How To Get Rid Of Water Retention While On Testosterone

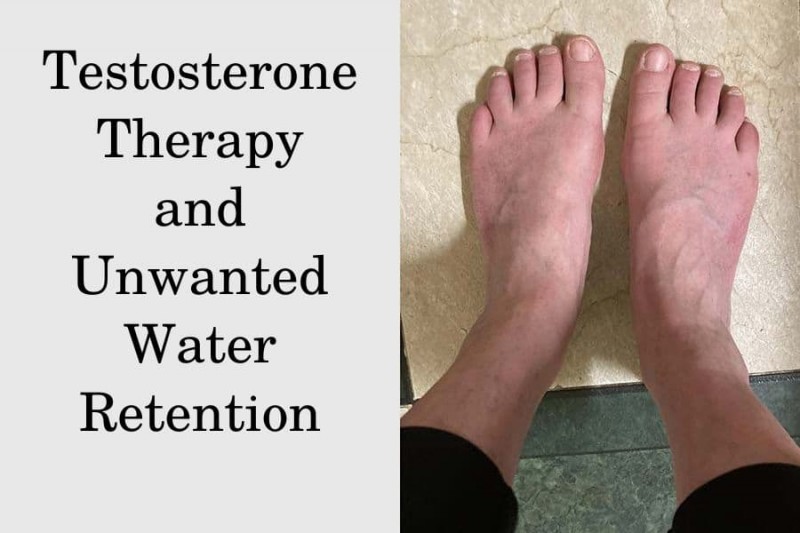
Water retention, a common side effect of testosterone therapy, can cause discomfort and obscure muscle definition. Understanding how to manage this is crucial for optimizing results and well-being.
This guide provides actionable strategies to combat water retention while maintaining the benefits of testosterone replacement therapy (TRT).
Understanding Water Retention on Testosterone
Testosterone influences hormone levels, impacting fluid balance. Increased estrogen, a byproduct of testosterone aromatization, can contribute to sodium retention.
This leads to increased fluid volume within the body, commonly manifesting as bloating and swelling.
Strategies for Reducing Water Retention
1. Monitor Sodium Intake
Sodium plays a significant role in fluid regulation. Excess sodium intake prompts the body to retain more water to maintain electrolyte balance.
Aim for the Dietary Guidelines for Americans' recommended limit of less than 2,300 milligrams per day. Read labels carefully and be mindful of hidden sodium in processed foods.
2. Optimize Potassium Intake
Potassium helps counteract the effects of sodium. Increasing potassium intake can promote fluid excretion and reduce water retention.
Good sources include bananas, sweet potatoes, spinach, and avocados. Consider supplementation if dietary intake is insufficient, but consult with a healthcare professional first.
3. Stay Hydrated
It seems counterintuitive, but adequate hydration is essential. Dehydration signals the body to conserve water, worsening retention.
Drink plenty of water throughout the day, aiming for at least eight glasses. Monitor urine color; it should be pale yellow.
4. Regulate Estrogen Levels
Elevated estrogen levels contribute to water retention. Managing estrogen through aromatase inhibitors (AIs) may be necessary.
AIs, such as anastrozole (Arimidex) or exemestane (Aromasin), can help reduce estrogen conversion. Discuss this option with your doctor; these medications require careful monitoring.
5. Consider Diuretics (With Caution)
Diuretics promote urination, helping the body eliminate excess fluid. These should be considered a last resort due to potential side effects.
Over-the-counter diuretics or prescription medications may deplete essential electrolytes. Consult with your physician before using any diuretics.
6. Adjust Testosterone Dosage
A high testosterone dosage can exacerbate water retention. Adjusting the dosage under medical supervision might alleviate symptoms.
Work with your healthcare provider to find the optimal dosage that balances benefits and side effects. Frequent blood work will ensure optimal hormone levels.
7. Regular Exercise
Exercise promotes fluid balance through sweating and improved circulation. Cardio and resistance training can both be beneficial.
Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise per week. Include strength training at least twice a week.
8. Manage Stress
Stress can impact hormone levels and fluid balance. Chronic stress can lead to increased cortisol, potentially contributing to water retention.
Practice stress-reducing techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises. Prioritize sleep and relaxation.
9. Monitor Carbohydrate Intake
High carbohydrate intake, especially refined carbohydrates, can cause your body to store more water. These cause a spike in insulin levels, signaling to the kidneys to retain more sodium.
Focus on consuming complex carbohydrates such as whole grains and fiber-rich vegetables. Adjust your carbohydrate intake based on your individual needs and activity level.
The Role of Medical Supervision
These strategies are general guidelines and should not replace medical advice. Regular monitoring and consultation with a healthcare professional are crucial.
Blood work and physical exams will help determine the underlying cause of water retention and guide appropriate treatment.
When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
Severe swelling, especially in the legs or ankles, accompanied by shortness of breath, requires immediate medical attention. This could indicate serious underlying conditions such as heart failure or kidney disease.
Do not attempt to self-treat in these cases.
Ongoing Management
Managing water retention on testosterone is an ongoing process. Regularly assess your progress and adjust your strategies as needed, under the guidance of your physician.
Consistent monitoring and communication with your healthcare provider are key to achieving optimal results and maintaining well-being. More research is ongoing to better understand the mechanisms of water retention and develop more targeted treatments.