How Much Weight Should Scaffolding Be Able To Support

Scaffolding collapses are on the rise, raising critical questions about safety standards. How much weight should scaffolding realistically support to prevent catastrophic failures and protect workers?
This article delves into the mandated weight-bearing capacities, the factors influencing safe load limits, and the urgent need for stricter enforcement to prevent injuries and fatalities on construction sites.
Understanding Load Capacity: The Numbers
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) sets specific guidelines for scaffolding load capacity. Scaffolding must be able to support, without failure, its own weight and at least four times the intended maximum load.
This "four times" rule is crucial. For example, if a scaffold is designed to hold 1,000 pounds, it must be able to withstand 4,000 pounds without collapsing.
OSHA categorizes scaffolding into three load classifications: Light-duty, medium-duty, and heavy-duty. Light-duty scaffolds must support 25 pounds per square foot, medium-duty 50 pounds per square foot, and heavy-duty 75 pounds per square foot.
Factors Affecting Safe Weight Limits
Material quality is paramount. Scaffolding built with substandard steel or damaged components significantly reduces its load-bearing capacity.
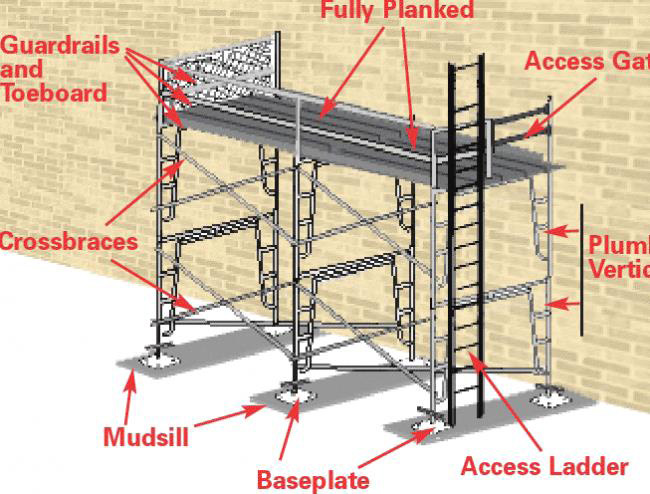
Incorrect assembly is a major contributing factor to collapses. Following the manufacturer's instructions and ensuring proper bracing and secure connections are essential.
Environmental conditions play a crucial role. Wind loads, rain, and snow can add significant weight and stress to a scaffold structure, potentially exceeding its safe load limit.
The Human Factor: Overloading and Misuse
Worker negligence and inadequate training often lead to overloading. Failure to accurately assess the weight of materials and personnel on the scaffold is a recurring problem.
Using scaffolding for purposes it was not designed for can also compromise its structural integrity. Improvisations and modifications should never be made without consulting a qualified engineer.
Poor maintenance contributes to weakened structures. Regular inspections and timely repairs are vital to identify and address potential hazards before they lead to a collapse.
Recent Incidents and Their Implications
Numerous scaffolding collapses across the country have resulted in serious injuries and fatalities. In 2023, a collapse in New York City injured seven workers, highlighting the persistent risks.
A similar incident in Houston, Texas in early 2024 resulted in one fatality, underscoring the urgent need for improved safety measures. These events serve as stark reminders of the potential consequences of inadequate load management.
Data from the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) indicates that scaffolding incidents are a leading cause of construction-related injuries. This data reinforces the need for proactive measures to prevent future accidents.
Enforcement and Compliance
While OSHA sets the standards, enforcement varies across states and regions. Some areas have stricter inspection protocols and penalties for violations than others.
Increased funding for OSHA inspections and training programs is crucial to ensure compliance. Employers must prioritize worker safety and provide adequate training on scaffolding safety procedures.
Whistleblower protection is essential to encourage workers to report unsafe conditions without fear of retaliation. Anonymous reporting mechanisms can help uncover violations and prevent accidents.
The Role of Technology
Technological advancements can play a key role in improving scaffolding safety. Smart sensors can monitor load levels in real-time and alert workers to potential overloads.
Drones can be used to conduct remote inspections of scaffolding structures, identifying potential hazards that might be missed by manual inspections. Augmented reality (AR) applications can assist workers in assembling scaffolding correctly.
Building Information Modeling (BIM) can be used to simulate scaffolding loads and identify potential weaknesses in the design before construction begins. This proactive approach can significantly reduce the risk of collapses.
Next Steps: Towards Safer Scaffolding Practices
A comprehensive review of existing scaffolding regulations is needed to ensure they reflect current best practices and technological advancements. Stricter enforcement of existing regulations is paramount to hold employers accountable for safety violations.
Increased investment in worker training and education is essential to promote a culture of safety on construction sites. Continuous research and development of innovative technologies can further improve scaffolding safety and prevent future incidents.
The goal is clear: to create safer working conditions for construction workers and eliminate preventable injuries and fatalities related to scaffolding failures. Failure to act decisively will continue to put lives at risk.