How To Calculate Insulin Resistance With Triglycerides

The aroma of freshly brewed coffee mingled with the clatter of breakfast dishes, a typical Sunday morning scene. Yet, amidst the warmth of family and the promise of a relaxing day, Sarah felt a nagging unease. Her doctor had recently mentioned the possibility of insulin resistance, a term that felt both vague and unsettling. Like many, she was trying to understand what it meant for her health and how to take control.
This article aims to shed light on a surprisingly simple yet effective way to estimate insulin resistance: using your triglyceride levels. We will explore the Triglyceride-Glucose (TyG) index, a calculation that can provide valuable insights into your metabolic health. The hope is to empower you with knowledge and encourage proactive steps towards a healthier future.
Understanding Insulin Resistance
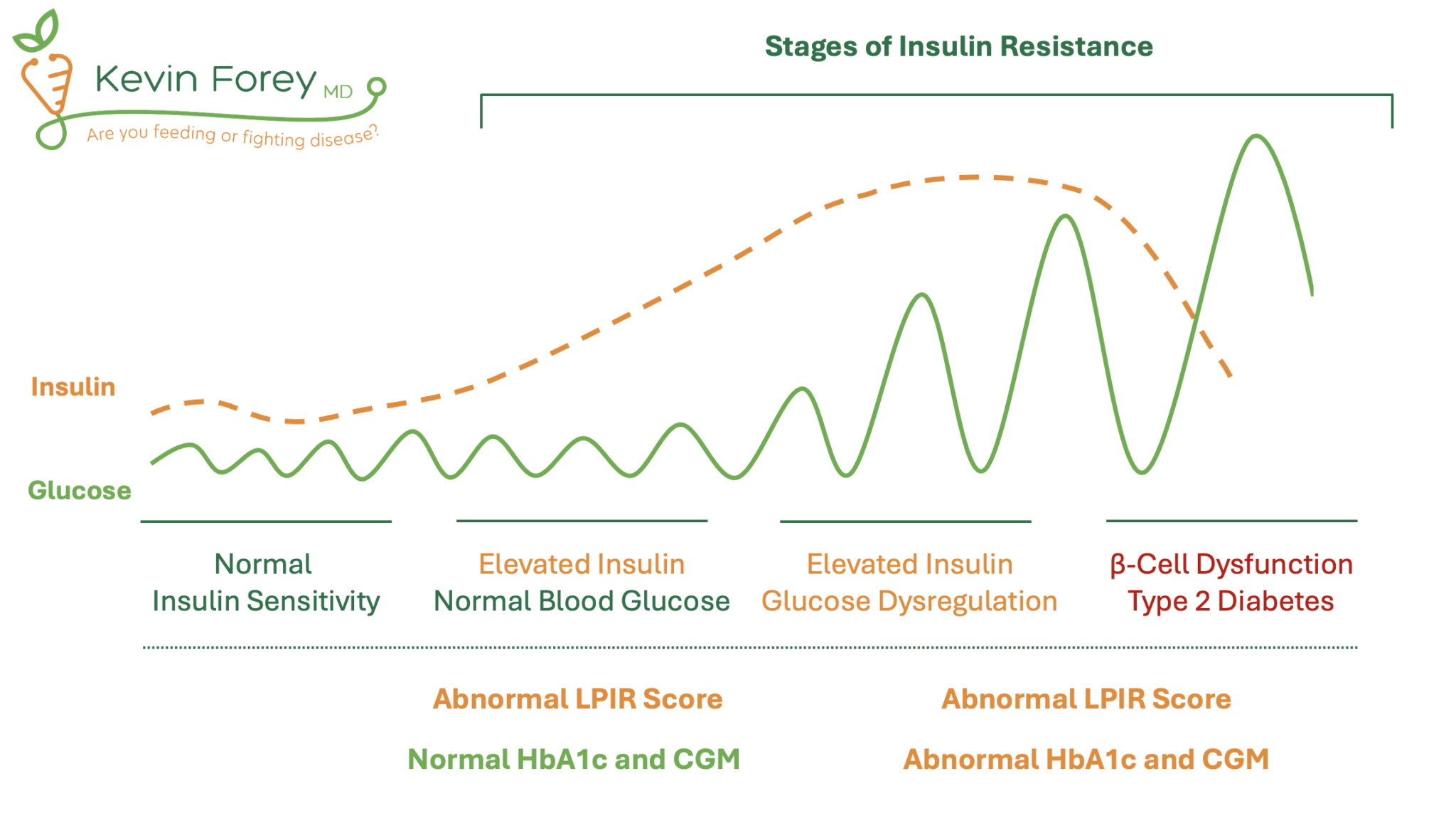
Insulin resistance is a condition where your body's cells don't respond properly to insulin. Insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas, acts like a key, unlocking cells to allow glucose (sugar) from the bloodstream to enter and be used for energy. When cells become resistant to insulin, the pancreas has to produce more and more insulin to maintain normal blood sugar levels.
Over time, this can lead to a variety of health problems. These includes prediabetes, type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and even non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Recognizing and addressing insulin resistance early is crucial for preventing these complications.
The Significance of Early Detection
The insidious nature of insulin resistance lies in its often silent progression. Many people are unaware they have it until they develop more serious health issues. Early detection allows for lifestyle interventions, such as dietary changes and increased physical activity, which can significantly improve insulin sensitivity and prevent or delay the onset of type 2 diabetes.
Regular check-ups with your doctor are essential for monitoring blood sugar levels and other relevant markers. However, tools like the TyG index can empower individuals to take a more active role in understanding their own metabolic health.
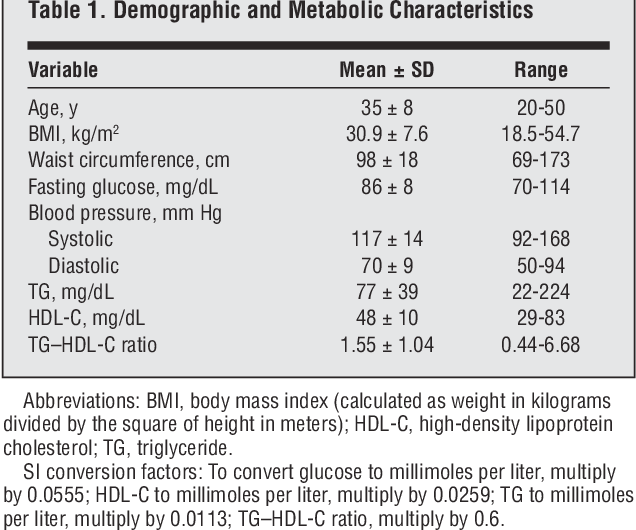
The Triglyceride-Glucose (TyG) Index: A Simple Calculation
The TyG index is a simple calculation that uses fasting triglyceride and fasting glucose levels to estimate insulin resistance. It is a readily available and inexpensive tool that can be easily calculated with information from a standard blood test.
This index has gained recognition in recent years as a valuable screening tool. Research suggests it can be a reliable indicator of insulin resistance, especially in populations where more complex testing methods are not readily accessible or affordable.
How to Calculate the TyG Index
The formula for calculating the TyG index is as follows:
Ln [Fasting triglycerides (mg/dL) x Fasting glucose (mg/dL) / 2]
Where "Ln" represents the natural logarithm. You can use a scientific calculator or an online TyG index calculator to perform this calculation easily. Be sure to use fasting levels, meaning you should have nothing to eat or drink (except water) for at least 8 hours before the blood test.
Interpreting Your TyG Index Score
While optimal TyG index ranges can vary slightly depending on the population studied, a general guideline is that a lower score is better. There isn't a universally agreed upon cutoff for defining insulin resistance using the TyG index, but most studies suggest values above 4.5 indicate a higher likelihood of insulin resistance.
It's crucial to discuss your TyG index score with your doctor. They can interpret your results in the context of your overall health profile, including other risk factors, medical history, and physical examination findings.
Why Triglycerides Matter
Triglycerides are a type of fat in your blood that your body uses for energy. High levels of triglycerides are often associated with insulin resistance, obesity, and other metabolic disorders. When your cells are resistant to insulin, glucose builds up in your bloodstream.
The liver then converts excess glucose into triglycerides, leading to elevated levels. This creates a vicious cycle, where high triglycerides further contribute to insulin resistance.
The Link Between Glucose and Insulin Resistance
Fasting glucose levels reflect how well your body is regulating blood sugar overnight. Elevated fasting glucose, even within the "normal" range, can be an early sign of insulin resistance. When combined with high triglycerides, it paints a clearer picture of your metabolic health.
The TyG index cleverly combines these two readily available markers to provide a more comprehensive assessment than either measurement alone.
Lifestyle Modifications for Improving Insulin Sensitivity
If your TyG index is elevated, don't despair. Lifestyle changes can make a significant difference in improving insulin sensitivity. These include dietary adjustments, regular physical activity, and stress management techniques.
Remember, small, sustainable changes are more effective than drastic, short-lived measures.
Dietary Strategies
Focus on a balanced diet rich in whole, unprocessed foods. This includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, lean protein, and whole grains. Limit your intake of sugary drinks, processed foods, and unhealthy fats.
Consider incorporating foods known to improve insulin sensitivity, such as those high in fiber and omega-3 fatty acids. Portion control is also crucial for managing blood sugar and triglyceride levels.
The Power of Exercise
Regular physical activity is one of the most effective ways to improve insulin sensitivity. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week. This could include brisk walking, jogging, swimming, or cycling.
Strength training is also beneficial, as it helps build muscle mass, which increases glucose uptake and improves insulin sensitivity. Find activities you enjoy, and make exercise a regular part of your routine.
Stress Management
Chronic stress can negatively impact blood sugar control and contribute to insulin resistance. Find healthy ways to manage stress, such as yoga, meditation, spending time in nature, or engaging in hobbies you enjoy.
Prioritize sleep, as sleep deprivation can also worsen insulin resistance. Aim for 7-8 hours of quality sleep each night.
Beyond the TyG Index: Comprehensive Assessment
While the TyG index is a valuable tool, it's important to remember that it's just one piece of the puzzle. It's not a substitute for a comprehensive medical evaluation.
Your doctor may recommend additional tests, such as an oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) or an insulin resistance test (HOMA-IR), to further assess your insulin sensitivity. They will also consider your family history, medical history, and other risk factors when making a diagnosis.
Working with Your Healthcare Provider
Open communication with your doctor is key to managing insulin resistance effectively. Discuss your concerns, ask questions, and actively participate in developing a personalized treatment plan.
Your doctor can provide guidance on lifestyle modifications, prescribe medications if necessary, and monitor your progress over time. Regular follow-up appointments are essential for ensuring that your treatment plan is working and making adjustments as needed.
A Step Towards a Healthier Future
Understanding your risk of insulin resistance is a powerful step towards taking control of your health. The TyG index offers a simple, accessible way to estimate your insulin sensitivity and identify potential problems early on.
Armed with this knowledge, you can make informed decisions about your diet, exercise habits, and overall lifestyle. Remember, even small changes can have a significant impact on your metabolic health and long-term well-being.
Sarah, like many others, found that understanding the TyG index empowered her to have a more informed conversation with her doctor and proactively address her health concerns. It wasn't about fear, but about knowledge and the ability to make positive changes, one small step at a time, towards a healthier and more vibrant life.