How Do You Reduce Background Noise In A Hearing Aid

Imagine sitting in a bustling café, the aroma of freshly brewed coffee mingling with the clatter of cups and lively conversations. For some, it's a vibrant atmosphere; for others, it's a cacophony. Now, picture trying to navigate this scene with a hearing aid, where the very device meant to clarify sound sometimes amplifies the unwanted noise, turning that pleasant coffee date into a frustrating ordeal. The struggle to filter out background noise is a common challenge for hearing aid users, but thankfully, advancements in technology and techniques are offering real solutions.
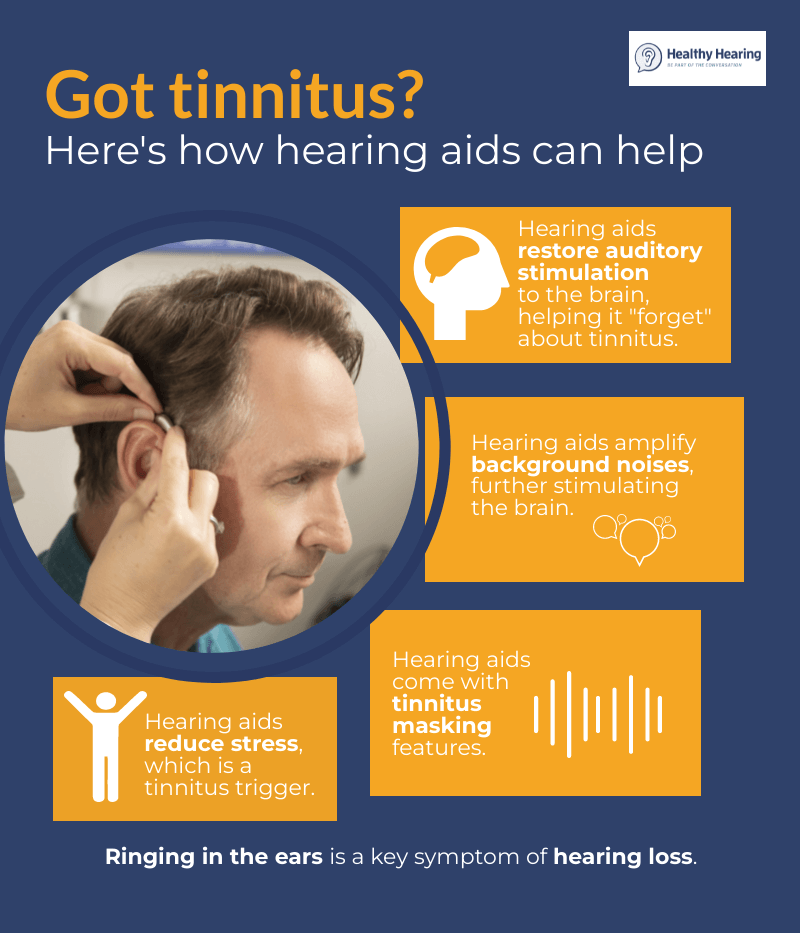
The ability to minimize background noise is paramount to successful hearing aid use. It profoundly impacts communication, social interaction, and overall quality of life. Modern hearing aids are equipped with sophisticated features designed to address this issue, but understanding how these technologies work and how to optimize their settings is crucial for users to truly benefit.
The Landscape of Hearing Aid Technology
Hearing aids have evolved dramatically. The bulky devices of the past have given way to sleek, sophisticated micro-electronics packed with cutting-edge signal processing capabilities.
Directional Microphones: Focusing on What Matters
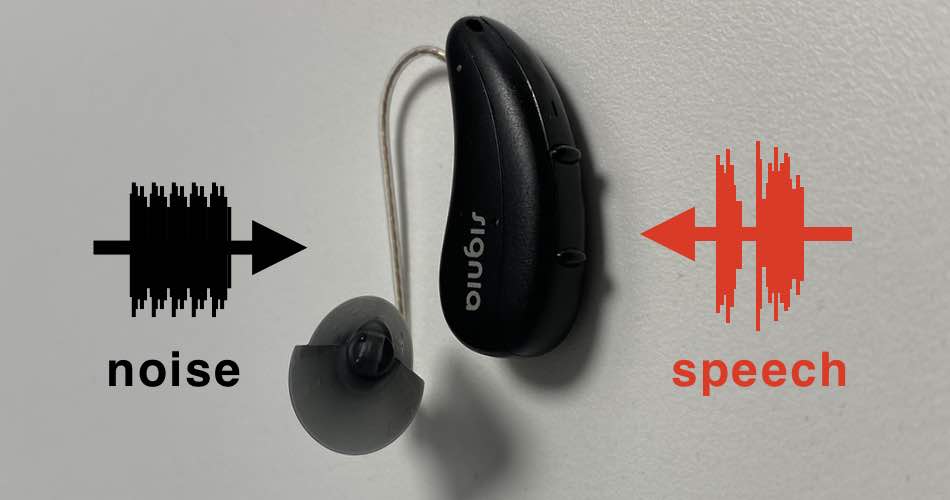
One of the most fundamental noise reduction strategies involves directional microphones. Unlike omnidirectional microphones, which pick up sound from all directions, directional microphones are designed to be more sensitive to sounds originating from the front of the wearer.
This allows the hearing aid to prioritize the speech of the person in front of you, while attenuating sounds coming from the sides or behind. Think of it as having a sonic spotlight that can be focused on the speaker.
Noise Reduction Algorithms: The Brain of the Hearing Aid
Modern hearing aids employ complex noise reduction algorithms to further refine the auditory landscape. These algorithms analyze the sound environment and attempt to differentiate between speech and noise.
Based on these analyses, the hearing aid can automatically reduce the amplification of noise frequencies while preserving the clarity of speech. The sophistication of these algorithms varies widely among different hearing aid models and manufacturers.
According to a study published in the Journal of the American Academy of Audiology, advanced noise reduction algorithms can significantly improve speech understanding in noisy environments for hearing aid users.
Adaptive Features: Personalizing the Listening Experience
Many newer hearing aids offer adaptive features that automatically adjust settings based on the listening environment. For example, the hearing aid might detect when you're in a restaurant and automatically activate a noise reduction program specifically tailored for that setting.
These adaptive capabilities rely on sophisticated sensors and machine learning algorithms to classify different sound environments and optimize performance accordingly. Some devices even learn your personal preferences over time, fine-tuning their response to your individual needs.
Connectivity and Apps: Taking Control
The rise of smartphone connectivity has revolutionized the hearing aid experience. Many hearing aids now connect wirelessly to smartphones via Bluetooth, allowing users to control settings, adjust volume, and even stream audio directly to their devices.
Dedicated apps provide a user-friendly interface for managing noise reduction features. You can often manually adjust noise reduction levels, switch between different listening programs, and even create custom settings for specific environments.
This level of control empowers users to actively manage their listening experience and optimize performance in challenging situations.
Beyond Technology: Practical Strategies for Reducing Noise
While technology plays a crucial role, there are several practical strategies that hearing aid users can employ to minimize background noise.
Optimizing Hearing Aid Fit and Settings
A properly fitted hearing aid is essential for optimal performance. An audiologist can ensure that the hearing aid is snug and comfortable, minimizing feedback and maximizing sound quality.
Furthermore, working closely with an audiologist to fine-tune the hearing aid settings is critical. They can adjust noise reduction parameters, optimize directional microphone settings, and create custom listening programs tailored to your specific needs.
Communication Strategies: Taking Charge of the Conversation
Simple communication strategies can make a significant difference in noisy environments. Requesting to sit in a quieter area of a restaurant, positioning yourself with your back to the noise source, and asking people to speak clearly and slowly can greatly improve understanding.
Assertively communicating your needs is key. Don't hesitate to inform others that you have a hearing impairment and may need them to speak up or repeat themselves.
Assistive Listening Devices: Bridging the Gap
In particularly challenging situations, assistive listening devices (ALDs) can provide additional support. These devices, such as remote microphones or FM systems, transmit sound directly to the hearing aid, bypassing background noise.
For example, a remote microphone can be placed near the speaker in a lecture hall or meeting, ensuring that their voice is amplified directly into your hearing aid. ALDs can be particularly helpful in situations where distance or background noise make it difficult to hear clearly.
Managing Expectations and Practicing Patience
It's important to have realistic expectations about what hearing aids can achieve. While modern technology has made remarkable strides in noise reduction, it's not a perfect solution. Some level of background noise is often unavoidable, particularly in very loud or complex environments.
Practicing patience and developing coping strategies can help manage frustration and maintain a positive attitude. Remember that adjusting to hearing aids and optimizing their performance is an ongoing process.
The Future of Noise Reduction in Hearing Aids
The field of hearing aid technology is constantly evolving. Researchers are exploring new approaches to noise reduction, including advanced signal processing techniques, artificial intelligence, and brain-computer interfaces.
"We are on the cusp of a new era in hearing healthcare,"
says Dr. Sarah Jones, a leading audiologist and researcher at the National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders (NIDCD). "Future hearing aids will be even more intelligent, personalized, and seamlessly integrated into our lives."
These advancements promise to further improve speech understanding in noisy environments and enhance the overall listening experience for hearing aid users.
A Quieter, More Connected World
Reducing background noise in hearing aids is not merely about improving audibility; it's about empowering individuals to fully participate in the world around them. It's about fostering meaningful connections, enhancing social interactions, and improving overall quality of life.
By understanding the technology, employing practical strategies, and working closely with audiologists, hearing aid users can unlock the full potential of their devices and embrace a world that is both clearer and more connected.