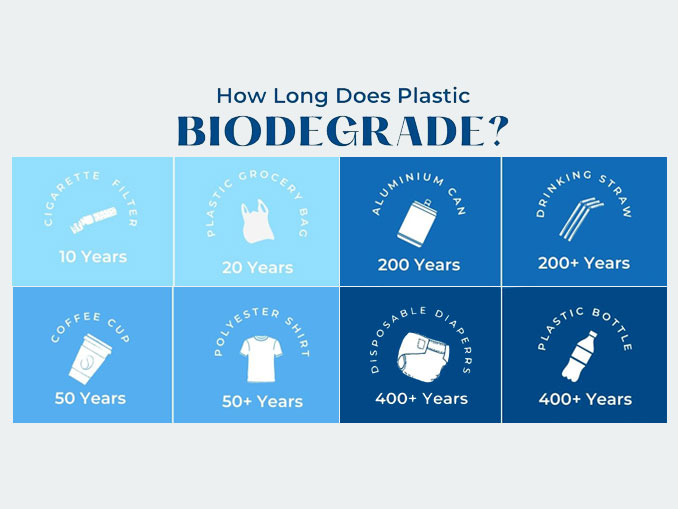
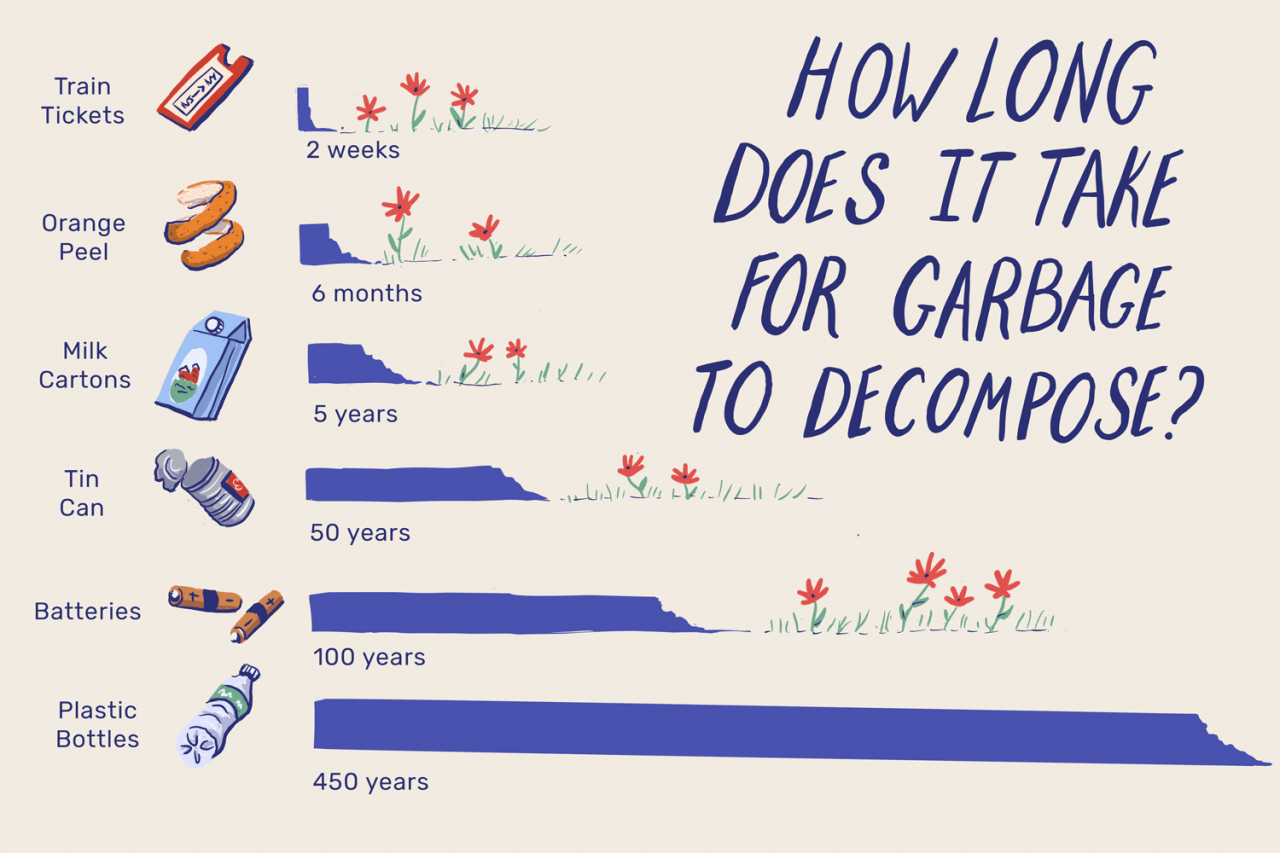
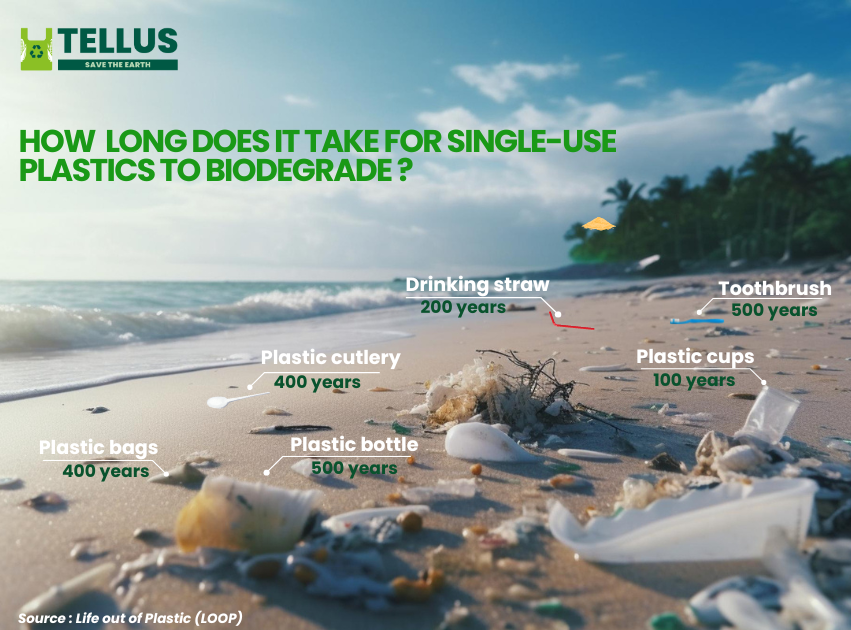
How Long Does It Take For Gum To Biodegrade

Imagine strolling down a sunny city street, the scent of freshly brewed coffee wafting from a nearby café. You’re enjoying a piece of your favorite bubblegum, its sweet flavor a little burst of joy. But as the flavor fades, you’re faced with the inevitable question: what to do with it? Do you search for a trash can, or, like so many others, succumb to the temptation of discreetly sticking it under a bench, unknowingly contributing to a sticky legacy that will outlive your own memories of that sunny afternoon.
The lingering presence of discarded chewing gum on sidewalks and public spaces is more than just an unsightly nuisance; it’s a testament to the surprisingly long time it takes for this seemingly innocuous substance to break down. While the exact timeframe is debated, the consensus is that chewing gum can persist in the environment for decades, if not centuries, posing environmental challenges and sparking innovative solutions.
The Sticky Truth: What's Chewing Gum Made Of?
To understand why chewing gum takes so long to biodegrade, it's crucial to examine its composition. Unlike the chewing gum of our grandparents' era, which was often made from natural tree sap, modern chewing gum relies on a synthetic rubber base. This base, along with sweeteners, flavorings, and softeners, creates the chewy texture we all know, but it also contributes to its remarkable durability.
The synthetic rubber, often a blend of polymers, is the primary culprit behind gum's persistence. These polymers are designed to be resistant to breakdown by saliva and digestive enzymes, which is why gum doesn't simply dissolve in your mouth.
The Biodegradation Breakdown
Biodegradation is the process by which organic substances are broken down by microorganisms like bacteria and fungi. Natural substances, like food scraps or leaves, decompose relatively quickly. However, synthetic polymers in chewing gum are resistant to these natural processes.
While some sources claim gum can take up to five years to disappear, this is often an oversimplification. In reality, the breakdown process is incredibly slow and depends on several factors, including the specific composition of the gum, the environmental conditions (temperature, moisture, and sunlight), and the presence of suitable microorganisms.
Even after several years, chewing gum doesn't truly disappear; it simply breaks down into smaller pieces. These microplastics can then persist in the environment, potentially entering waterways and food chains, a concern highlighted by numerous environmental organizations.
The Impact: More Than Just a Sticky Situation
The ubiquitous presence of discarded chewing gum has significant environmental and economic consequences. Cities and businesses spend millions of dollars annually on gum removal, employing specialized equipment and cleaning crews to combat the sticky mess.
Beyond the monetary cost, there's the aesthetic impact. Gum-covered sidewalks and public spaces detract from the overall appearance of communities and can contribute to a sense of neglect. This is why initiatives aimed at responsible gum disposal are crucial.
Furthermore, discarded gum can pose a threat to wildlife. Birds and other animals may mistake gum for food, leading to digestive problems and even death. This underlines the importance of proper waste disposal and responsible environmental stewardship.
Innovations and Solutions: A Sticky Situation Solved?
Fortunately, the challenges posed by discarded chewing gum have spurred innovation and creative solutions. Researchers and companies are exploring various approaches, from developing biodegradable gum to implementing effective recycling programs.
One promising avenue is the development of chewing gum made from biodegradable polymers. These polymers are designed to break down more readily in the environment, reducing the long-term impact of discarded gum. Several companies are already producing or researching such alternatives, offering a more sustainable option for consumers.
Another approach focuses on improved waste management and recycling. Some cities and businesses have implemented specialized gum recycling programs, where discarded gum is collected and processed into new products, such as plastic pellets for manufacturing. TerraCycle, for instance, offers a gum recycling program in several countries.
"We need to shift from a linear 'take-make-dispose' model to a circular economy where resources are reused and waste is minimized," says Tom Szaky, CEO of TerraCycle.
Public awareness campaigns also play a crucial role in promoting responsible gum disposal. By educating consumers about the environmental impact of discarded gum and encouraging them to use designated bins, these campaigns can help reduce the amount of gum littering our streets.
The Future of Chewing Gum: A Sustainable Chew?
The future of chewing gum hinges on a combination of technological innovation, responsible consumer behavior, and effective waste management strategies. As biodegradable alternatives become more readily available and recycling programs expand, the environmental impact of chewing gum can be significantly reduced.
Consumer choices also play a vital role. By opting for biodegradable gum, properly disposing of waste, and supporting companies committed to sustainability, individuals can contribute to a cleaner, healthier environment.
Ultimately, addressing the problem of discarded chewing gum requires a collective effort. From manufacturers developing eco-friendly products to consumers adopting responsible habits, we all have a role to play in creating a more sustainable future. Let's choose to be part of the solution, not part of the sticky problem.
Conclusion: A Thought to Chew On
So, how long does it take for gum to biodegrade? The answer, it turns out, is complex and multifaceted. While the exact timeframe remains uncertain, the undeniable truth is that conventional chewing gum persists in the environment for an extended period, posing environmental challenges and aesthetic concerns.
However, the story doesn't end there. Through innovation, awareness, and responsible action, we can pave the way for a future where chewing gum is no longer a source of pollution but rather a momentary pleasure enjoyed without lasting consequences. The choice, ultimately, is ours: will we continue to contribute to the sticky legacy, or will we embrace a more sustainable approach? The answer may just be a matter of taste.