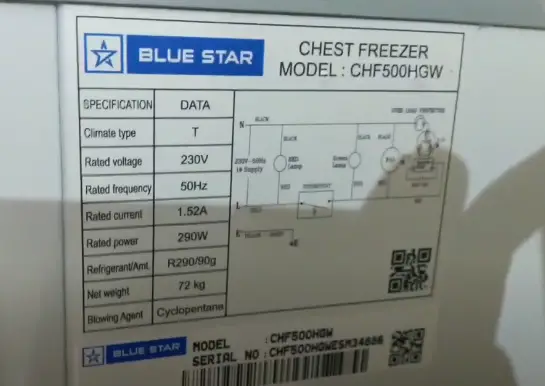
How Much Electric Does A Deep Freezer Use

As electricity prices fluctuate and consumers become increasingly conscious of their energy footprint, understanding the power consumption of household appliances is paramount. Deep freezers, often essential for long-term food storage, are a significant energy draw, but their actual usage can vary widely depending on several factors.
This article delves into the average energy consumption of deep freezers, exploring the factors influencing their power usage and offering insights into minimizing energy costs. Understanding these aspects empowers consumers to make informed decisions about appliance selection and usage, contributing to both household savings and environmental sustainability.
Factors Influencing Deep Freezer Energy Consumption
The energy consumption of a deep freezer is not a fixed figure. Several key factors contribute to the amount of electricity a deep freezer uses.
These factors include the size and type of the freezer, its age and efficiency, the ambient temperature, and how frequently the freezer is opened.
Size and Type
Larger deep freezers naturally consume more energy than smaller ones due to their increased volume and the need to maintain a consistent temperature across a larger space. Chest freezers, known for their superior insulation, generally use less energy than upright freezers.
The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) states that chest freezers are typically more energy-efficient because cold air doesn't escape as easily when the door is opened compared to upright models.
Age and Efficiency
Older deep freezers are often less energy-efficient than newer models. Newer freezers are equipped with improved insulation, more efficient compressors, and advanced temperature control systems.
Many modern freezers are Energy Star certified, indicating they meet stringent energy efficiency standards set by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Energy Star appliances can significantly reduce energy consumption compared to non-certified models.
Ambient Temperature and Usage Habits
The temperature of the surrounding environment also impacts energy consumption. A deep freezer located in a hot garage will need to work harder to maintain its internal temperature than one situated in a cool basement.
Frequent opening of the freezer door lets cold air escape, forcing the compressor to work harder to restore the desired temperature. Overfilling the freezer can also impede airflow and reduce efficiency.
Average Energy Consumption: Numbers and Estimates
While specific energy consumption varies, understanding the average range provides a useful benchmark. A typical deep freezer consumes between 100 and 400 kilowatt-hours (kWh) of electricity per year.
According to estimates from energy efficiency experts, a smaller chest freezer might use around 200 kWh per year, while a larger upright freezer could consume closer to 400 kWh.
Using the national average electricity rate of approximately $0.14 per kWh (as reported by the Energy Information Administration), the annual cost to run a deep freezer can range from $28 to $56.
Tips for Minimizing Deep Freezer Energy Consumption
Fortunately, there are several strategies to reduce the energy footprint of your deep freezer. Proper maintenance, strategic placement, and mindful usage habits can make a significant difference.
- Ensure the freezer door seals properly to prevent cold air leaks.
- Defrost the freezer regularly to remove ice buildup, which can reduce efficiency.
- Keep the freezer at an optimal temperature (around 0°F or -18°C).
- Avoid placing the freezer in direct sunlight or near heat sources.
- Fill empty space with water-filled jugs to improve thermal mass and stability.
By implementing these tips, consumers can not only lower their energy bills but also extend the lifespan of their deep freezer. Choosing an Energy Star certified model when purchasing a new freezer is another highly effective way to minimize energy consumption.
The Broader Impact
Reducing the energy consumption of household appliances like deep freezers has a broader impact beyond individual savings. Widespread adoption of energy-efficient practices can collectively contribute to a reduction in overall energy demand.
Decreased energy demand reduces the strain on power grids and lowers carbon emissions associated with electricity generation. This contributes to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly future.
In conclusion, understanding the energy consumption of a deep freezer and implementing strategies to minimize its usage is a practical step towards both economic savings and environmental responsibility. By making informed choices and adopting energy-efficient habits, consumers can play a significant role in creating a more sustainable future.



![How Much Electric Does A Deep Freezer Use How Many Amps Does A Freezer Use [Surge, Running, Low Amp]](https://ecocostsavings.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/02/freezer-wattage.jpg)