How Many Watts Do I Need To Run My House

Imagine stepping into your home on a sweltering summer day. The air conditioner hums to life, chasing away the heat as the refrigerator diligently keeps your groceries fresh. Simultaneously, your laptop is charging, and the aroma of dinner wafts from the kitchen where the oven is preheating. But have you ever stopped to consider the collective power—the wattage—required to keep your modern life humming along?
Understanding your home's energy needs is more than just a matter of curiosity. It's the key to making informed decisions about energy efficiency, choosing the right generator for emergencies, and even considering sustainable energy solutions like solar panels. This article will guide you through the process of calculating your household wattage needs, helping you take control of your energy consumption and potentially save money in the process.
Deciphering Wattage: The Basics
Wattage, simply put, is the unit of power that measures how much energy an electrical device uses. Every appliance and electronic device in your home has a wattage rating, usually found on a sticker or plate on the appliance itself. This number indicates the amount of power the device draws when it's operating.
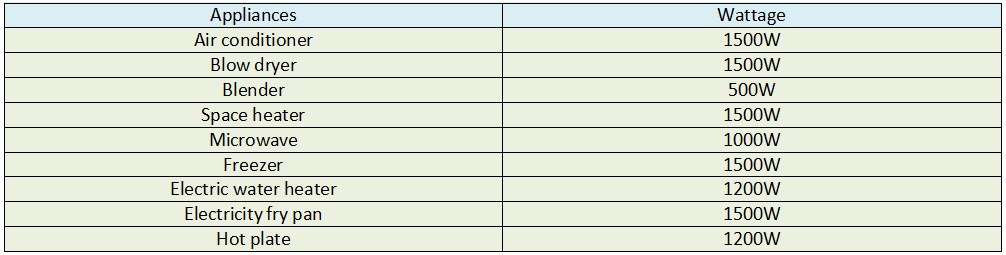
To estimate your total home wattage needs, you'll need to take inventory of your appliances and their respective wattages. Begin by creating a list, dividing appliances into categories like "Lighting," "Kitchen," "Electronics," and "HVAC" (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning).
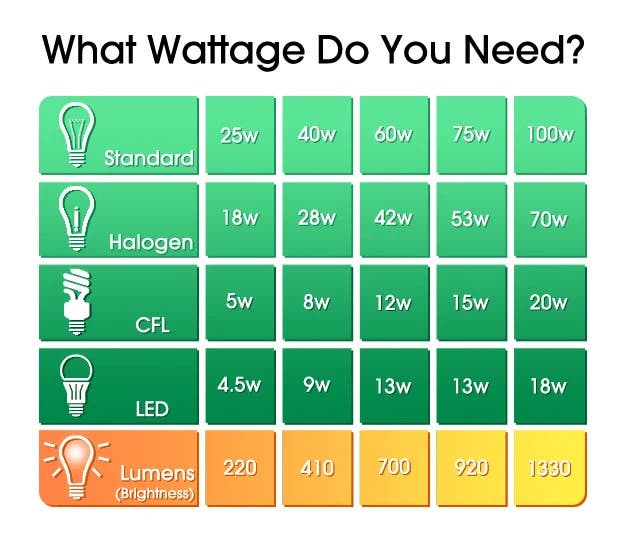
For example, a typical refrigerator might consume between 100 and 400 watts, while a microwave oven could draw anywhere from 600 to 1500 watts. LED light bulbs generally use significantly less power than incandescent bulbs, with a 60-watt incandescent bulb being replaced by an LED that uses only 8-12 watts.
Calculating Your Needs: A Room-by-Room Approach
Go through each room in your house and list the appliances you use regularly. Note down the wattage of each appliance. If the wattage isn't listed, look for the amperage (amps) and voltage (volts) instead. You can then calculate wattage using the formula: Watts = Amps x Volts.
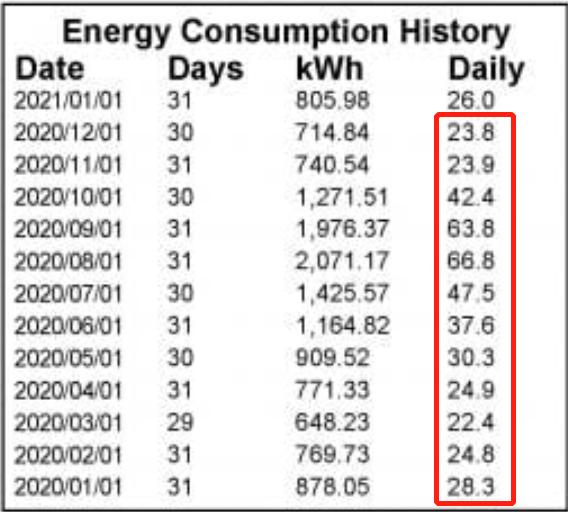
Once you have a list of your appliances and their wattages, estimate how many hours each appliance is used per day. Multiply the wattage by the hours of use to get the daily watt-hours for each appliance. Summing up the daily watt-hours for all appliances gives you the total daily watt-hours for your home.
To get a better understanding of your monthly energy consumption, multiply the total daily watt-hours by the number of days in a month. Divide this number by 1000 to convert watt-hours to kilowatt-hours (kWh), which is the unit used on your electricity bill. This calculation provides a rough estimate of your home's energy consumption.
Factors Affecting Wattage Needs
Several factors can influence your home's wattage needs. The size of your home, the number of occupants, your lifestyle, and the climate you live in all play a role. Larger homes and households with more people tend to consume more energy.
Geographical location significantly impacts your energy consumption. Homes in hotter climates require more energy for air conditioning, while those in colder climates need more power for heating. Energy-efficient appliances can make a substantial difference in reducing your overall wattage needs.
Appliances with the Energy Star label are designed to consume less energy than standard models, saving you money on your electricity bill and reducing your carbon footprint. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), Energy Star certified appliances can save consumers up to 30% on their energy bills.
Peak Demand vs. Average Consumption
It's crucial to distinguish between your home's average wattage consumption and its peak demand. Peak demand refers to the maximum amount of power your home requires at any given time.
This usually occurs when multiple high-wattage appliances are running simultaneously, such as the air conditioner, oven, and clothes dryer. Knowing your peak demand is particularly important when selecting a generator or considering solar energy systems. A generator or solar panel system must be capable of handling your home's peak demand to avoid overloading and potential power outages.
Beyond the Numbers: Energy Efficiency and Conservation
Calculating your wattage needs is just the first step. The real power lies in using this knowledge to make informed decisions about energy efficiency and conservation. Simple changes, such as switching to LED lighting, unplugging electronics when not in use, and using smart power strips, can significantly reduce your energy consumption.
Consider investing in energy-efficient appliances when it's time to replace older models. Proper insulation, sealing air leaks, and adjusting your thermostat can also help you conserve energy and lower your monthly electricity bill. Regularly maintaining your HVAC system can also help improve its efficiency.
Ultimately, understanding your home's wattage needs empowers you to take control of your energy consumption and contribute to a more sustainable future. By carefully assessing your appliance usage, identifying areas for improvement, and adopting energy-efficient practices, you can create a home that is both comfortable and environmentally responsible.