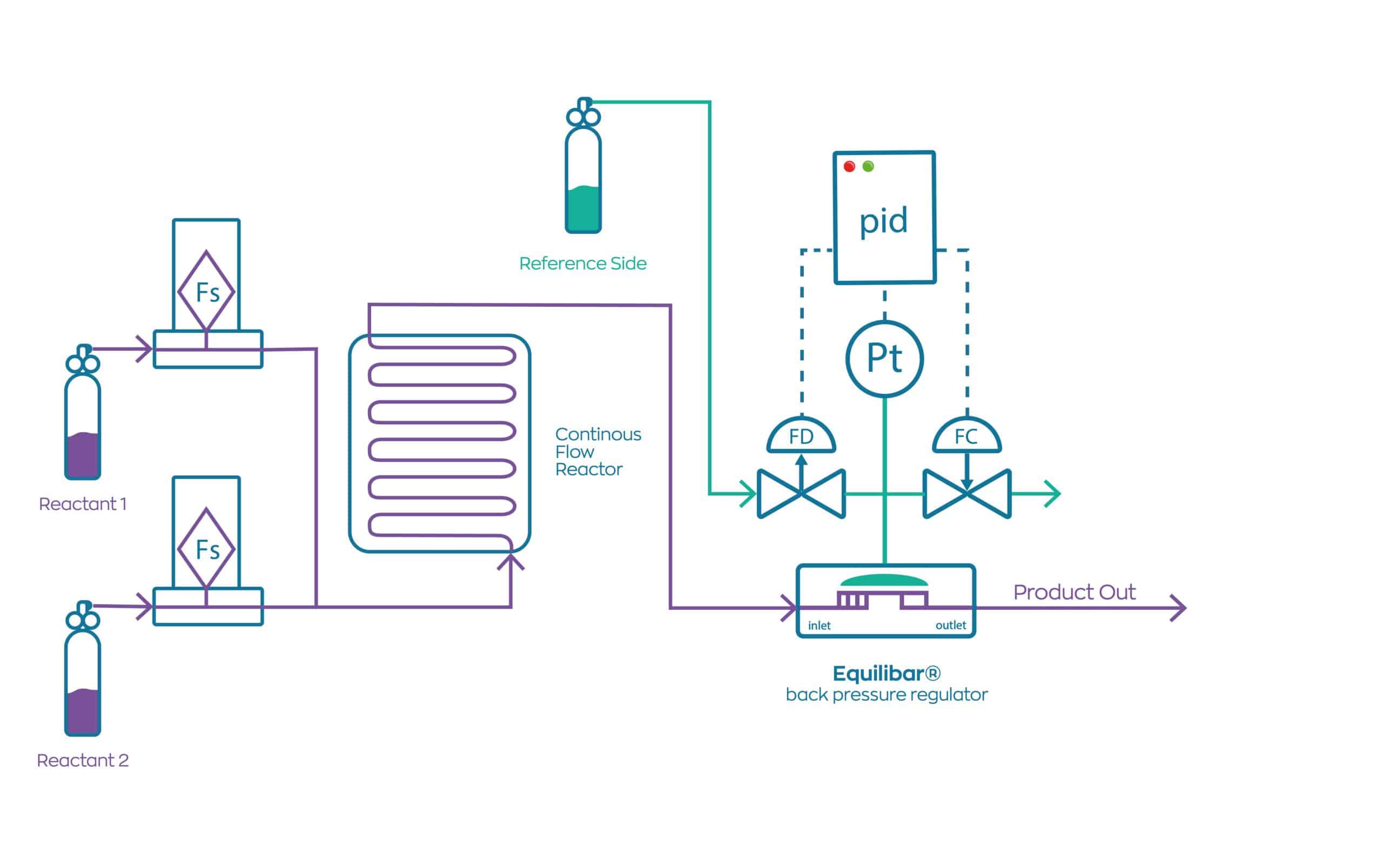
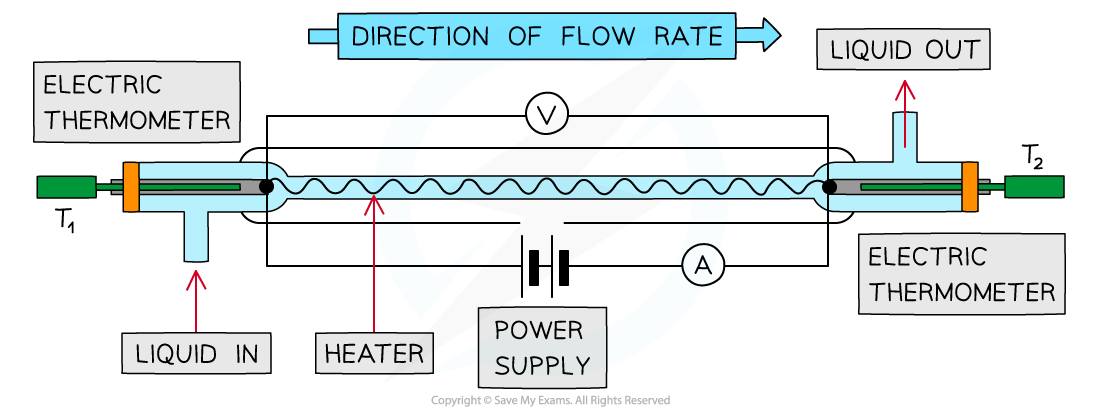
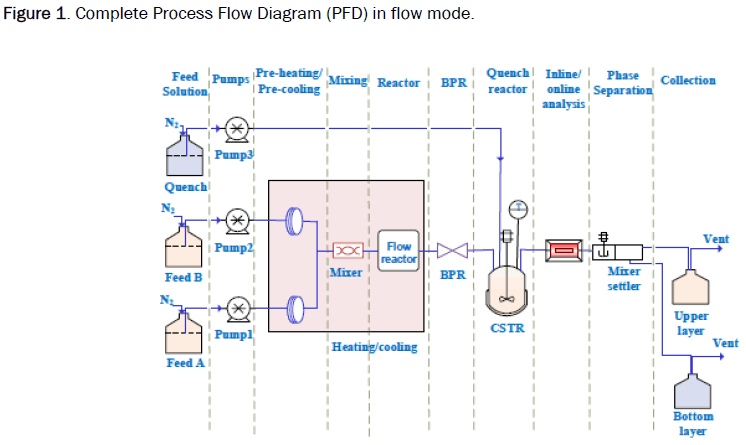
How Will The Current Generation Of Continuous Flow

The rise of continuous biomanufacturing is poised to revolutionize drug production, potentially slashing costs and accelerating access to life-saving medications. This paradigm shift promises faster, more efficient, and higher-quality biopharmaceutical production, but faces significant hurdles in adoption and standardization.
Continuous flow biomanufacturing replaces traditional batch processes with an integrated, uninterrupted system. This article examines how this next generation of biomanufacturing will impact the pharmaceutical landscape, focusing on its benefits, challenges, and the necessary steps for widespread implementation.
The Promise of Continuous Biomanufacturing
Continuous manufacturing offers substantial advantages over batch processing. Increased productivity is a major draw, with potential output gains of up to 50% according to a 2019 report by McKinsey. This translates directly to lower production costs and faster delivery of drugs to patients.
Improved product quality and consistency are also key benefits. The closed, integrated nature of continuous systems allows for tighter control over process parameters, minimizing variability and the risk of contamination, as highlighted in a study published by the Journal of Pharmaceutical Innovation.
Flexibility and scalability are enhanced. Continuous systems can be easily adapted to produce different products or scaled up to meet increasing demand, offering manufacturers greater agility in responding to market needs, as observed by experts at the FDA.
Challenges and Obstacles to Adoption
Despite the clear advantages, the transition to continuous biomanufacturing is not without its challenges. The initial investment in new equipment and infrastructure can be substantial, deterring some manufacturers, especially smaller companies.
Regulatory hurdles also pose a significant barrier. Current regulations are largely geared towards batch manufacturing, requiring manufacturers to navigate complex approval pathways for continuous processes, a concern raised by the Biopharmaceutical Emerging Best Practices Association (BEPBA).
A lack of standardized equipment and processes further complicates adoption. The absence of widely accepted standards hinders interoperability and increases the risk associated with implementing continuous systems, according to a white paper released by the International Society for Pharmaceutical Engineering (ISPE).
The Role of Technology and Innovation
Technological advancements are crucial for overcoming the challenges associated with continuous biomanufacturing. Advanced sensors and process analytical technology (PAT) are essential for real-time monitoring and control of critical process parameters.
Data analytics and modeling play a vital role in optimizing process performance. These tools enable manufacturers to predict and mitigate potential issues, ensuring consistent product quality and maximizing efficiency, as demonstrated in a case study by Amgen.
Automation and digitalization are also key enablers. Integrating automated systems and digital platforms streamlines operations, reduces human error, and enhances data management, as emphasized by researchers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT).
The Impact on Different Stakeholders
The shift to continuous biomanufacturing will have a profound impact on various stakeholders in the pharmaceutical industry. Manufacturers stand to benefit from lower production costs, faster time to market, and improved product quality.
Patients will gain access to more affordable and readily available medications. The increased efficiency of continuous manufacturing can lead to lower drug prices and a more reliable supply chain, according to a report by the World Health Organization (WHO).
Regulators will need to adapt their processes and guidelines to accommodate continuous manufacturing. This includes developing new assessment criteria and inspection protocols that are tailored to the unique characteristics of these systems, as indicated by the European Medicines Agency (EMA).
The Future of Biomanufacturing
Continuous biomanufacturing is poised to become the dominant paradigm in the pharmaceutical industry. Widespread adoption will require collaboration among manufacturers, regulators, and technology providers to address the existing challenges and establish clear standards.
Increased investment in research and development is essential. This will drive further innovation in process technology, data analytics, and automation, paving the way for more efficient and cost-effective biopharmaceutical production, as noted by the National Institute for Innovation in Manufacturing Biopharmaceuticals (NIIMBL).
Education and training are also crucial for preparing the workforce for the future of biomanufacturing. Developing specialized programs will equip professionals with the skills and knowledge needed to operate and maintain continuous systems effectively, as advocated by the American Association of Pharmaceutical Scientists (AAPS).
Next Steps and Ongoing Developments
The FDA is actively working to develop guidance documents and regulatory pathways for continuous manufacturing. These efforts are aimed at providing clarity and predictability for manufacturers seeking to adopt these technologies.
Industry consortia and standard-setting organizations are collaborating to develop common standards for equipment and processes. These standards will facilitate interoperability and reduce the risk associated with implementing continuous systems.
Pilot projects and demonstration facilities are being established to showcase the benefits of continuous biomanufacturing. These initiatives provide a platform for manufacturers to gain hands-on experience and evaluate the feasibility of adopting these technologies in their own operations.
The transition to continuous biomanufacturing is an ongoing process. While challenges remain, the potential benefits are too significant to ignore. By embracing innovation, fostering collaboration, and adapting regulatory frameworks, the pharmaceutical industry can unlock the full potential of continuous manufacturing and improve the lives of patients worldwide.
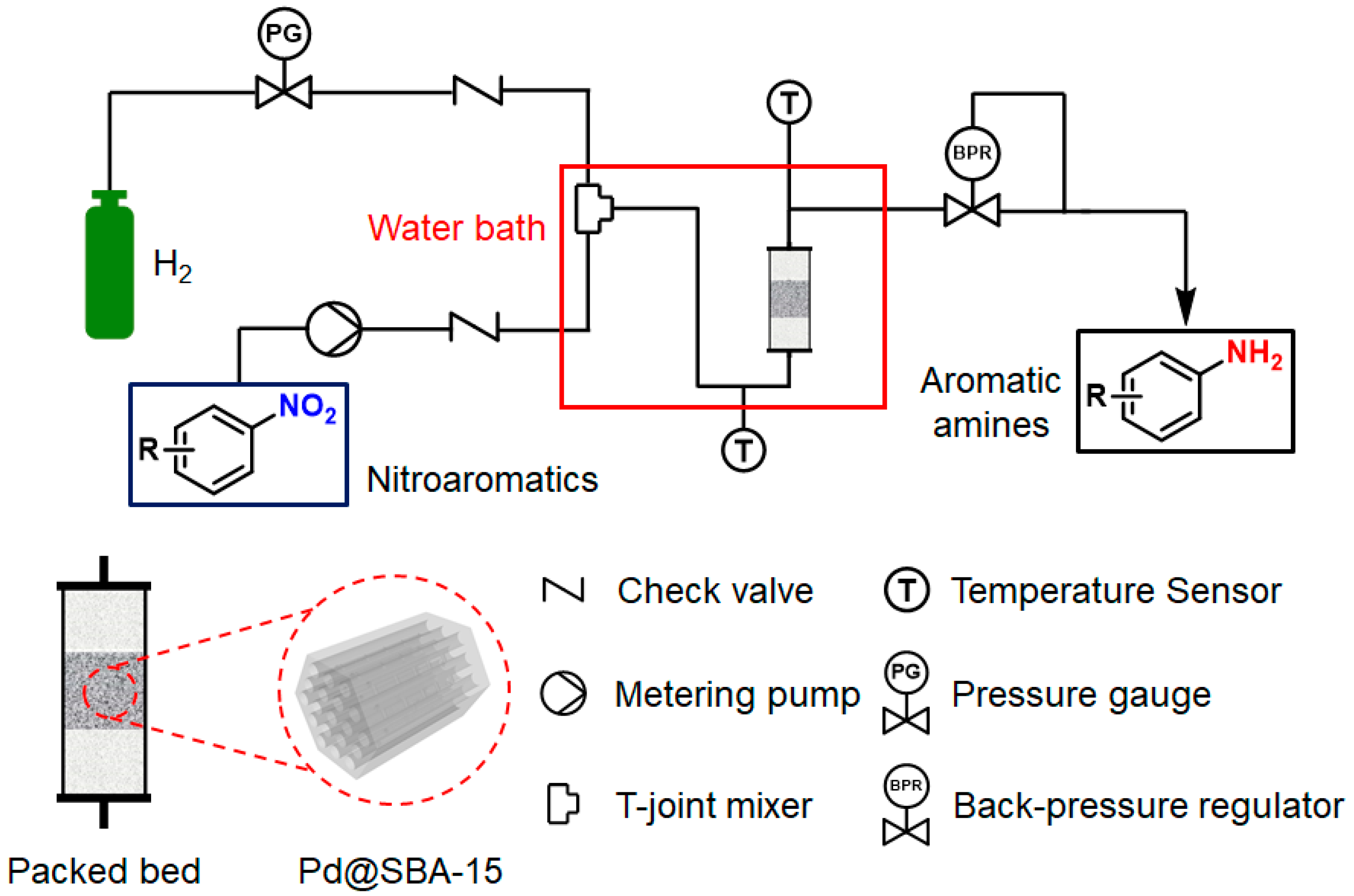

![How Will The Current Generation Of Continuous Flow Continuous flow methods [12]. | Download Scientific Diagram](https://www.researchgate.net/publication/359994355/figure/fig2/AS:11431281103934884@1669882317157/Continuous-flow-methods-12.png)