How Long Does Btc Transfer Take

Imagine this: You're sending a virtual handshake across the digital world, a confirmation of trust and value in the form of Bitcoin. It's late, the glow of your screen reflects in your eyes as you hit ‘send,’ eager for the transaction to complete. But then, the waiting game begins. How long will it take for that BTC to reach its destination? This is the question that often dances in the minds of both seasoned crypto veterans and curious newcomers alike.
Understanding the time it takes for a Bitcoin transaction to complete involves several layers – network congestion, transaction fees, and the underlying mechanics of the blockchain itself. While instantaneous digital transfers have become the norm in many aspects of our lives, Bitcoin transactions operate under a different set of rules, influenced by the decentralized nature of the network and the processes that secure it.
The Anatomy of a Bitcoin Transaction
To appreciate the duration of a Bitcoin transfer, we must first dissect the journey it undertakes. A Bitcoin transaction isn't a simple point-to-point exchange like sending an email.
Instead, it's a broadcast, announced to a vast network of computers – the miners – who compete to validate it.
The Role of Miners
Miners are the unsung heroes of the Bitcoin ecosystem. These individuals or entities dedicate significant computing power to solve complex mathematical problems.
Successfully solving this puzzle allows them to bundle pending transactions into a block and add it to the blockchain, a chronological and immutable record of all Bitcoin transactions.
This process, known as mining, is what secures the network and ensures the integrity of the Bitcoin system.
The 10-Minute Average
On average, a new block is added to the Bitcoin blockchain approximately every 10 minutes. This 10-minute interval is a target set by Bitcoin's creator, Satoshi Nakamoto, and is maintained by adjusting the difficulty of the mining puzzle.
However, a single confirmation doesn't guarantee finality. It's recommended to wait for multiple confirmations before considering a transaction irreversible.
Typically, six confirmations are considered the gold standard, offering a very high degree of certainty – though this can take an hour or more.
Factors Influencing Transfer Time
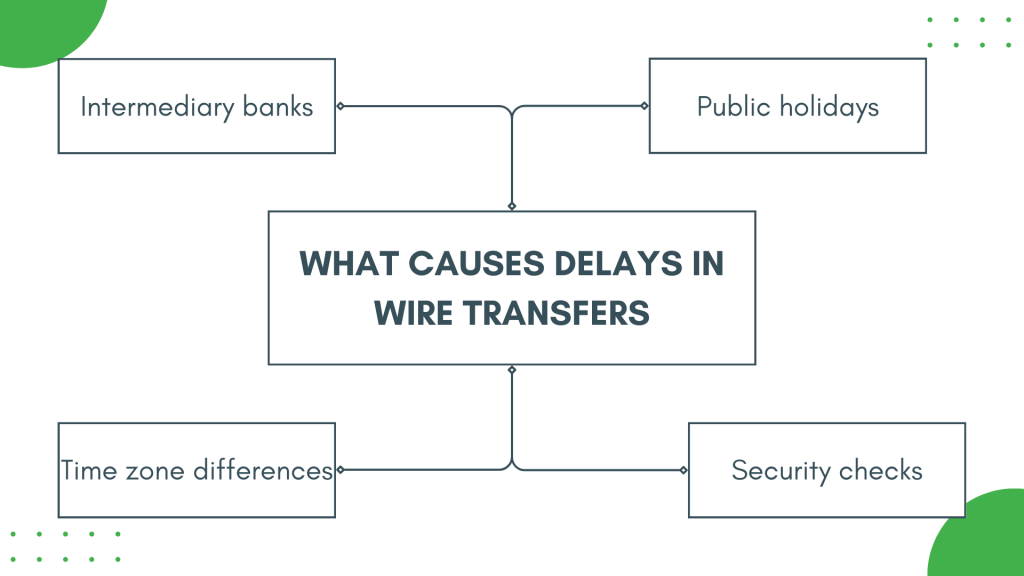
The 10-minute block time is just an average. Actual transfer times can vary significantly based on several factors.
Let's delve into the most important ones.
Transaction Fees
Transaction fees play a crucial role in determining how quickly a transaction is processed. Users attach a fee to their transaction as an incentive for miners to include it in a block.
Miners prioritize transactions with higher fees, as they receive these fees as a reward for their work.
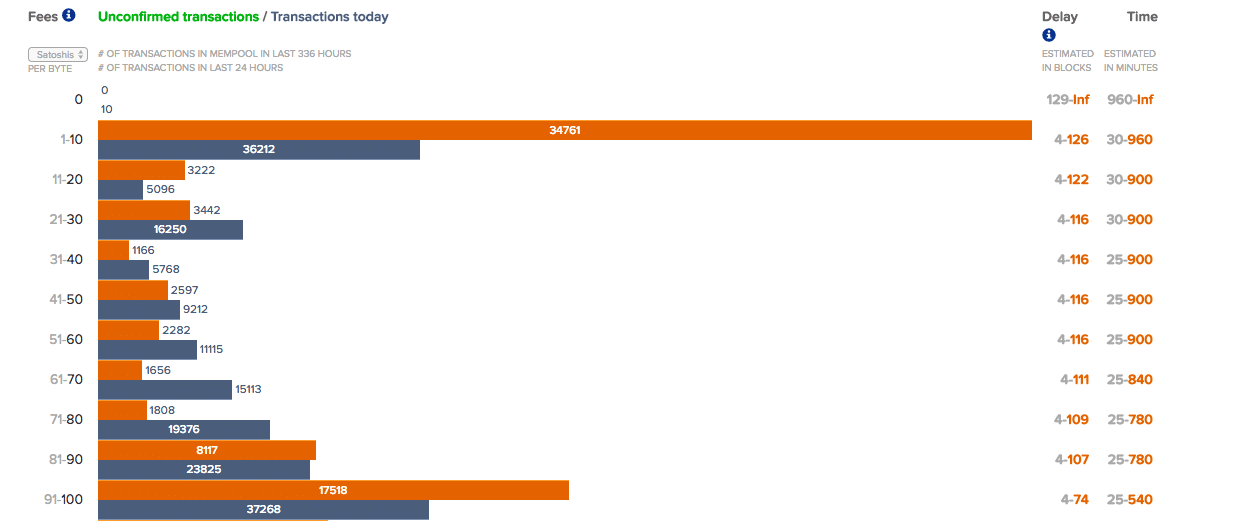
During periods of high network congestion, transactions with low fees may languish unconfirmed for hours, or even days, while those with higher fees are processed more swiftly.
Network Congestion
The Bitcoin network, like any system, has a limited capacity. When the number of transactions waiting to be processed exceeds this capacity, the network becomes congested.
This congestion can lead to longer confirmation times and higher fees as users compete to have their transactions prioritized.
Events like market volatility or major news announcements can trigger surges in transaction volume, exacerbating network congestion.
Transaction Size
The size of a transaction, measured in bytes, also affects its processing time. More complex transactions, involving multiple inputs and outputs, are larger in size and require more computational resources to validate.
Miners may be less inclined to include large transactions, especially during periods of congestion, unless they are accompanied by sufficiently high fees.
Confirmation Time Variability
Confirmation times are probabilistic, not deterministic. Even if a transaction is included in a block, it doesn't guarantee immediate finality.
The Bitcoin network is susceptible to rare events like block re-organizations, where a longer chain of blocks replaces a shorter one, potentially invalidating recently confirmed transactions.
This is why waiting for multiple confirmations is considered best practice, especially for high-value transactions.
Practical Tips for Faster Transactions
While you can't control the overall state of the Bitcoin network, there are steps you can take to optimize your transactions for faster processing.
Consider these practical tips:
Choose Appropriate Fees
Use a fee estimation tool to determine the optimal fee for your transaction. These tools analyze current network conditions and suggest fees that are likely to result in timely confirmation.
Many Bitcoin wallets automatically estimate and set appropriate fees, but it's always a good idea to double-check.
Consolidate Transactions
If you have multiple small Bitcoin inputs, consider consolidating them into a single, larger transaction before making a payment. This reduces the transaction size and can improve its chances of being processed quickly.
Use SegWit Addresses
Segregated Witness (SegWit) is a protocol upgrade that optimizes transaction data and reduces transaction fees.
Using SegWit-compatible addresses can result in faster and cheaper transactions.
Consider Layer-2 Solutions
Layer-2 solutions, such as the Lightning Network, offer alternative ways to transact Bitcoin off-chain, providing near-instantaneous and low-cost payments.
These solutions are particularly well-suited for small, frequent transactions.
The Future of Bitcoin Transaction Speed
The Bitcoin community is constantly exploring ways to improve the network's scalability and transaction speed.
Several promising developments are underway.
Taproot
Taproot is a recent upgrade to the Bitcoin protocol that enhances privacy and efficiency. It also allows for more complex smart contracts, potentially opening the door to new Layer-2 solutions.
Continued Layer-2 Development
Ongoing development and adoption of Layer-2 solutions like the Lightning Network hold significant promise for scaling Bitcoin's transaction capacity and reducing confirmation times.
Sharding
Sharding, a technique used in other blockchain projects, involves dividing the blockchain into smaller, more manageable pieces.
While sharding presents technical challenges for Bitcoin, it could potentially lead to significant improvements in transaction speed and scalability.
A Moment of Reflection
So, how long does a Bitcoin transfer take? The answer, as we've explored, is nuanced. It's a journey influenced by network conditions, user choices, and the very architecture of the decentralized system itself.
While waiting for confirmations can sometimes feel like watching paint dry, it's a reminder of the trade-offs inherent in a secure, censorship-resistant, and decentralized currency.
As technology advances and the Bitcoin network evolves, we can anticipate further improvements in transaction speed and efficiency, bringing us closer to a future where digital handshakes happen not just securely, but also with greater ease and speed.