How Long Does Methylene Blue Stay In Your System

The striking blue discoloration often associated with methylene blue treatment, whether for medical conditions or increasingly, as a component of wellness trends, begs a fundamental question: how long does this compound actually linger in the body? Understanding its pharmacokinetics is crucial, not only for medical professionals administering the drug but also for individuals exploring its purported benefits.
This article delves into the intricacies of methylene blue's presence in the human body, exploring its absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion. It aims to provide a comprehensive overview based on scientific data and expert opinions, offering clarity on the factors influencing its duration and potential implications.
Understanding Methylene Blue's Pharmacokinetics
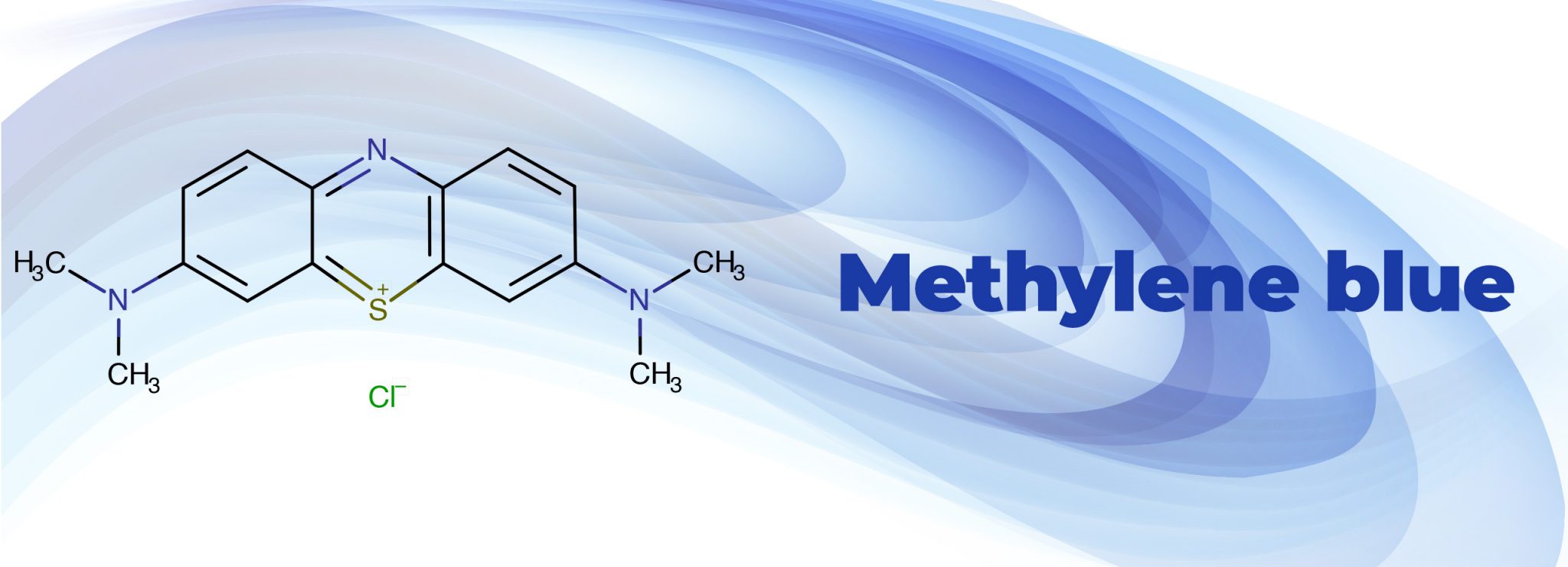
Methylene blue, chemically known as 3,7-bis(dimethylamino)phenothiazin-5-ium chloride, exhibits a complex pharmacokinetic profile. Once administered, it is rapidly absorbed into the bloodstream. The route of administration – intravenous, oral, or topical – significantly impacts the absorption rate and overall bioavailability.
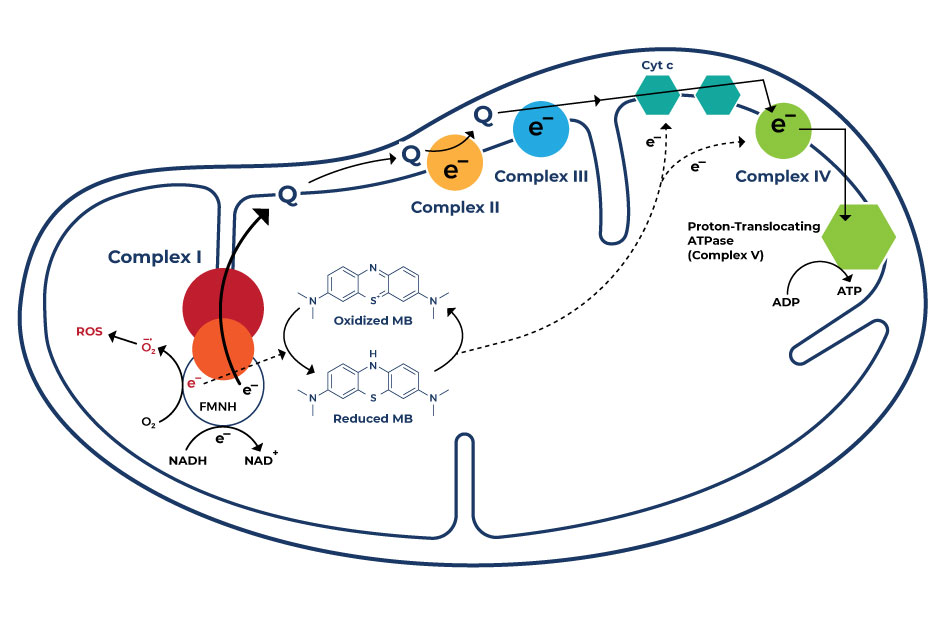
Following absorption, methylene blue distributes widely throughout the body. It crosses the blood-brain barrier, a critical factor in its potential therapeutic applications for neurological conditions. Distribution is influenced by factors such as tissue perfusion and binding affinity.
Metabolism and Excretion
The primary metabolic pathway for methylene blue involves reduction to leucomethylene blue, a colorless form. This process occurs mainly in the liver and, to a lesser extent, in other tissues. Cytochrome P450 enzymes, a family of liver enzymes responsible for metabolizing many drugs, play a role, though not the dominant one, in methylene blue's breakdown.
Excretion of methylene blue and its metabolites occurs primarily through the kidneys, resulting in blue-green urine. A smaller amount is excreted in the feces. The rate of excretion is a key determinant of how long the compound remains detectable in the body.
Factors Influencing Duration in the System
Several factors influence how long methylene blue stays in your system. Individual variations in metabolism, kidney function, and liver function play a significant role. Dosage and frequency of administration are also critical determinants.
Age can also impact methylene blue's pharmacokinetics. Younger individuals with more efficient metabolic processes may clear the drug faster compared to older individuals. Furthermore, pre-existing medical conditions, especially those affecting the liver or kidneys, can prolong its presence in the body.
Body weight and composition may also play a role. Individuals with higher body fat percentages might experience a slightly prolonged elimination due to the potential for drug accumulation in adipose tissue, though this is not a primary factor for methylene blue.
Half-Life and Detection Time
The half-life of methylene blue, which is the time it takes for the concentration of the drug in the body to reduce by half, is estimated to be between 5.25 and 6.8 hours after intravenous administration. This means that after roughly 5-7 hours, half of the initial dose is eliminated from the bloodstream.
However, the total detection time can be significantly longer than its half-life. Methylene blue can be detectable in urine for up to several days after the last dose, even after the initial therapeutic effects have subsided. This is due to the gradual elimination of metabolites and residual drug from tissues.
Detection in blood is typically shorter, ranging from 24 to 48 hours, depending on the sensitivity of the analytical method used. Therefore, the method of detection and the specific tissue being analyzed significantly impact the perceived "duration" of methylene blue in the system.
Medical and Non-Medical Use Considerations
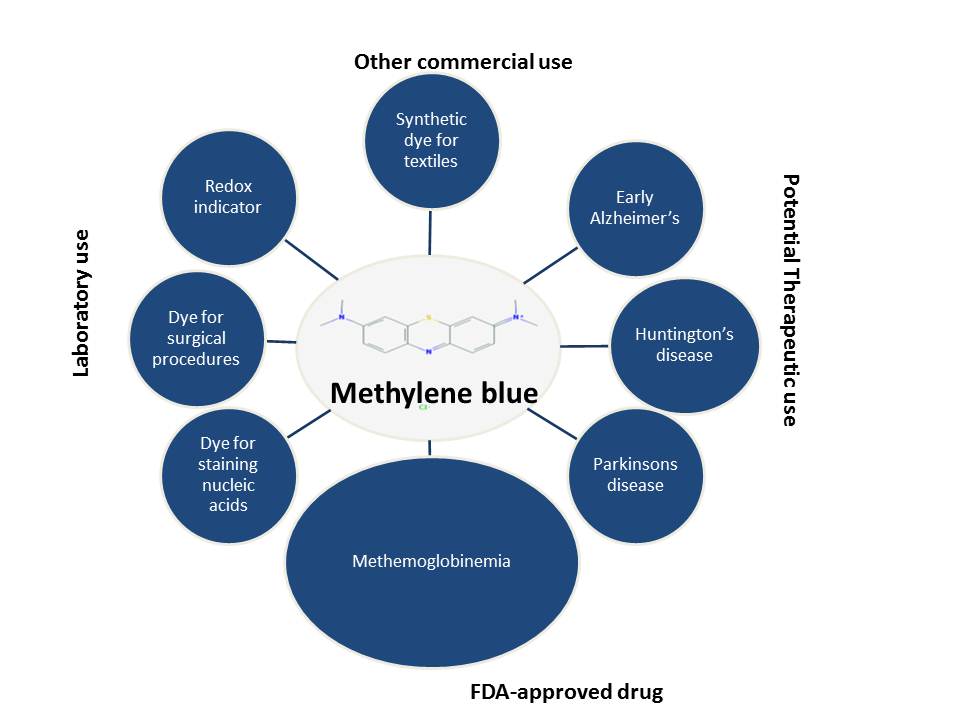
In medical settings, methylene blue is used to treat conditions such as methemoglobinemia, a blood disorder where hemoglobin is unable to effectively release oxygen to body tissues. It is also employed as a diagnostic agent and in certain surgical procedures. Dosages are carefully calculated and monitored by medical professionals.
Outside of traditional medicine, methylene blue has gained traction in the wellness community as a nootropic and potential cognitive enhancer. Advocates claim it can improve memory, focus, and overall brain function. However, scientific evidence supporting these claims is still limited and requires further investigation.
The unregulated use of methylene blue, particularly in non-medical settings, raises concerns about potential risks and side effects. High doses can cause adverse reactions such as nausea, vomiting, dizziness, and in rare cases, more serious complications like serotonin syndrome when combined with certain medications. It's important to consult a healthcare professional before using methylene blue for any purpose.
Expert Opinions and Research Gaps
Medical professionals emphasize the importance of understanding methylene blue's potential interactions with other drugs. It can interfere with the metabolism of certain medications, potentially leading to adverse effects.
Dr. Anya Sharma, a clinical pharmacologist, notes: "While methylene blue has a relatively short half-life, its effects can be prolonged, particularly in individuals with impaired liver or kidney function. Careful monitoring is essential to minimize risks."
Further research is needed to fully elucidate the long-term effects of methylene blue, especially with chronic use. Studies are also warranted to investigate its efficacy and safety as a cognitive enhancer in healthy individuals. The optimal dosage and administration protocols for different applications need to be clearly defined through rigorous clinical trials.
Conclusion: A Need for Informed Usage
Methylene blue's duration in the body is influenced by a complex interplay of factors, ranging from individual physiology to dosage and route of administration. While its half-life is relatively short, it can be detectable for several days after administration, particularly in urine.
Whether used for medical purposes or as part of wellness practices, a thorough understanding of its pharmacokinetics and potential risks is crucial. Consulting with a healthcare professional is essential to ensure safe and effective use. As research continues to shed light on its potential benefits and risks, informed decision-making remains paramount.