How Fast Can You Lose 60 Pounds

The allure of shedding significant weight rapidly is undeniable. The promise of fitting into old clothes, feeling healthier, and boosting self-esteem can drive individuals to pursue aggressive weight loss strategies. But the question remains: how quickly can one safely and effectively lose 60 pounds, and what are the potential pitfalls of rapid weight loss?
This article delves into the realities of weight loss, exploring sustainable strategies recommended by health professionals and highlighting the risks associated with extreme approaches. We'll examine guidelines from reputable organizations like the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the National Institutes of Health (NIH), offering a balanced perspective on achieving significant weight loss goals without compromising health.
Understanding Healthy Weight Loss Rates
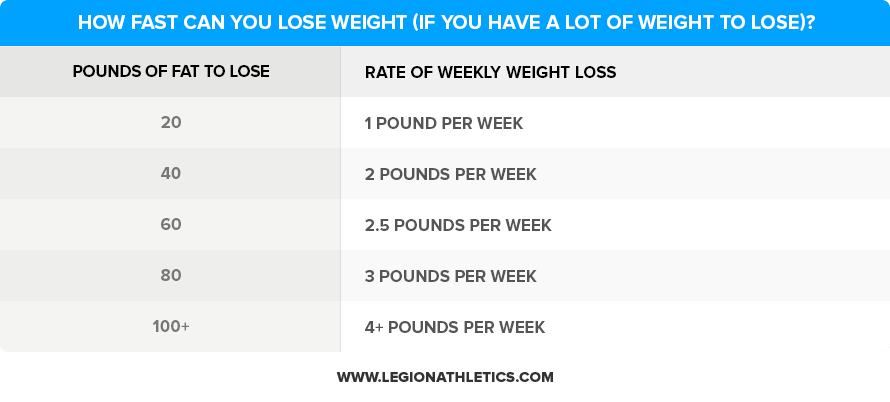
The CDC generally recommends a weight loss rate of 1 to 2 pounds per week as a safe and sustainable pace. This translates to a calorie deficit of 500 to 1,000 calories per day. Achieving this typically involves a combination of dietary changes and increased physical activity.
Losing 60 pounds at this rate could take approximately 30 to 60 weeks, or roughly 7 to 14 months. It's crucial to understand that this is an average, and individual results may vary based on factors like metabolism, activity level, starting weight, and overall health.
Dr. Emily Carter, a registered dietitian, emphasizes that "Individual responses to weight loss interventions can vary significantly. What works for one person might not work for another, and it's essential to consult with a healthcare professional to develop a personalized plan."
The Dangers of Rapid Weight Loss
While the desire for quick results is understandable, rapid weight loss – often defined as losing more than 2 pounds per week – can pose serious health risks. These risks can include gallstones, nutrient deficiencies, muscle loss, and a slowed metabolism.
Gallstones are a common complication of rapid weight loss, occurring when the liver releases more cholesterol into bile. This excess cholesterol can form gallstones, leading to pain, nausea, and potentially requiring surgery.
Nutrient deficiencies can arise when individuals severely restrict their calorie intake, depriving their bodies of essential vitamins and minerals. This can lead to fatigue, weakened immune function, and other health problems.
Muscle loss is another significant concern, as the body may start breaking down muscle tissue for energy when calorie intake is drastically reduced. This can decrease strength and slow down metabolism, making it harder to maintain weight loss in the long run.
Furthermore, rapid weight loss can sometimes lead to an eating disorder or disordered eating patterns. The psychological impact of extreme restriction can be detrimental, fostering unhealthy relationships with food and body image.
Safe and Sustainable Strategies for Losing 60 Pounds
Instead of focusing on speed, prioritizing sustainable strategies is key to achieving lasting weight loss and improved health. This involves making gradual dietary changes, incorporating regular physical activity, and seeking support from healthcare professionals.
Dietary modifications should focus on whole, unprocessed foods, such as fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. Reducing intake of sugary drinks, processed foods, and unhealthy fats is also crucial.
Regular physical activity is essential for burning calories and improving overall health. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise per week, as recommended by the American Heart Association.
Strength training is also important for building and maintaining muscle mass, which can help boost metabolism and prevent muscle loss during weight loss. Aim for at least two strength training sessions per week, targeting all major muscle groups.
Seeking support from healthcare professionals, such as registered dietitians or doctors, can provide personalized guidance and help individuals develop a safe and effective weight loss plan. They can assess individual needs, identify potential health risks, and provide ongoing support and motivation.
The Role of Medical Interventions
In some cases, medical interventions like weight loss medications or bariatric surgery may be considered for individuals struggling with obesity. However, these interventions are typically reserved for individuals with a BMI of 30 or higher, or a BMI of 27 or higher with weight-related health conditions, such as diabetes or high blood pressure.
Weight loss medications can help suppress appetite or block the absorption of fat, but they often come with side effects and are not a long-term solution for weight management. Bariatric surgery, such as gastric bypass or sleeve gastrectomy, can lead to significant weight loss, but it is a major surgical procedure with potential risks and complications.
It's crucial to have a thorough discussion with a healthcare professional to determine if medical interventions are appropriate and to understand the potential risks and benefits.
Long-Term Maintenance and Lifestyle Changes
Losing 60 pounds is a significant accomplishment, but maintaining that weight loss is equally important. This requires adopting long-term lifestyle changes that support a healthy weight.
Continuing to prioritize a healthy diet and regular physical activity is essential. It's also important to develop healthy coping mechanisms for stress and emotional eating, as these can often derail weight loss efforts.
Regularly monitoring weight and seeking support from friends, family, or support groups can also help individuals stay on track and maintain their weight loss over time. Studies show that individuals who have social support are more likely to maintain their weight loss than those who don't.
Conclusion
While the desire to lose 60 pounds quickly is understandable, prioritizing a safe and sustainable approach is crucial for long-term health and well-being. Aiming for a weight loss rate of 1 to 2 pounds per week through a combination of dietary changes, increased physical activity, and professional guidance is the most effective way to achieve significant weight loss without compromising health. Remember, the journey to a healthier weight is a marathon, not a sprint.
Focus on building healthy habits, seeking support when needed, and celebrating small victories along the way. By adopting a patient and sustainable approach, individuals can achieve their weight loss goals and enjoy the long-term benefits of a healthier lifestyle.