How Many Carbs In Apple Cider

As autumn leaves paint the landscape in vibrant hues, apple cider becomes a quintessential beverage, warming hands and souls alike. But beyond its comforting taste, many health-conscious individuals wonder about its nutritional content, particularly its carbohydrate count. Understanding the carbohydrate content of apple cider is crucial for those managing blood sugar levels, following specific diets, or simply seeking to make informed dietary choices.
This article delves into the carbohydrate composition of apple cider, drawing from nutritional data and expert insights to provide a clear and comprehensive overview. We'll explore the factors influencing carb levels, compare different types of cider, and offer guidance for incorporating this seasonal favorite into a balanced diet.
Understanding Carbohydrates in Apple Cider
The primary carbohydrates in apple cider are sugars, primarily fructose, glucose, and sucrose. These sugars are naturally occurring within the apples themselves. During the cider-making process, these sugars are extracted from the fruit, resulting in a sweet and flavorful beverage.
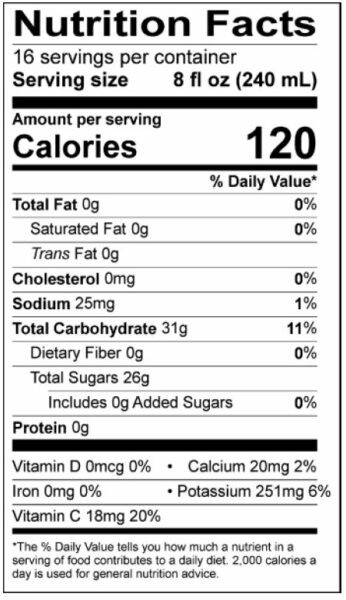
According to the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA), an 8-ounce (240 ml) serving of unsweetened apple cider typically contains around 28-30 grams of carbohydrates. This amount is primarily composed of sugars, with minimal amounts of fiber.
Factors Affecting Carbohydrate Content
Several factors can influence the carbohydrate content of apple cider. The variety of apples used plays a significant role. Some apple varieties are naturally sweeter than others, leading to a higher sugar content in the resulting cider.
The production process can also impact carb levels. Some cider producers may add sweeteners, such as high-fructose corn syrup or sugar, to enhance the flavor of their product. This will significantly increase the total carbohydrate count.
Furthermore, the level of filtration can have a subtle effect. Unfiltered cider, which contains more pulp, might have a slightly higher carbohydrate content than filtered cider, although the difference is generally minimal.
Comparing Different Types of Apple Cider
It's essential to differentiate between various types of apple cider to accurately assess their carbohydrate content. Raw, unfiltered apple cider, often sold directly from orchards, typically has a carbohydrate count closer to the 28-30 gram range mentioned earlier.
Pasteurized apple cider, commonly found in grocery stores, may have a similar carbohydrate content to raw cider, provided no additional sweeteners are added. Reading the nutrition label is critical to confirm this.
However, spiced or flavored apple ciders often contain added sugars. These varieties can have significantly higher carbohydrate levels, sometimes exceeding 40 grams per serving. Always check the ingredient list for added sugars like sucrose, corn syrup, or artificial sweeteners.
Apple cider blends can also present variable carbohydrate counts, depending on the blend of apples used, and the presence of added sugars. Examining the nutrition facts label is crucial for accurate determination.
Impact on Health and Diet
For individuals managing diabetes or following low-carbohydrate diets, understanding the carbohydrate content of apple cider is paramount. The relatively high sugar content can significantly impact blood sugar levels.
Individuals with diabetes should carefully monitor their blood glucose levels after consuming apple cider. Portion control is crucial to avoid spikes in blood sugar. Choosing unsweetened varieties is also recommended.
Those on low-carb diets, such as the ketogenic diet, need to be especially mindful of the carbohydrate count. A single serving of apple cider can consume a significant portion of their daily carbohydrate allowance.
The glycemic index (GI) and glycemic load (GL) are also relevant considerations. Apple cider has a moderate GI, meaning it can raise blood sugar levels relatively quickly. However, its GL is moderate, indicating a smaller impact on blood sugar levels compared to foods with higher GL values.
Tips for Enjoying Apple Cider Responsibly
Despite its carbohydrate content, apple cider can be enjoyed as part of a balanced diet with moderation and mindful choices. Opting for unsweetened varieties is a key strategy.
Consider diluting apple cider with water or sparkling water to reduce the sugar concentration. This can help moderate its impact on blood sugar levels and reduce overall carbohydrate intake.
Pairing apple cider with protein and healthy fats can also help slow down the absorption of sugars, leading to a more gradual rise in blood sugar levels. For instance, enjoy a small serving of cider with a handful of nuts or cheese.
Look for apple cider that is made using naturally sweet apples only, and avoid those that have added sugar. Local farmers markets and orchards are a great place to find these kinds of ciders.
Finally, be aware of portion sizes. A small serving of apple cider can provide a taste of fall without significantly impacting your overall carbohydrate intake.
A Seasonal Treat to Be Savored
Apple cider, with its warm and inviting flavor, is undoubtedly a beloved autumn beverage. By understanding its carbohydrate content and making informed choices, individuals can enjoy this seasonal treat responsibly and in moderation.
Remember to read nutrition labels, opt for unsweetened varieties, and practice portion control. This ensures that apple cider remains a delightful part of a balanced and healthy lifestyle.
Ultimately, awareness and moderation are the keys to enjoying the pleasures of apple cider without compromising your health goals. Enjoy the fall season with full knowledge and a delicious, controlled experience.

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/apple-cider-vinegar_annotated-efa1261a10684527a9aed559fa78cb58.jpg)








:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/apples-9793d00448be46e480172523008aa44e.jpg)





/apples_annotated-d93fdf795d3f42d3ad538f48677d0467.jpg)
