How Much Power Should My Solar Panels Produce

Calculating the optimal size and power output of a solar panel system can feel like navigating a complex equation. The 'right' amount of solar power is deeply personal and contingent on factors ranging from energy consumption habits to geographical location and budget constraints. Understanding these elements is crucial to making an informed decision and maximizing the return on your solar investment.
Determining the ideal solar panel system output is a balancing act. Homeowners need to carefully assess their energy needs, available sunlight, and financial goals. This calculation directly impacts the system's cost, efficiency, and the overall savings achieved over its lifespan.
Understanding Your Energy Consumption
The first step in determining the appropriate solar panel system size is to analyze your household's energy consumption. Review your past electricity bills to identify your average monthly or annual energy usage in kilowatt-hours (kWh). This data provides a baseline for understanding how much electricity your solar panels need to generate.
Seasonal variations in energy consumption should also be considered. For example, homes in warmer climates typically use more electricity during the summer months for air conditioning, while those in colder regions might see higher usage in the winter due to heating. Take these fluctuations into account to ensure your solar system can meet your needs throughout the year.
Assessing Sunlight Availability
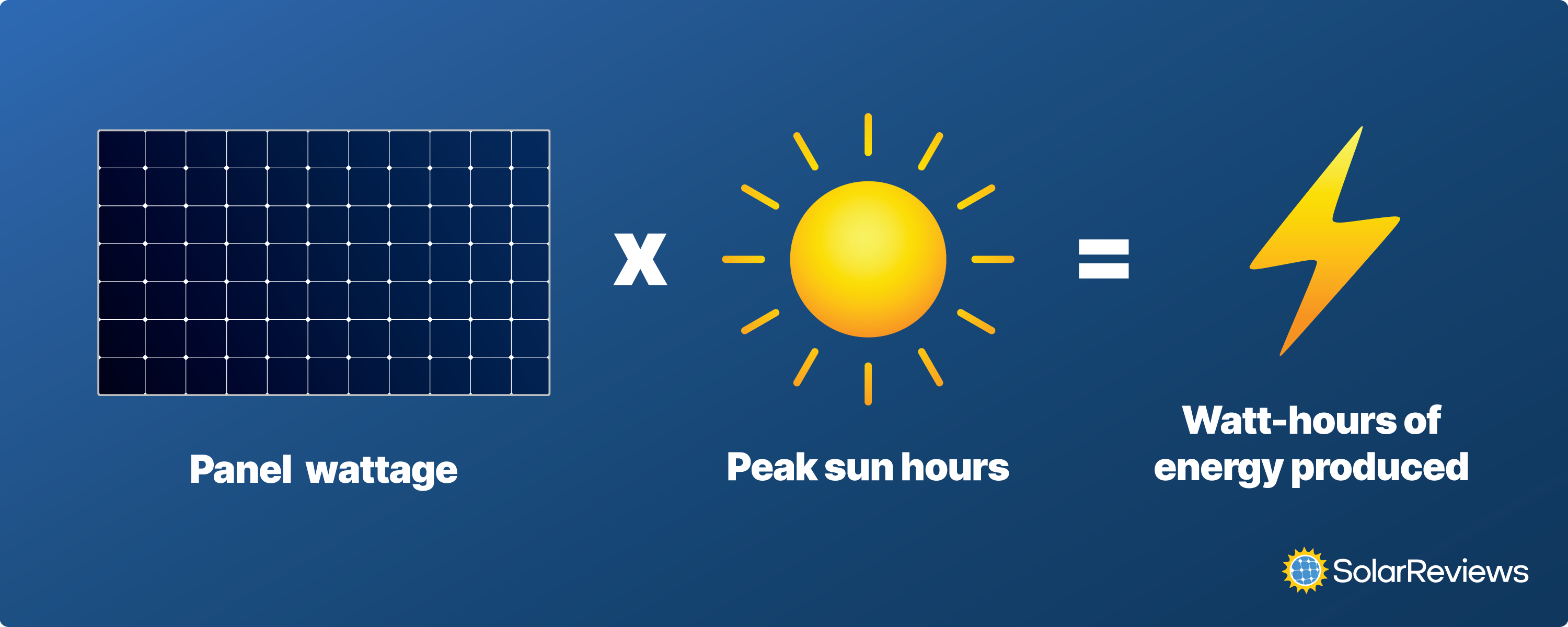
The amount of sunlight your location receives significantly impacts solar panel output. The term "sun hours," or peak sun hours, refers to the average number of hours per day that your location receives the equivalent of full sunlight intensity. This varies greatly depending on geographic location and weather patterns.
The National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) provides data and tools for assessing solar irradiance in different regions. Consulting these resources can help you estimate the potential energy production of solar panels installed at your specific location. Consider also any shading from trees or nearby buildings, which can reduce sunlight exposure and overall system performance.
Calculating System Size and Output
Once you know your energy consumption and sunlight availability, you can begin calculating the necessary solar panel system size. This involves a few key steps. First, determine your desired percentage of energy offset; do you want to cover 50%, 100%, or some other portion of your electricity needs with solar power?
Next, use a solar panel calculator or consult with a solar installer to estimate the number of panels required to achieve that level of offset. These tools typically consider panel efficiency, system orientation (tilt and direction), and local weather conditions. The calculator will then tell you the total wattage the solar panels need to produce.
Factors Affecting Solar Panel Output
Several factors can influence the actual power output of your solar panels. Panel efficiency, measured as the percentage of sunlight converted into electricity, is a key consideration. Higher-efficiency panels generally produce more power in a given area.
Temperature can also affect performance; solar panels tend to be less efficient at higher temperatures. Regular maintenance, such as cleaning the panels to remove dirt and debris, can help maintain optimal output. Inverter efficiency must also be considered: the inverter converts direct current (DC) electricity from the panels into alternating current (AC) electricity usable in your home, and some energy is lost in the conversion process.
Financial Considerations and Incentives
The cost of a solar panel system is a significant factor in determining the optimal size. Smaller systems are generally less expensive upfront, but they may not provide enough energy to meet your needs. Larger systems offer greater energy independence but require a larger initial investment.
Government incentives, such as the federal solar tax credit, can significantly reduce the overall cost of a system. State and local incentives may also be available, further improving the financial viability of solar energy. Carefully research and factor in these incentives when evaluating your options. According to the Solar Energy Industries Association (SEIA), the federal investment tax credit (ITC) allows homeowners to deduct 30% of the cost of installing a solar energy system from their federal taxes.
Seeking Professional Guidance
While online tools and resources can be helpful, consulting with a qualified solar installer is highly recommended. A professional can assess your specific needs and site conditions to recommend the best system size and configuration for your home. They can also provide detailed cost estimates and guide you through the permitting and installation process.
Choosing the right solar panel system is a complex but rewarding process. Careful planning and consideration of factors such as energy consumption, sunlight availability, and financial incentives can help you maximize the benefits of solar energy and reduce your reliance on traditional power sources. Making informed decisions will lead to long-term savings and a more sustainable energy future.


![How Much Power Should My Solar Panels Produce How much electricity do solar panels produce? [UK, 2024]](https://images.prismic.io/sunsave-website/ZnxEJZbWFbowe4jR_graphic-Solarpaneloutput.jpg?auto=format,compress?auto=compress,format)