If A Company Fails To Record Estimated Bad Debts Expense

The failure of a company to accurately record estimated bad debts expense can have significant repercussions, impacting financial reporting accuracy, investor confidence, and potentially leading to regulatory scrutiny. This accounting oversight, stemming from either negligence or intentional manipulation, distorts the true financial picture of an organization.
At the heart of the issue is the fundamental accounting principle of matching expenses to revenues in the period they are incurred. This article explores the implications of neglecting to record estimated bad debts, examining its causes, consequences, and potential preventative measures.
Understanding Bad Debts Expense
Bad debts expense represents the estimated amount of credit sales that a company expects to be uncollectible. Companies extend credit to customers, anticipating that a portion of these receivables may ultimately not be paid.
Accrual accounting requires companies to recognize this potential loss in the same period as the related sales revenue, reflecting a realistic view of financial performance. Ignoring this estimate violates this principle, painting an artificially rosy picture of profitability.
The Mechanics of Non-Recording
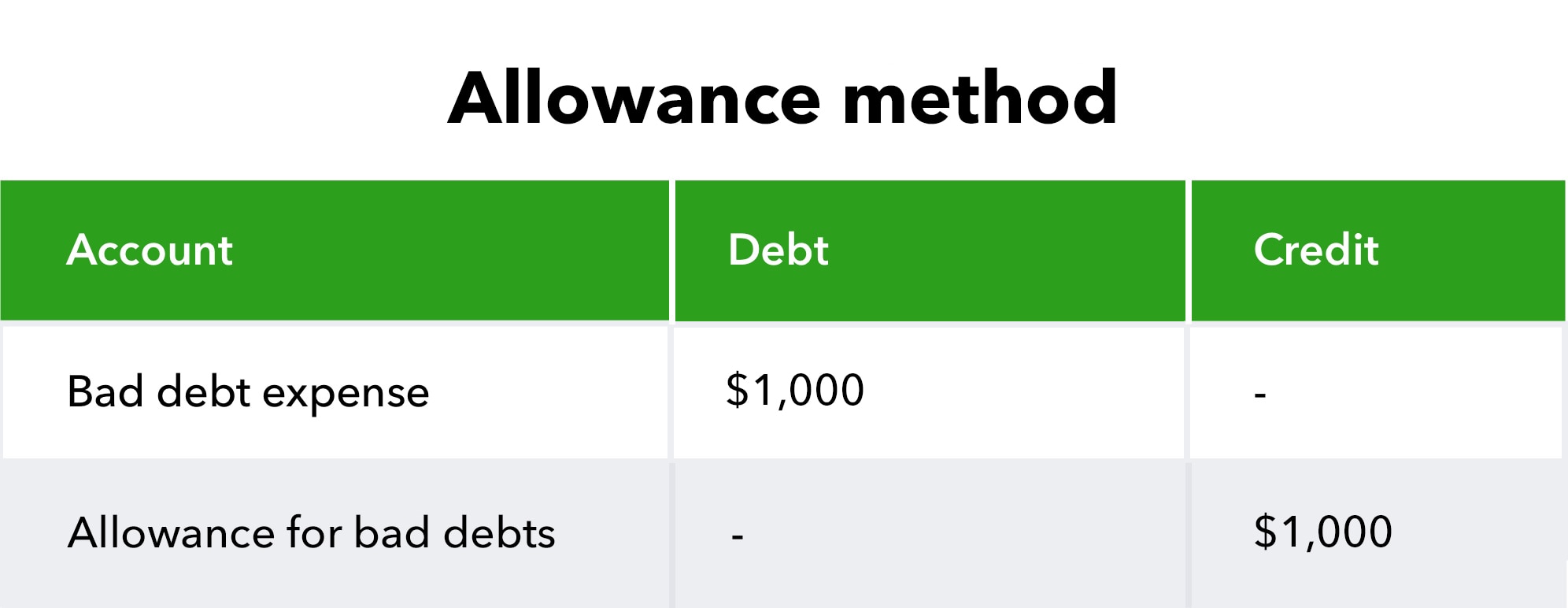
The failure to record bad debts expense usually involves not creating or understating the allowance for doubtful accounts. This allowance is a contra-asset account that reduces the gross amount of accounts receivable to its net realizable value – the amount a company realistically expects to collect.
When a company doesn't adjust its allowance for doubtful accounts appropriately, it overstates its assets (accounts receivable) and its net income. This misrepresentation can mislead investors and other stakeholders about the company's financial health.
Consequences of the Omission
The most immediate impact is a distorted financial statement. Net income is inflated, making the company appear more profitable than it actually is.
This, in turn, can lead to several other detrimental effects. Investors may make ill-informed decisions based on inaccurate financial data, potentially overvaluing the company's stock.
Furthermore, creditors may extend more credit than is prudent, unaware of the true risk associated with the company. Management may also make poor operational decisions based on misleading financial metrics, leading to overspending or underinvestment in crucial areas.
From a regulatory standpoint, companies that intentionally or negligently fail to record bad debts expense may face penalties from regulatory bodies like the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). These penalties can include fines, cease-and-desist orders, and even criminal charges in severe cases.
Why Companies Fail to Record Bad Debts
The reasons for failing to record estimated bad debts expense vary. Sometimes, it's a case of genuine oversight or a lack of understanding of accounting principles.
However, in other instances, it's a deliberate attempt to manipulate financial results. Companies facing pressure to meet earnings targets may be tempted to artificially inflate their profits by suppressing expenses.
In some cases, management may be overly optimistic about the company's ability to collect receivables, leading them to underestimate the bad debts expense. Regardless of the motive, the consequences remain the same: inaccurate financial reporting and potential harm to stakeholders.
Preventative Measures and Best Practices
Implementing strong internal controls is crucial to prevent the failure to record estimated bad debts expense. This includes establishing clear policies and procedures for estimating and recording bad debts.
Regular review and audit of the allowance for doubtful accounts by independent auditors can help ensure its accuracy. Companies should also foster a culture of ethical financial reporting, where transparency and accuracy are valued above short-term gains.
Training accounting staff on proper accounting principles and the importance of accurate financial reporting is equally important. Using sophisticated accounting software that can automatically calculate estimated bad debts expense based on historical data and industry benchmarks can also minimize errors.
The Human Cost of Accounting Errors
The repercussions of misstated financials extend beyond just numbers on a spreadsheet. Consider the case of ACME Corporation, a once-thriving manufacturing company that failed to adequately account for its bad debts.
Fueled by artificially inflated profits, the company embarked on an aggressive expansion plan, taking on significant debt. When the true extent of uncollectible receivables became apparent, ACME Corporation faced a severe financial crisis.
The company was forced to lay off hundreds of employees, devastating the local community and impacting families who relied on those jobs. This real-world example highlights the human cost of accounting errors and the importance of accurate financial reporting.
Looking Ahead
In an increasingly complex business environment, the importance of accurate financial reporting cannot be overstated. The failure to record estimated bad debts expense, while seemingly a minor oversight, can have far-reaching and devastating consequences.
By understanding the causes, consequences, and preventative measures, companies can ensure the integrity of their financial reporting and protect the interests of their stakeholders. Maintaining ethical accounting practices is not only a legal obligation but also a fundamental requirement for building trust and long-term sustainability.
Ultimately, a commitment to accurate and transparent financial reporting is essential for fostering a healthy and stable economic environment.