How Much Do Financial Advisors Make Per Year

The allure of a career guiding individuals and families toward financial security is strong, but a common question looms large: How much do financial advisors actually earn? Compensation in this field is far from uniform, influenced by a multitude of factors including experience, credentials, location, and the structure of their firm.
Understanding the salary landscape for financial advisors is crucial for those considering the profession, as well as for clients seeking to gauge the value they receive for the fees they pay. This article delves into the data surrounding financial advisor compensation, providing a comprehensive overview of earning potential in this dynamic sector.
The Earning Spectrum: Averages and Influencing Factors
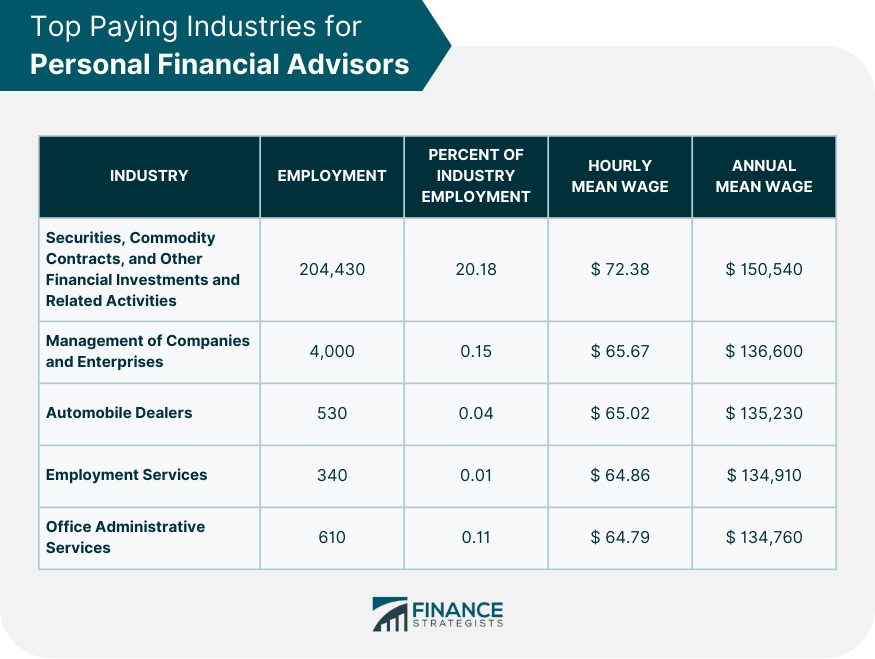
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), the median annual wage for personal financial advisors was $99,410 in May 2023. However, this figure provides only a partial glimpse into the earning potential. The BLS data shows that the lowest 10 percent earned less than $49,710, while the highest 10 percent earned more than $225,260.
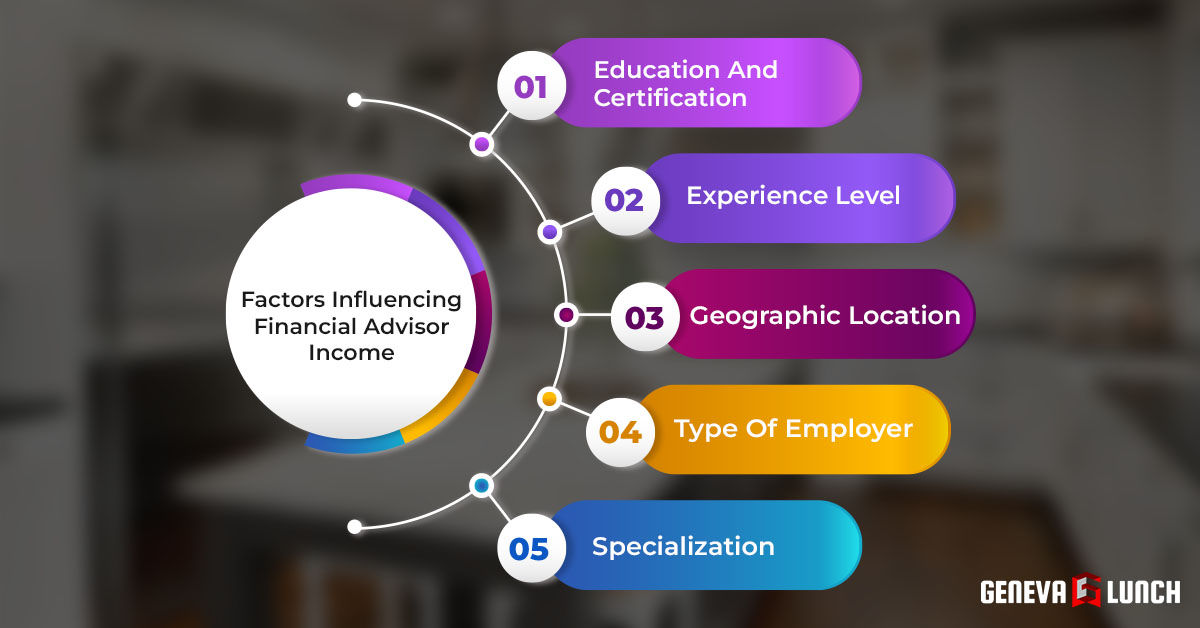
Several factors contribute to this wide range. Experience plays a significant role, with seasoned advisors typically commanding higher salaries and bonuses. Educational qualifications, such as a Certified Financial Planner (CFP) designation, and advanced degrees like an MBA can also positively impact earning potential.
The type of firm an advisor works for is another key determinant. Advisors at large brokerage houses may earn differently compared to those at independent Registered Investment Advisory (RIA) firms. Compensation structures can vary significantly, including salary plus commission, fee-based models, or a combination of both.
Location, Location, Location
Geographic location also influences earning potential. Financial advisors in major metropolitan areas, such as New York City or San Francisco, often command higher salaries due to the higher cost of living and greater concentration of wealth. However, competition can also be more intense in these areas.
According to Indeed.com, states with higher average salaries for financial advisors include New York, California, and Massachusetts. Conversely, states with lower average salaries may include those with lower costs of living or fewer high-net-worth individuals.
Compensation Structures: Fees vs. Commissions
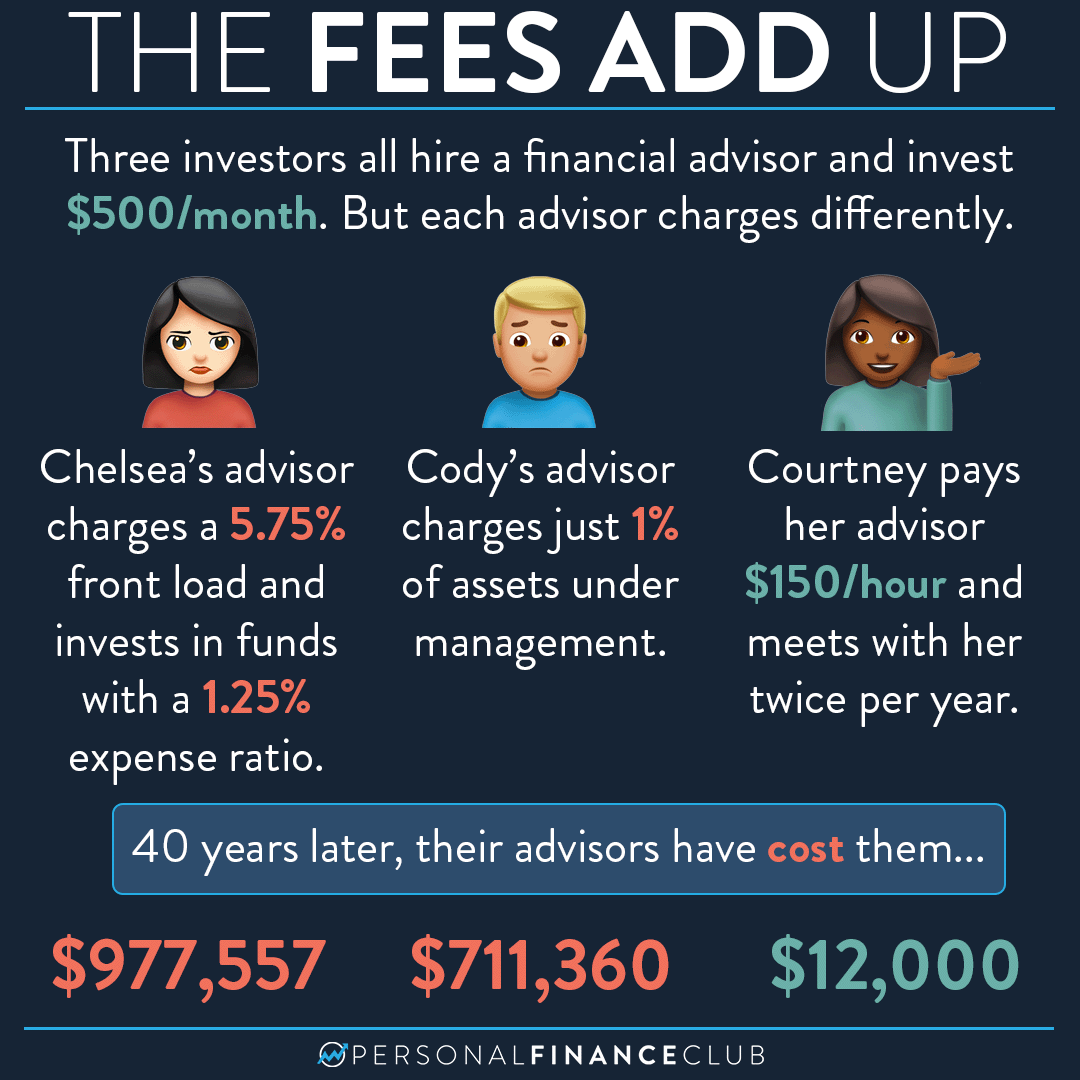
The way a financial advisor is compensated can significantly impact their earnings and potential conflicts of interest. Commission-based advisors earn a percentage of the products they sell, such as insurance policies or mutual funds. This model can incentivize advisors to recommend products that generate higher commissions, even if they aren't the best fit for the client.
Fee-based advisors, on the other hand, charge a fee for their advice, either as a percentage of assets under management (AUM) or as a flat fee. This model is often perceived as more transparent and aligned with the client's best interests, as the advisor's compensation is directly tied to the growth of the client's portfolio.
A hybrid model, combining fees and commissions, is also common. Understanding the advisor's compensation structure is crucial for clients to assess potential biases and ensure they are receiving objective advice.
The Rise of Independent RIAs
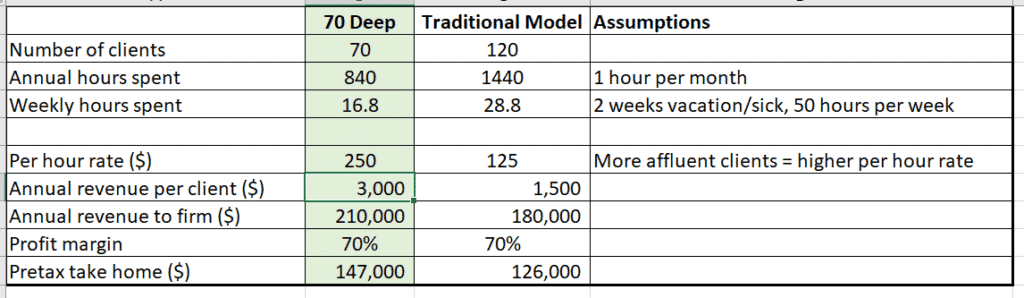
The independent RIA sector has experienced significant growth in recent years. This shift is driven, in part, by a growing demand for unbiased financial advice and a desire for greater autonomy among advisors.
While starting an independent RIA requires significant upfront investment and regulatory compliance, it can also offer greater earning potential. Independent advisors have the freedom to set their own fees and tailor their services to meet the specific needs of their clients.
However, independent advisors are also responsible for all aspects of running their business, including marketing, compliance, and technology. This requires a diverse skillset and a strong commitment to entrepreneurship.
Beyond the Salary: Benefits and Job Satisfaction
While salary is a primary consideration, it's important to consider other benefits, such as health insurance, retirement plans, and paid time off. Many firms offer comprehensive benefits packages to attract and retain top talent.
Furthermore, job satisfaction plays a crucial role. Financial advisors often derive satisfaction from helping clients achieve their financial goals and build a secure future. The ability to make a positive impact on people's lives can be a significant motivator.
Ultimately, the compensation for financial advisors is a complex and multifaceted issue. By understanding the various factors that influence earning potential, both aspiring advisors and prospective clients can make informed decisions.