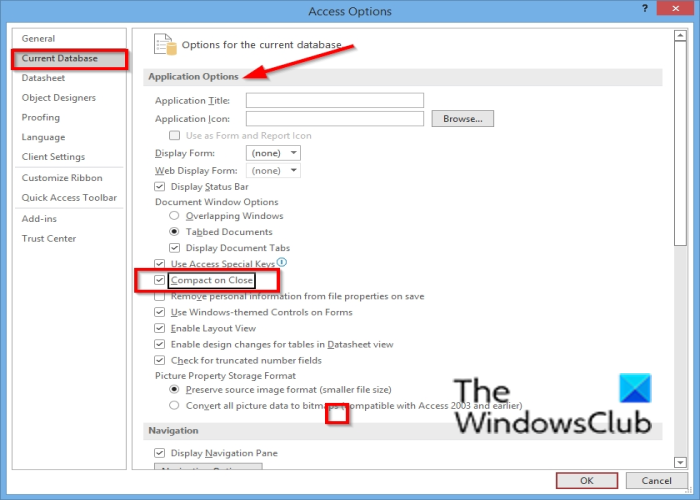
Open the database. Go to File > Options > Current Database. Scroll down to the *Application Options* section.
Check the box labeled “Compact on Close”. Close and reopen the database for the setting to take effect.
From now on, every time you close the database, Access will automatically compact and repair it.
Troubleshooting
Sometimes, the Compact and Repair process may fail. Here are a few troubleshooting steps.
Ensure all other users are out of the database. Exclusive access is often required for successful compaction and repair.
Check for sufficient disk space. A lack of space can halt the process. Also, check your permissions on the folder where database is saved. It might require admin permission.
Dealing with Corruption Issues
If manual and automatic repair attempts fail, the database may be severely corrupted.
Try importing all objects (tables, queries, forms, reports, etc.) into a new, blank database. This can often salvage data from a corrupted file.
If the database is located on a network drive, make sure there is no network issue. Move it to local machine and run compact and repair again.
Preventative Measures
Regularly compact and repair your Access database to prevent corruption and maintain optimal performance.
Back up your database frequently. This provides a safety net in case of severe data loss or corruption.
Avoid abrupt shutdowns of Access while the database is in use. Improper termination can lead to data corruption. Microsoft strongly advises using Compact and Repair regularly.
Next Steps
Implement the Compact and Repair strategies outlined in this guide immediately to safeguard your Access database.
Monitor database performance closely and schedule regular maintenance. If corruption persists, consider professional database recovery services.
Stay informed about the latest Access updates and best practices for data management to ensure long-term database health. Data integrity is paramount.








:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/004-how-to-compact-and-repair-an-access-database-456760e0ccf1487bb7f76503a8e9b472.jpg)