How Long Does It Take To Adjust To Night Shift

The graveyard shift, swing shift, the night shift – whatever the moniker, working outside the typical 9-to-5 schedule presents unique challenges to the human body. Adjusting to a nocturnal lifestyle is rarely seamless and understanding the timeline for adaptation is crucial for both employees and employers.
This article delves into the complexities of adjusting to night shift work, exploring the physiological processes involved, the factors influencing adaptation, and strategies to mitigate its negative impacts. We will examine research from sleep experts and organizations like the National Sleep Foundation and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) to provide a comprehensive overview.
The Body's Internal Clock
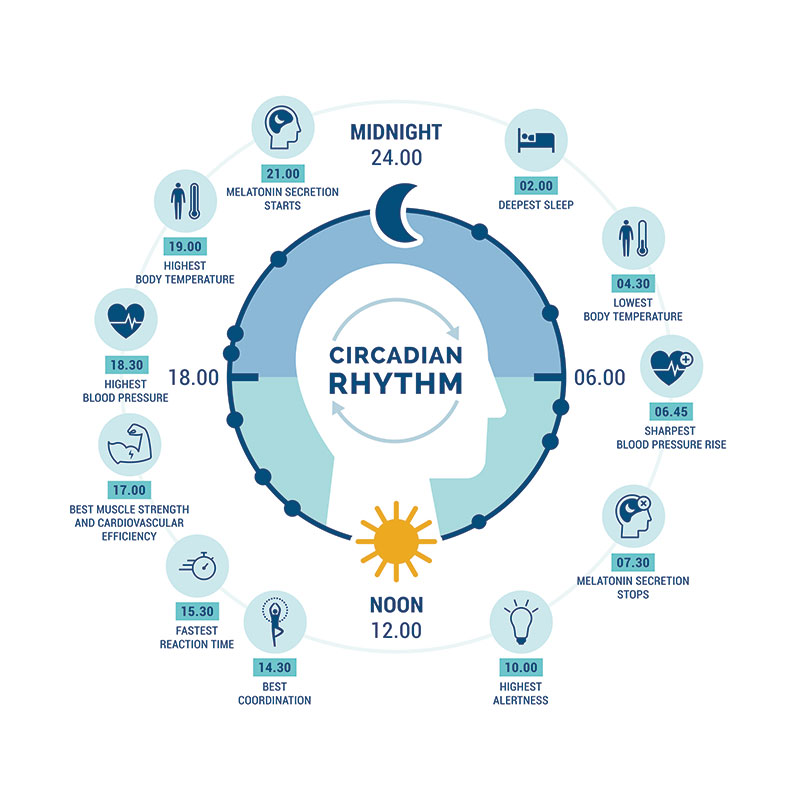
The human body operates on a roughly 24-hour cycle known as the circadian rhythm. This internal clock regulates various bodily functions, including sleep-wake cycles, hormone release, and body temperature. Disrupting this rhythm, as night shift work inevitably does, can lead to a cascade of physiological and psychological consequences.
According to the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH), it can take anywhere from several days to several weeks to fully adjust to a night shift schedule. Some individuals may never fully adapt, experiencing chronic sleep deprivation and related health issues.
Factors Influencing Adaptation
The time it takes to adjust to night shift work is highly individual and influenced by several factors. These include the consistency of the schedule, individual chronotype (whether you're a morning lark or a night owl), age, and overall health.
A consistent night shift schedule allows the body to gradually realign its circadian rhythm. Rotating shifts, where workers frequently switch between day and night shifts, are particularly disruptive and make adaptation more difficult. According to a study published in the journal "Sleep", individuals on rotating shifts often experience more severe sleep disturbances and health problems.
Age also plays a role; younger individuals tend to adapt more quickly than older adults. Pre-existing health conditions and lifestyle habits, such as smoking or excessive caffeine consumption, can further impede the adaptation process.
The Physiological and Psychological Toll
The consequences of not adjusting adequately to night shift work extend beyond simple fatigue. Chronic sleep deprivation can lead to a range of health problems, including increased risk of cardiovascular disease, gastrointestinal disorders, and mood disturbances.
Studies have also linked night shift work to a higher incidence of workplace accidents and errors. Impaired cognitive function and reduced alertness can compromise performance and increase the likelihood of mistakes, particularly in safety-sensitive occupations.
"The impact on social life and family relationships is also a significant concern. Night shift workers often struggle to maintain regular social interactions and can experience feelings of isolation and loneliness," explains Dr. Emily Carter, a sleep specialist at the Sleep Disorders Center.
Strategies for Mitigating the Effects
While adjusting to night shift work can be challenging, several strategies can help mitigate its negative effects. These include optimizing the sleep environment, managing light exposure, and adopting healthy lifestyle habits.
Creating a dark, quiet, and cool sleep environment is crucial for maximizing sleep quality during the day. Using blackout curtains, earplugs, and a white noise machine can help block out external disturbances. According to the American Academy of Sleep Medicine, maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, even on days off, is also essential for regulating the circadian rhythm.
Light exposure plays a key role in regulating the sleep-wake cycle. Exposure to bright light during work hours can help suppress melatonin production and promote alertness. Conversely, minimizing light exposure before and during sleep is important for promoting restful sleep.
Tips for Night Shift Workers
Several specific actions can improve the adaptation to a nocturnal sleep schedule.
- Maintain a consistent sleep schedule: Even on days off, try to stick to a similar sleep-wake pattern.
- Optimize your sleep environment: Make sure your bedroom is dark, quiet, and cool.
- Manage light exposure: Get bright light exposure during your shift and minimize it before sleep.
- Limit caffeine and alcohol: Avoid these substances close to bedtime.
- Practice relaxation techniques: Meditation or deep breathing can help you wind down before sleep.
- Stay active and eat healthy: Regular exercise and a balanced diet can improve overall health and sleep quality.
The CDC offers similar advice for shift workers, emphasizing the importance of communicating with family and friends to manage social isolation and maintain healthy relationships.
Employer Responsibilities
Employers also have a responsibility to support the health and well-being of their night shift workers. This includes providing adequate breaks, promoting a culture of safety, and offering resources for managing sleep and fatigue.
"Implementing strategies such as fatigue risk management systems and providing access to sleep education programs can significantly improve the health and productivity of night shift workers," says John Smith, a safety manager at Acme Corporation.
Recognizing the challenges of night shift work and implementing strategies to mitigate its negative effects is crucial for ensuring the health, safety, and well-being of this often-overlooked segment of the workforce.
Conclusion
Adjusting to night shift work is a complex process that can take varying amounts of time, depending on individual factors and the consistency of the work schedule. While some individuals may adapt relatively quickly, others may struggle to maintain a healthy sleep-wake cycle and experience chronic health problems.
By understanding the physiological processes involved and implementing strategies to mitigate the negative effects, both employees and employers can work together to create a healthier and safer work environment for those who work while the world sleeps. Prioritizing sleep health is not just a matter of personal well-being, but also a crucial factor in workplace safety and productivity.