How Many Watts Does A Deep Freezer Use

As grocery prices fluctuate and consumers seek cost-effective food storage solutions, understanding the energy consumption of appliances like deep freezers has become increasingly important. Knowing how many watts a deep freezer uses can significantly impact household energy bills and inform purchasing decisions.
This article delves into the power consumption of deep freezers, examining the factors that influence wattage and providing practical tips for minimizing energy use. We will explore how different models, sizes, and usage habits affect the electricity bill, enabling consumers to make informed choices.
Understanding Deep Freezer Wattage
The wattage of a deep freezer represents the amount of electrical power it consumes during operation. This figure is a crucial factor in determining its energy efficiency and overall cost of ownership.
Several factors contribute to a deep freezer's wattage. These include the unit's size (measured in cubic feet), its age, insulation quality, and ambient temperature.
Key Factors Affecting Wattage
The size of a deep freezer directly correlates with its power consumption. Larger freezers, naturally, require more energy to maintain their internal temperature.
Older models tend to be less energy-efficient than newer ones due to advancements in insulation and compressor technology. Newer freezers often meet stringent Energy Star standards, indicating higher efficiency.
Insufficient insulation causes the freezer to work harder to maintain a consistent temperature, thus increasing wattage. Proper insulation minimizes heat transfer from the surrounding environment.
The temperature of the room where the freezer is located also plays a crucial role. Higher ambient temperatures force the freezer to expend more energy to keep its contents frozen.
Typical Wattage Ranges
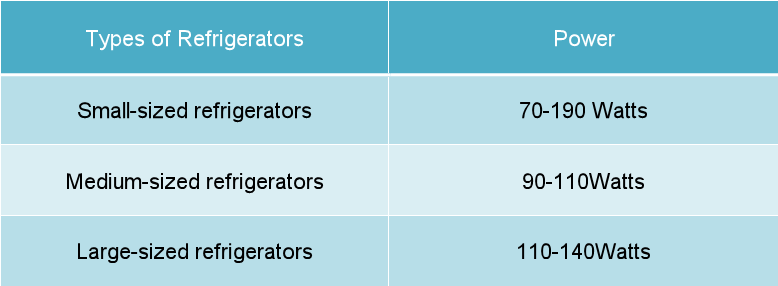
On average, a deep freezer uses between 100 and 200 watts while running. However, this figure fluctuates depending on the factors mentioned above.
According to data from the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA), a chest freezer typically consumes less energy than an upright freezer of the same capacity. This is primarily due to the superior insulation and design of chest freezers, which minimize cold air loss when the lid is opened.
Consider an example: a 7-cubic-foot chest freezer might use around 100 watts, while a comparable upright freezer could use closer to 150 watts. Larger units can easily exceed 200 watts.
Calculating Energy Consumption and Cost
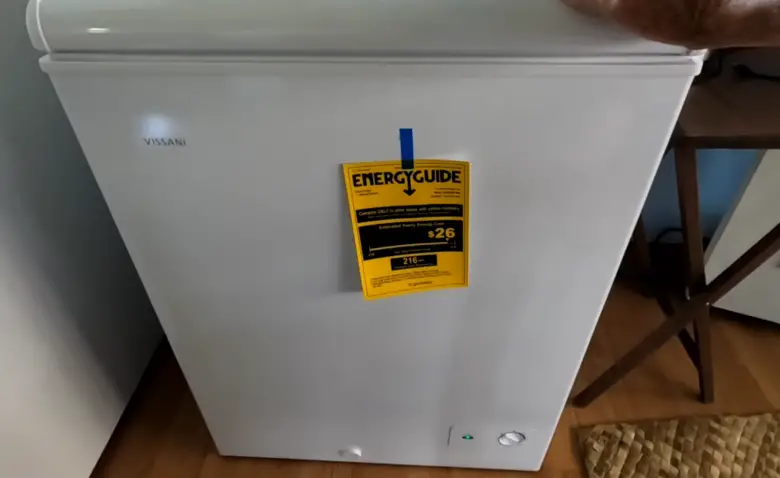
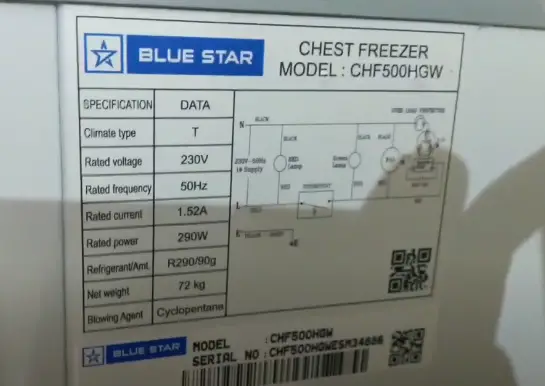
To estimate the energy consumption of a deep freezer, you'll need to know its wattage and the number of hours it operates per day. This can be found on the appliance's energy guide label.
The formula is simple: (Wattage x Hours of Operation per Day) / 1000 = Kilowatt-hours (kWh) per Day. Multiply this figure by the number of days in a month to get the monthly kWh consumption.
Finally, multiply the monthly kWh consumption by your electricity rate (cost per kWh) to determine the estimated monthly cost of operating the freezer. Keeping a well-stocked freezer can actually improve energy efficiency, as the frozen items help to maintain a consistent temperature and reduce the amount of work the compressor needs to do.
Tips for Minimizing Deep Freezer Energy Use
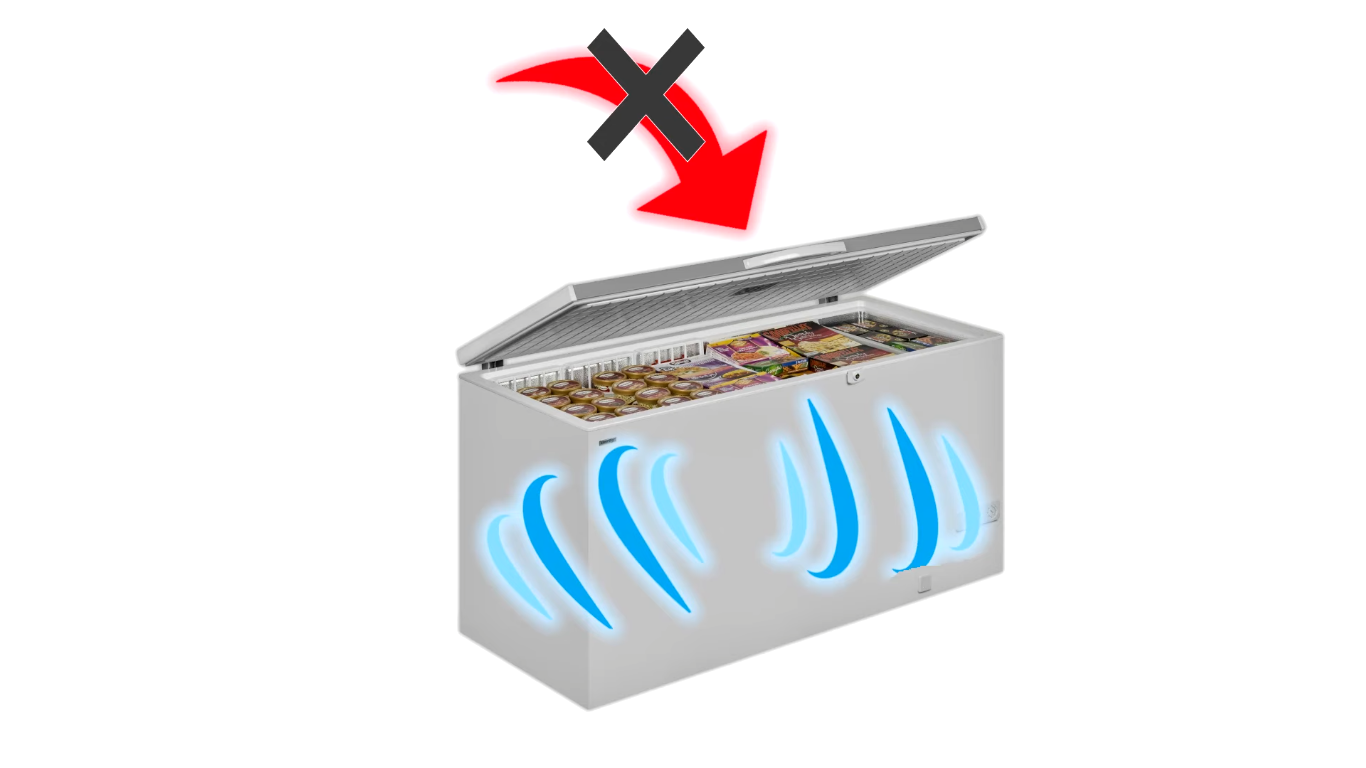
Consumers can take several steps to reduce the energy consumption of their deep freezers. Proper placement and maintenance are essential.
Ensure the freezer is located in a cool, well-ventilated area away from direct sunlight and heat sources. Regularly defrost the freezer to prevent ice buildup, which reduces efficiency.
Check the door seals to ensure they are airtight. Replace worn seals to prevent cold air from escaping. Consider investing in an energy-efficient Energy Star certified model when purchasing a new deep freezer.
Maintaining the freezer at the optimal temperature (0°F or -18°C) is also crucial. Avoid overfilling the freezer, which can restrict airflow and reduce efficiency.
The Broader Impact
Understanding and managing the energy consumption of appliances like deep freezers has broader implications for both individual households and society. Reducing energy consumption contributes to lower utility bills and a smaller carbon footprint.
By making informed decisions about appliance purchases and implementing energy-saving practices, consumers can play a significant role in promoting sustainability. Government initiatives and incentives, such as rebates for energy-efficient appliances, further encourage responsible energy consumption.
Ultimately, a collective effort to reduce energy waste contributes to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly future. By understanding the wattage of a deep freezer and taking steps to minimize its energy use, consumers can save money and contribute to a healthier planet.