How To Determine How Much To Pay Yourself

Small business owners often grapple with a critical question: How much should they pay themselves? Determining a fair and sustainable salary requires careful consideration of business finances, market rates, and personal needs.
This guide provides actionable steps to help you navigate this complex decision and ensure both your personal well-being and the financial health of your company.
Assess Your Business Finances
First, understand your company's financial position. Analyze your profit and loss statements, balance sheets, and cash flow projections.
Calculate your available cash flow after covering all business expenses, including salaries for other employees, operating costs, taxes, and debt payments. This is the pool from which your salary will be drawn.
Consider setting aside a percentage of revenue for reinvestment in the business. Industry averages suggest a reinvestment rate of 10-20%, but this can vary based on your company's growth stage and goals.
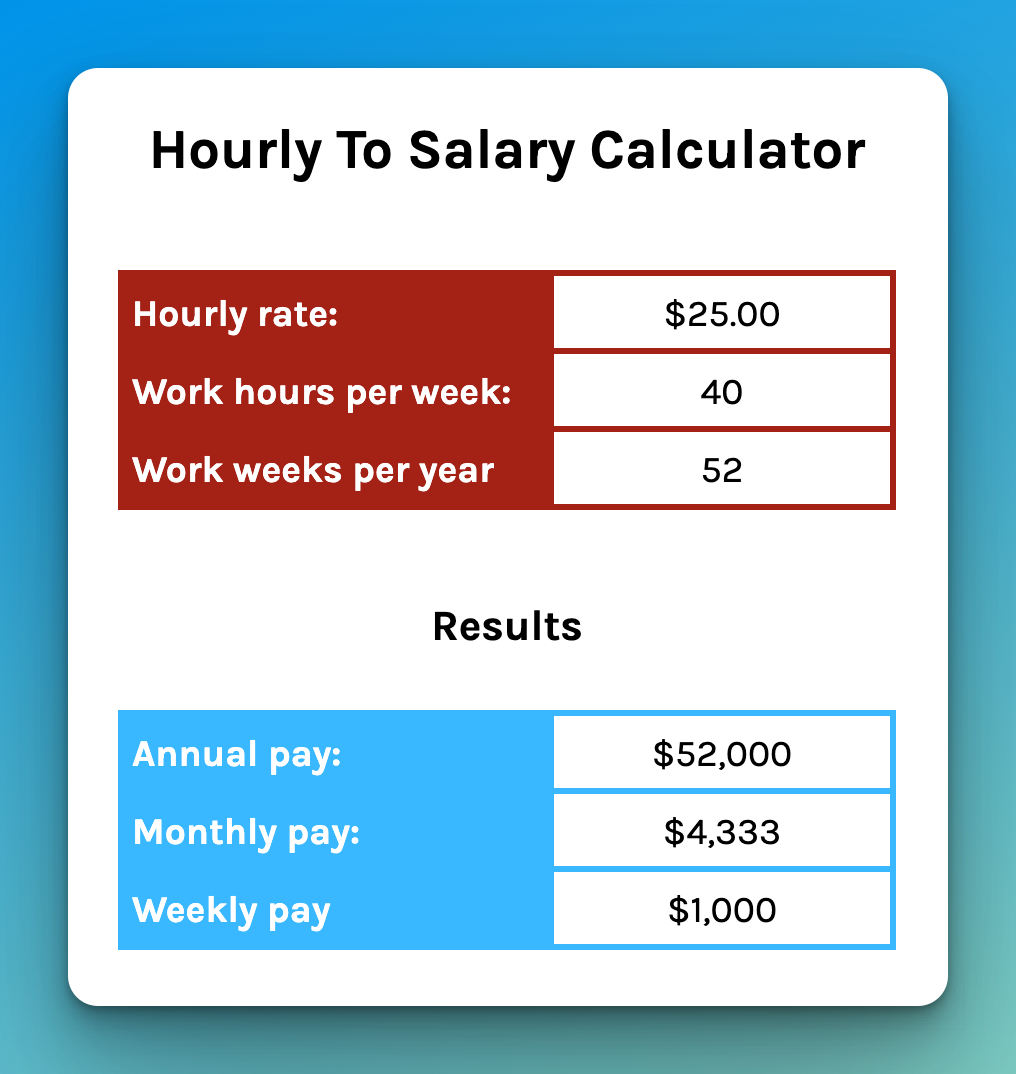
Research Market Rates for Your Role
Don't undervalue your contribution. Research the average salary for similar roles in your industry and geographic location.
Use online resources like Salary.com, Glassdoor, and PayScale to gather data on compensation for comparable positions. Factor in your experience, skills, and the size and complexity of your business.
Professional organizations and industry associations often provide salary surveys and benchmarking reports that can offer valuable insights.
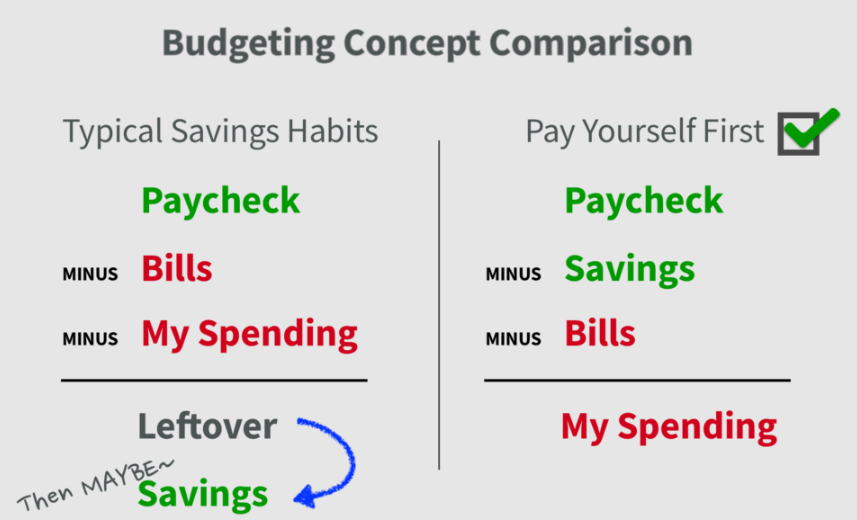
Consider Your Personal Financial Needs
Your personal financial needs are a critical component of determining your salary. Create a detailed budget outlining your monthly expenses, including housing, food, transportation, healthcare, and debt payments.
Don't forget to factor in savings goals, such as retirement contributions, emergency funds, and education expenses for yourself or your family. Determine the minimum income required to cover these needs.
However, remember to balance your personal needs with the financial realities of your business.
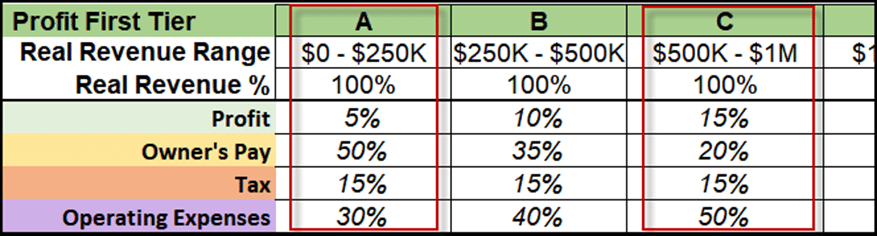
Establish a Clear Payment Structure
Decide on a payment structure that aligns with your business model and financial stability. Common options include a fixed salary, a salary plus bonus, or a draw against profits.
A fixed salary provides predictability and stability, but it may not be suitable for businesses with fluctuating revenue. A salary plus bonus allows you to reward yourself for achieving specific performance goals.
A draw against profits is common in partnerships and LLCs, where owners take a share of the company's earnings. This approach requires careful financial management and consistent profitability.
Regularly Review and Adjust Your Salary
Your salary should not be set in stone. Review and adjust it regularly, at least annually, to reflect changes in your business performance, market conditions, and personal needs.
As your business grows and becomes more profitable, you may be able to increase your salary. Conversely, if your business faces financial challenges, you may need to temporarily reduce your pay.
Document all salary changes and maintain accurate records for tax purposes.
Tax Implications
Understand the tax implications of your chosen compensation structure. Consult with a tax advisor to ensure compliance with all applicable laws and regulations.
Owner salaries are typically subject to income tax and self-employment tax (Social Security and Medicare). Proper tax planning can help you minimize your tax liability and avoid penalties.
Explore options like setting up a retirement plan (e.g., Solo 401(k) or SEP IRA) to reduce your taxable income and save for the future.
Key Takeaway: Finding the right balance between compensating yourself fairly and ensuring the financial stability of your business is crucial for long-term success.
Consider seeking advice from a financial advisor or business consultant to develop a personalized compensation strategy. This will ensure that is aligned with your goals and circumstances.