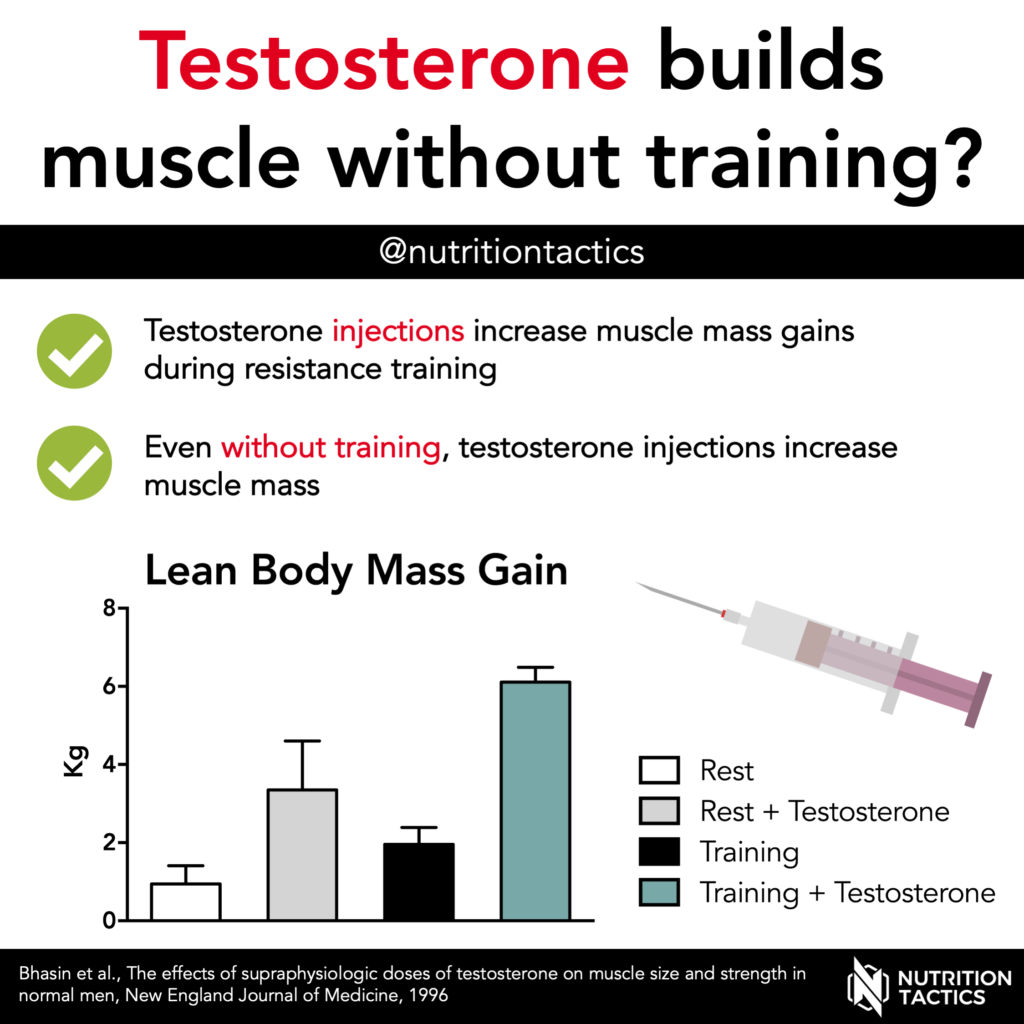
How Much Testosterone Should I Take To Gain Muscle

The question of how much testosterone to take for muscle gain is fraught with complexity and potential risk, demanding a nuanced understanding of the hormone, its effects, and the legal and health implications of its use. While the allure of enhanced muscle growth is strong, the decision to use testosterone should not be taken lightly and should always involve consultation with a qualified medical professional.
This article aims to provide a balanced overview of the factors involved in determining appropriate testosterone dosages for muscle gain, drawing on scientific literature and expert opinions. It will delve into the medical considerations, potential benefits, and significant risks associated with testosterone use for this purpose.
Understanding Testosterone and Muscle Growth
Testosterone, a primary male sex hormone, plays a vital role in muscle protein synthesis, the process by which the body builds and repairs muscle tissue. Higher testosterone levels generally lead to increased muscle mass and strength, which explains why it's often sought after by bodybuilders and athletes.
However, the relationship between testosterone and muscle growth is not linear. The body has natural limits, and exceeding these limits through exogenous testosterone administration can lead to adverse health consequences.
The Role of a Medical Professional
The crucial first step for anyone considering testosterone for muscle gain is to consult with an endocrinologist or a physician specializing in hormone therapy. A doctor can assess your current testosterone levels, overall health, and medical history to determine if testosterone therapy is appropriate.
They can also rule out underlying medical conditions that may be contributing to low testosterone levels or that could be exacerbated by testosterone supplementation. Self-treating with testosterone without medical supervision is strongly discouraged.
Testosterone Dosage: A Complex Calculation
Determining the right testosterone dosage for muscle gain is highly individualized. Several factors influence the optimal dose, including age, body composition, genetics, and the individual's response to the hormone.
Medical professionals often prescribe testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) to men with clinically low testosterone levels, typically in the range of 100-200mg per week. This dose aims to restore testosterone levels to the normal physiological range, which can improve muscle mass to some extent, alongside other benefits like increased energy and libido.
It's crucial to understand that dosages significantly higher than TRT levels, often used by bodybuilders, carry a much greater risk of side effects. These supraphysiological doses push testosterone levels far beyond the normal range.
Risks and Side Effects of High-Dose Testosterone
The risks associated with high-dose testosterone use are significant and well-documented. Some of the most common side effects include acne, hair loss (male pattern baldness), and gynecomastia (development of breast tissue in men).
More serious potential risks include cardiovascular issues, such as increased cholesterol levels and blood pressure, which can increase the risk of heart attack and stroke. Testosterone can also suppress the body's natural testosterone production, leading to testicular atrophy and infertility.
Furthermore, mood swings, aggression, and psychological dependence are also potential side effects. Long-term studies on the effects of high-dose testosterone use are limited, making it difficult to fully assess the long-term health risks.
Legal Considerations
In many countries, including the United States, testosterone is a controlled substance, requiring a prescription for legal use. Obtaining testosterone without a prescription is illegal and can have serious legal consequences.
Purchasing testosterone from unregulated sources, such as online pharmacies or black market dealers, carries significant risks. The products may be counterfeit, contaminated, or contain incorrect dosages.
Alternatives to Testosterone for Muscle Gain
For individuals seeking to increase muscle mass without resorting to testosterone, several safe and effective alternatives are available. A well-balanced diet rich in protein, combined with a consistent strength training program, is the foundation for muscle growth.
Supplements like creatine, whey protein, and branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) can also support muscle growth and recovery. Prioritizing sleep and managing stress are also important factors in optimizing muscle growth.
It is important to consult with a registered dietitian or certified personal trainer to create a customized plan that meets your individual needs and goals.
The Ethical Considerations
The use of testosterone for muscle gain raises ethical considerations, particularly in competitive sports. Most athletic organizations prohibit the use of performance-enhancing drugs like testosterone, as they provide an unfair advantage.
Using testosterone to gain muscle may also create unrealistic expectations about body image and contribute to a culture of body dysmorphia. It’s important to pursue fitness goals in a healthy and sustainable manner.
Conclusion
Ultimately, the decision of whether or not to use testosterone for muscle gain is a personal one that should be made in consultation with a medical professional. There is no one-size-fits-all answer to the question of how much testosterone to take.
Understanding the potential benefits, risks, and legal implications is crucial before making a decision. Prioritizing health and safety should always be the paramount concern. Dr. [Example Doctor Name], an endocrinologist at [Example Hospital Name], emphasizes, "The allure of quick muscle gain should never outweigh the potential for long-term health consequences. Informed consent and medical supervision are non-negotiable."