Immersive And Non Immersive Virtual Reality

The world of virtual reality (VR) is rapidly evolving, presenting a diverse landscape of experiences ranging from fully immersive simulations to non-immersive applications. Understanding the nuances between these two categories is crucial for consumers, developers, and businesses looking to leverage the power of VR technology.
This article delves into the key distinctions between immersive and non-immersive VR, exploring their applications, technological underpinnings, and potential impact on various sectors. We aim to provide a clear and objective overview of this rapidly expanding technological domain.
Defining Immersive VR
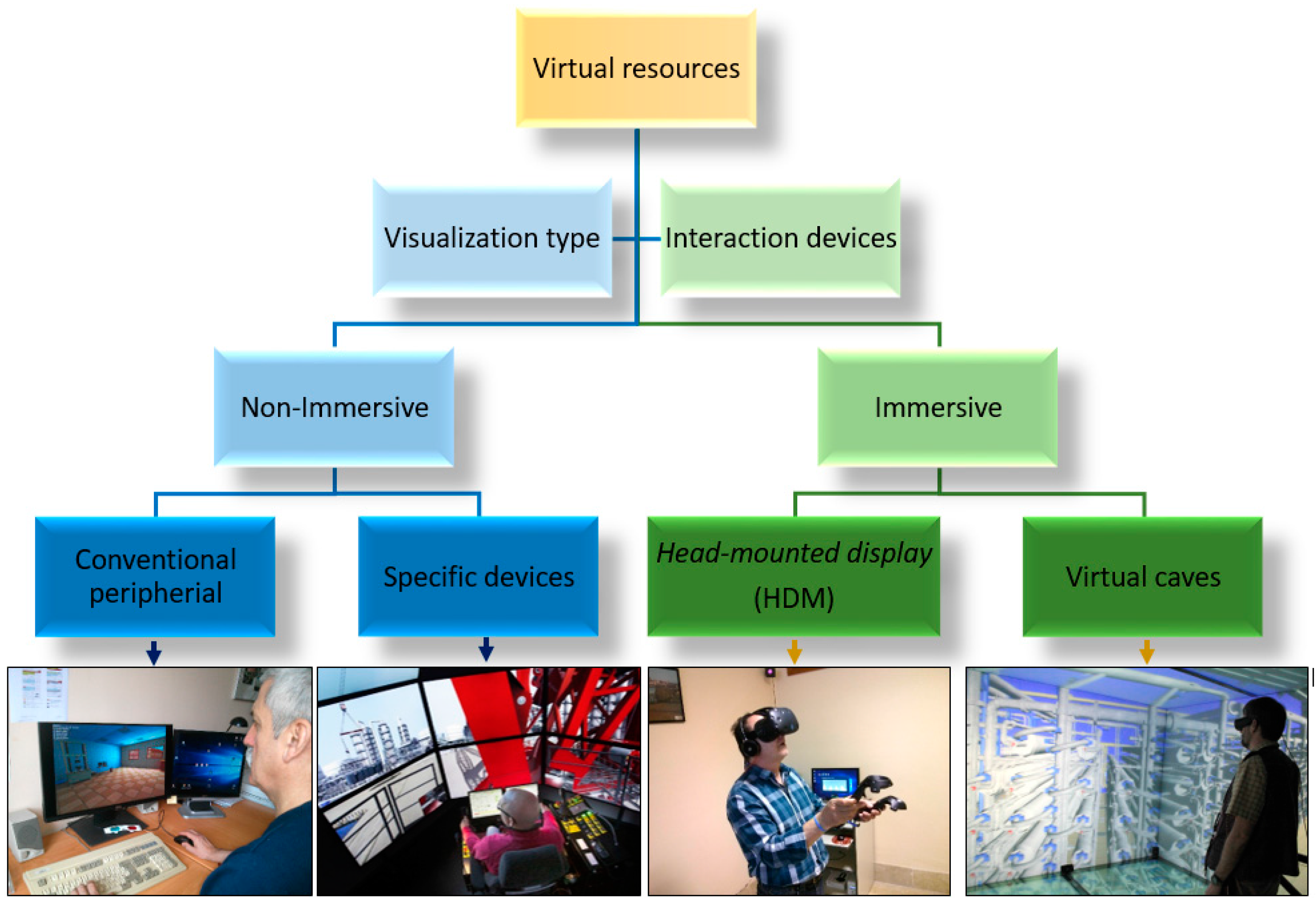
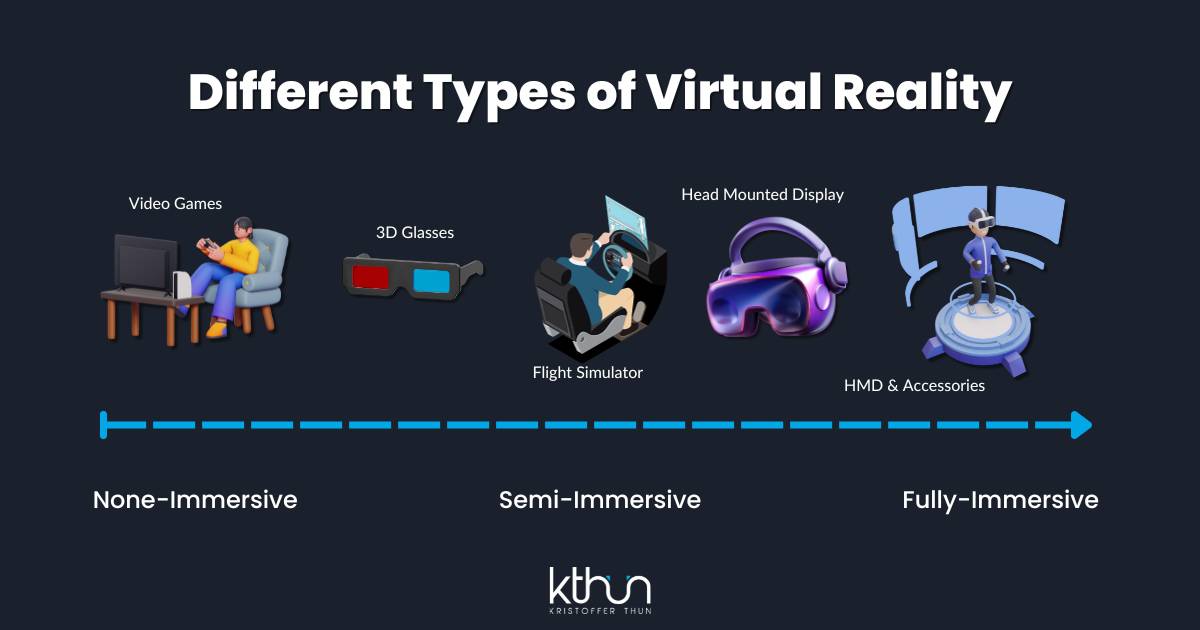
Immersive VR is characterized by its ability to completely engulf the user's senses, creating a sense of presence within a simulated environment. This is typically achieved through the use of headsets that display stereoscopic images and headphones that provide spatial audio.
Presence, the feeling of actually being in the virtual world, is the defining characteristic. The higher the degree of presence, the more convincing and engaging the VR experience becomes.
Key to this experience is head tracking, which allows the virtual environment to react dynamically to the user's movements, reinforcing the illusion of reality. Technologies like motion capture and specialized controllers further enhance immersion by enabling natural interaction with the virtual world.
Applications of Immersive VR
Immersive VR has found applications in various fields, including gaming, training, and therapy. In gaming, headsets like the Oculus Rift and HTC Vive transport players into realistic and interactive worlds.
The U.S. military, for example, utilizes VR for combat simulations, providing soldiers with realistic training scenarios without the risks associated with live exercises. Medical professionals are also using VR to practice complex surgeries and treatments in a safe and controlled environment.
Furthermore, therapists are employing VR to treat phobias, PTSD, and anxiety disorders by exposing patients to controlled simulations of their fears or triggers.
Understanding Non-Immersive VR
Non-immersive VR, on the other hand, provides a window into a virtual world without completely isolating the user from their physical surroundings. These experiences are often accessed through devices like smartphones, tablets, or computers.
Instead of a headset, users typically interact with the virtual environment through a screen and standard input devices such as a mouse, keyboard, or touchscreen. This allows for a less intense, but still engaging, form of virtual interaction.
Augmented Reality (AR), which overlays digital content onto the real world, is often considered a subset of non-immersive VR. AR applications range from interactive games to practical tools for navigation and information retrieval.
Applications of Non-Immersive VR
Non-immersive VR is widely used in education, entertainment, and e-commerce. Online museums and virtual tours allow users to explore historical sites and art collections from the comfort of their homes.
In e-commerce, retailers use non-immersive VR to create virtual showrooms where customers can browse and interact with products in a realistic setting. Similarly, educational institutions are using virtual field trips to expose students to different cultures and environments without the cost and logistical challenges of traditional travel.
Furthermore, mobile AR applications, such as Pokémon GO, have demonstrated the potential of non-immersive VR to blend digital entertainment with the physical world, creating engaging and interactive experiences for users of all ages.
Key Differences and Considerations
The fundamental difference between immersive and non-immersive VR lies in the degree of sensory immersion and the feeling of presence. Immersive VR aims to create a complete illusion of being in another world, while non-immersive VR provides a more limited and controlled interaction with virtual content.
Cost is another significant factor. Immersive VR setups typically require more expensive hardware, including high-end headsets, powerful computers, and specialized controllers. Non-immersive VR, on the other hand, can be accessed with readily available devices like smartphones and tablets, making it more accessible to a wider audience.
Accessibility, motion sickness, and social factors are also key considerations. While immersive VR offers a more intense experience, it can also induce motion sickness in some users and may lead to social isolation. Non-immersive VR, with its more limited sensory input, is generally less prone to these issues and allows for more flexible social interaction.
The Future of Virtual Reality
Both immersive and non-immersive VR are poised for continued growth and innovation. Advances in display technology, processing power, and sensor technology will likely lead to more realistic and seamless immersive experiences.
The development of more intuitive and natural user interfaces will further enhance immersion and make VR more accessible to a wider range of users. Likewise, non-immersive VR will continue to evolve, with AR technology becoming increasingly integrated into everyday life.
As VR technology matures, we can expect to see its applications expand into new and unforeseen areas, transforming the way we learn, work, and interact with the world around us. Whether it's a fully immersive simulation or a subtle overlay of digital content onto our reality, VR is set to play an increasingly important role in our lives.