How Much Is It To Start A Business
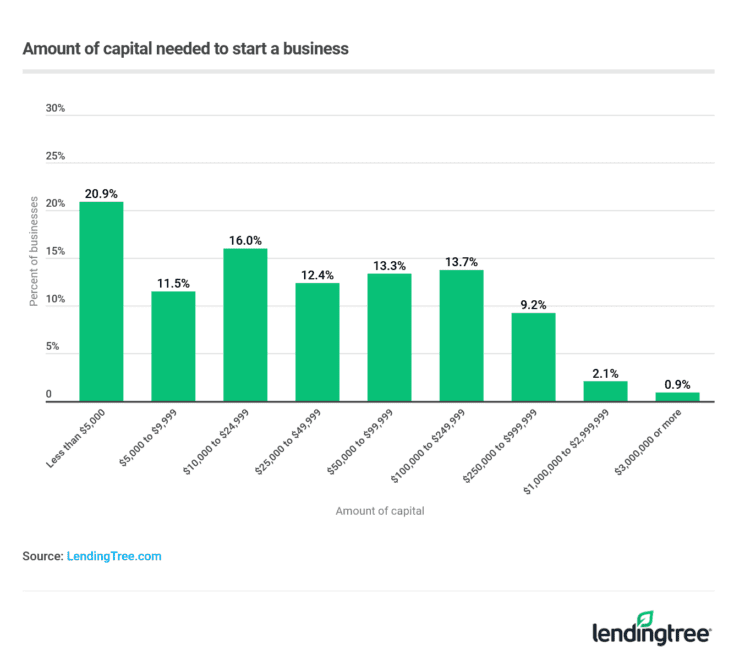
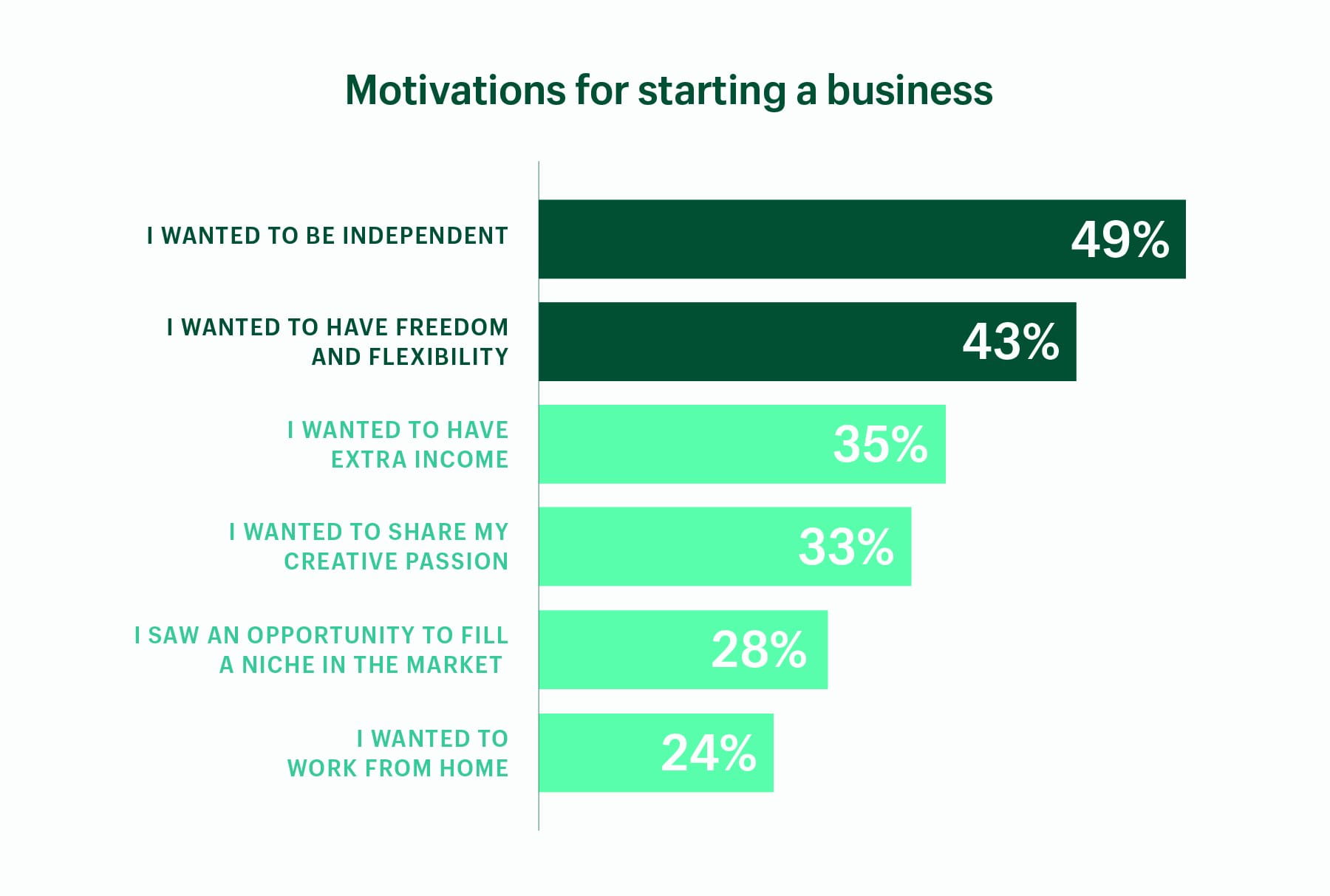
The allure of entrepreneurship is strong, fueled by dreams of financial independence and the satisfaction of building something from the ground up. However, the path to launching a successful business is paved with challenges, and one of the most significant hurdles is securing the necessary capital. The question that often looms largest for aspiring business owners is a deceptively simple one: how much does it really cost to start a business?
The answer, unfortunately, isn't a straightforward dollar amount. The startup costs for a new business are wildly variable, depending on factors like industry, business model, location, and the owner's personal resources. This article will delve into the key cost components, explore how different business types impact startup expenses, and provide insights on how to estimate and manage these crucial financial burdens.
Understanding the Key Cost Components
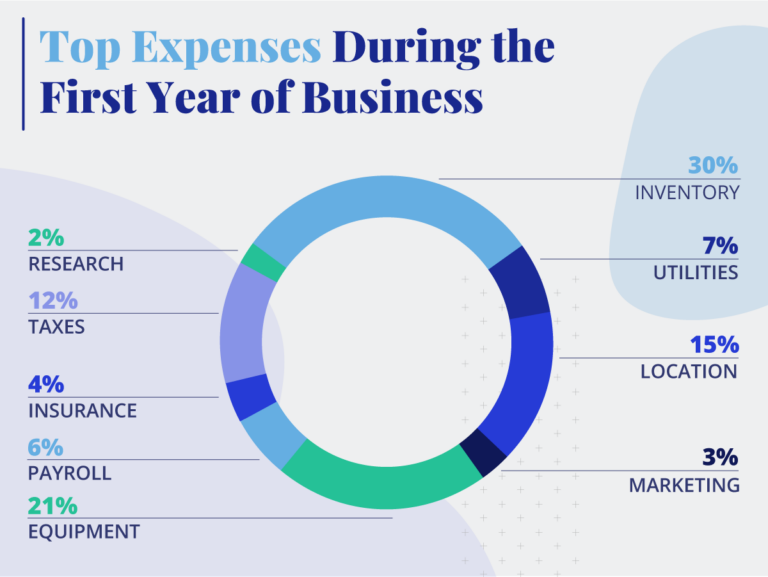
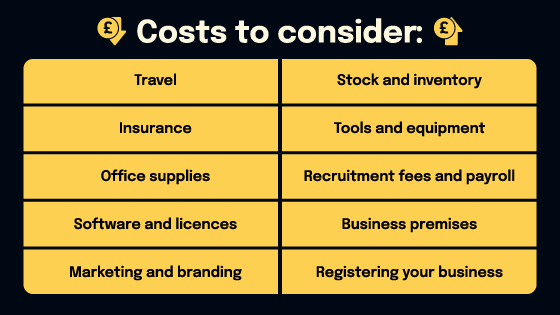
Several core elements consistently contribute to the initial investment required to start a business. These include legal and administrative fees, office space or equipment, marketing and advertising, inventory, and salaries.
Legal and Administrative Fees
Navigating the legal landscape is crucial. Registering your business, obtaining necessary licenses and permits, and setting up a legal structure (e.g., LLC, corporation) all incur costs. According to the Small Business Administration (SBA), these costs can range from a few hundred dollars to several thousand, depending on the complexity and location of the business.
Office Space and Equipment
The need for physical space dramatically impacts startup costs. A home-based online business might have minimal overhead, while a retail store or restaurant requires significant investment in rent, utilities, and equipment. Real estate costs vary widely by location, making this a major factor in overall expenses.
Marketing and Advertising
Attracting customers is essential, and marketing requires a budget. This can include website development, social media marketing, traditional advertising, and public relations. The amount you spend here will depend on your target market and your marketing strategy.
Inventory and Supplies
For businesses selling physical products, inventory is a significant upfront expense. The cost of goods sold (COGS) can quickly deplete initial capital. Careful inventory management is crucial to minimize waste and optimize cash flow.
Salaries and Wages
If you plan to hire employees, salaries and wages are a recurring expense that must be factored in from the start. Even if you initially plan to work solo, you may need to pay yourself a salary to cover living expenses.
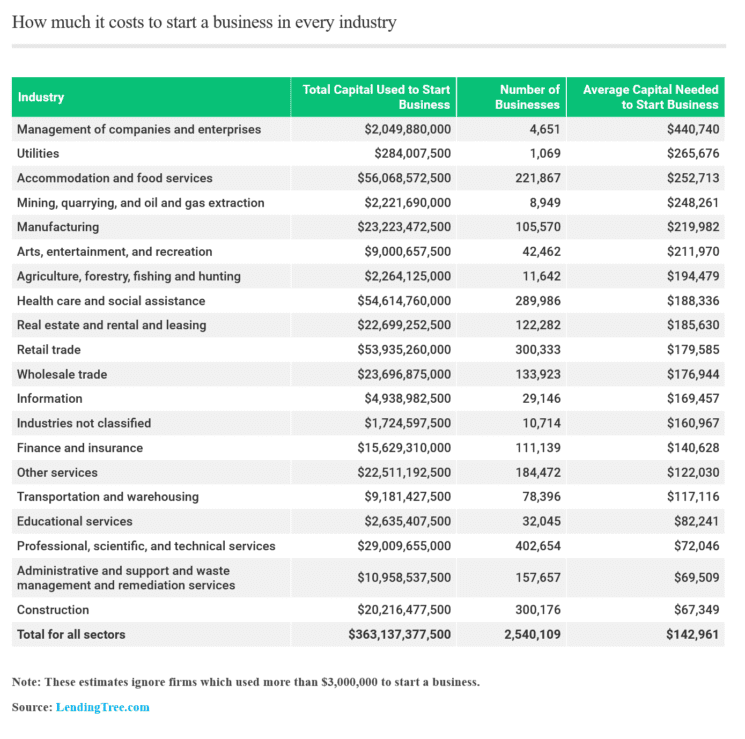
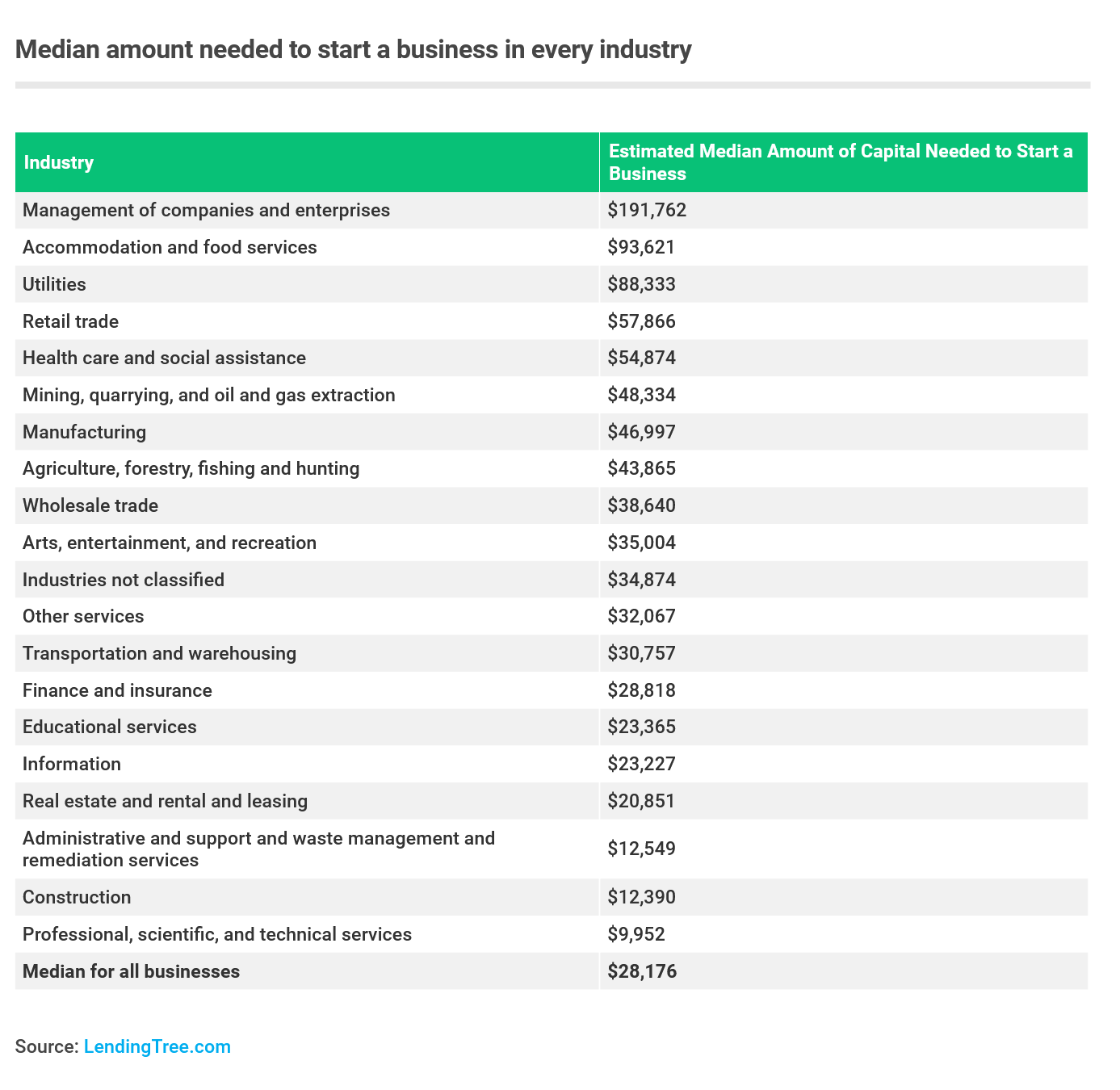
Startup Costs by Business Type
The type of business significantly impacts the required startup capital. A service-based business, like consulting, might have lower initial costs than a manufacturing or retail operation. Let’s look at some examples.
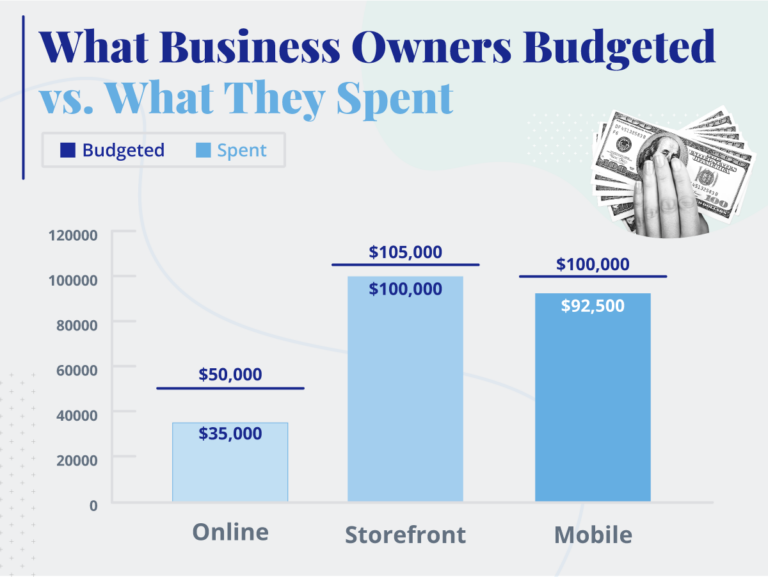
Online Businesses
E-commerce ventures often have lower startup costs than brick-and-mortar stores. Website development, marketing, and inventory are the primary expenses. Platforms like Shopify and Etsy can reduce the barrier to entry for online retailers.
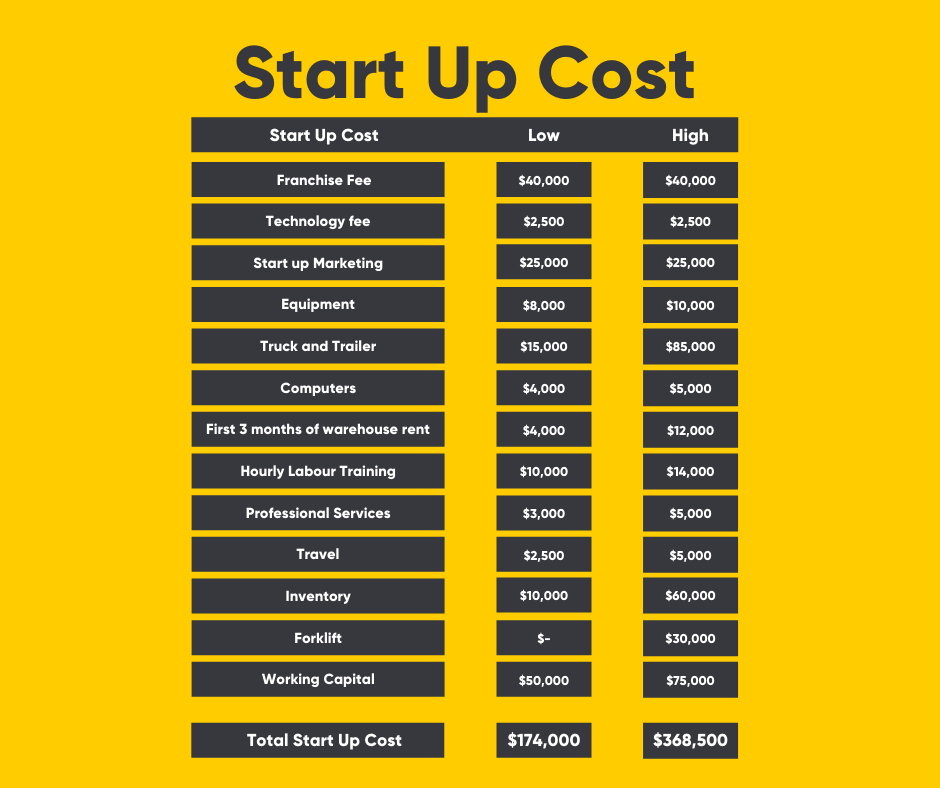
Restaurants and Retail Stores
These businesses typically require substantial capital. Rent, renovations, equipment, inventory, and staffing all contribute to high startup costs. Location is a key determinant of both rent and potential revenue.
Service-Based Businesses
Consulting, freelancing, and other service-based businesses can be started with relatively little capital. The primary investments are often in marketing, equipment, and software. Many consultants operate from home, reducing overhead costs.
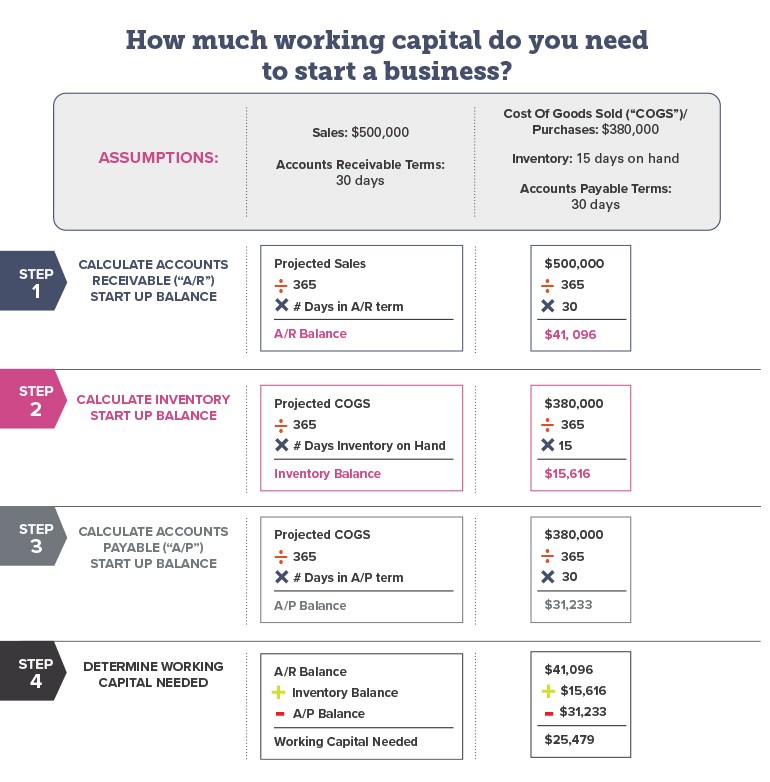
Estimating and Managing Startup Costs
Accurate cost estimation is essential for securing funding and managing cash flow. Here are some tips for aspiring entrepreneurs.
Develop a detailed business plan. This plan should include a comprehensive budget that outlines all anticipated startup costs and projected revenue. A well-researched business plan is critical for securing loans and attracting investors.
Shop around for the best deals. Compare prices for everything from office space to marketing services. Negotiation can often lead to significant cost savings.
Consider bootstrapping. Starting small and reinvesting profits can minimize the need for external funding. This approach requires patience and discipline but can reduce debt and maintain control of the business.
Seeking Funding and Resources
Numerous funding options are available to new businesses. These include bank loans, SBA loans, angel investors, venture capital, and crowdfunding.
SBA loans are a popular option for small businesses. The SBA doesn't lend money directly but guarantees loans made by participating lenders. This reduces the risk for lenders and makes it easier for small businesses to qualify for funding.
Angel investors and venture capitalists provide funding in exchange for equity in the company. This option is more suitable for high-growth potential startups.
Looking Ahead
The cost of starting a business is a significant consideration, but it shouldn't deter aspiring entrepreneurs. With careful planning, diligent cost management, and access to appropriate funding, anyone can successfully launch their own venture. The key is to understand the specific costs associated with your chosen industry and to develop a realistic budget that allows you to manage your finances effectively.
The entrepreneurial landscape is constantly evolving, with new technologies and business models emerging regularly. Staying informed about industry trends and best practices is crucial for long-term success. By embracing innovation and adapting to change, entrepreneurs can overcome the challenges of starting a business and achieve their dreams of building something great.