Importance Of Corporations In Society

Corporations, often viewed through a lens of either unbridled capitalism or necessary economic engines, occupy a central and multifaceted role in modern society. Their influence extends far beyond simply generating profit, impacting employment, innovation, infrastructure, and even social progress. Understanding their significance requires a nuanced perspective that acknowledges both their potential benefits and inherent challenges.
This article examines the crucial roles corporations play in shaping society, exploring their economic contributions, social impact, and the evolving expectations placed upon them.
Economic Engines and Job Creation
At their core, corporations are powerful economic engines. They drive economic growth by producing goods and services, fostering competition, and attracting investment.
Data from the U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis consistently shows that corporate profits contribute significantly to the nation's Gross Domestic Product (GDP). Furthermore, corporations are major employers, providing livelihoods for millions of people globally.
Beyond direct employment, corporations stimulate indirect job creation through their supply chains and the ripple effect of consumer spending. The World Bank emphasizes the importance of a thriving corporate sector for sustained economic development, particularly in emerging economies.
Innovation and Technological Advancement
Corporations are often at the forefront of innovation and technological advancement. The research and development (R&D) spending of large corporations fuels breakthroughs in medicine, technology, and other fields.
Companies like Microsoft, Apple, and Tesla invest billions of dollars annually in R&D, leading to new products, services, and technologies that improve lives and drive economic progress. Their innovations often have far-reaching consequences, transforming industries and creating entirely new markets.
The Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) recognizes the crucial role of corporate R&D in fostering long-term economic growth and societal well-being.
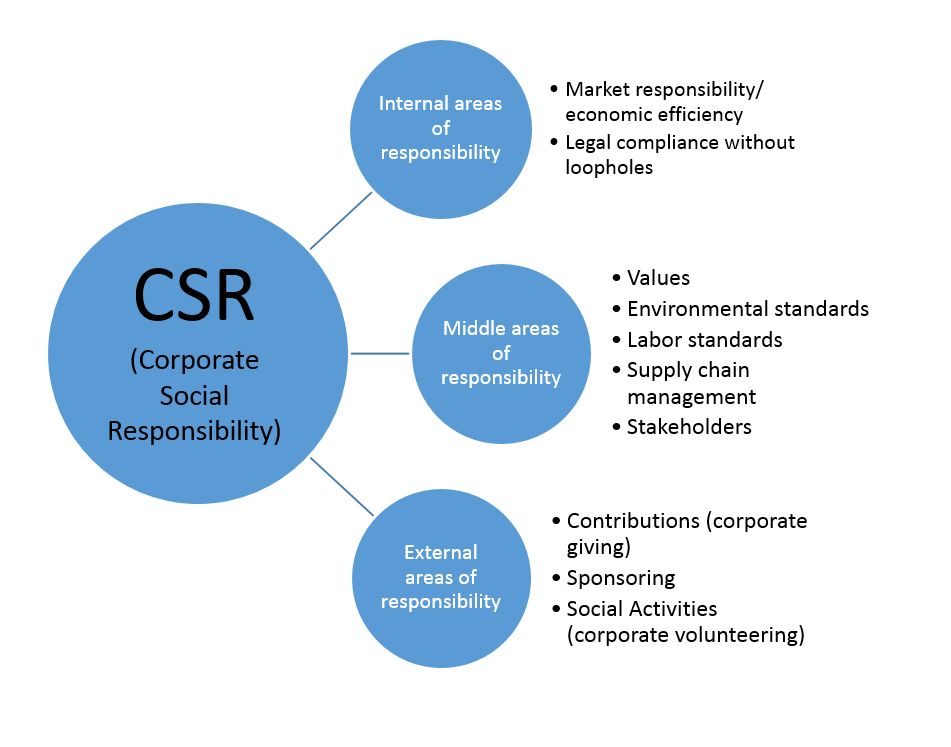
Social Impact and Corporate Social Responsibility
Increasingly, corporations are being held accountable for their social and environmental impact. The concept of Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) has gained significant traction, with stakeholders demanding that companies operate ethically and sustainably.
CSR initiatives can range from reducing carbon emissions and promoting diversity and inclusion to supporting local communities and philanthropic endeavors. Many companies now publish annual sustainability reports detailing their environmental, social, and governance (ESG) performance.
However, critics argue that some CSR efforts are merely "greenwashing," designed to improve public image without making substantial changes to core business practices. Genuine CSR requires a commitment to transparency, accountability, and measurable impact.
Challenges and Criticisms
Despite their positive contributions, corporations also face significant challenges and criticisms. Concerns about income inequality, environmental degradation, and undue political influence are frequently raised.
Critics point to instances of corporate malfeasance, such as accounting scandals, environmental disasters, and exploitative labor practices, as evidence of the need for greater regulation and oversight. The International Labour Organization (ILO) advocates for fair labor standards and decent work conditions in all industries.
The debate over corporate power and its impact on society is ongoing, with advocates for reform calling for stronger regulations, greater corporate accountability, and a shift towards stakeholder capitalism, which prioritizes the interests of all stakeholders, not just shareholders.
The Evolving Role of Corporations
The role of corporations in society is constantly evolving. As societal expectations shift and new challenges emerge, corporations are being pressured to adapt and demonstrate a greater commitment to social and environmental responsibility.
The rise of ESG investing, which considers environmental, social, and governance factors in investment decisions, is further incentivizing companies to prioritize sustainability. Consumers are also increasingly demanding ethical and sustainable products and services, further influencing corporate behavior.
Ultimately, the long-term success of corporations will depend on their ability to navigate these complex challenges and demonstrate that they can be a force for good in society. This requires a fundamental shift in mindset, from prioritizing short-term profits to creating long-term value for all stakeholders.
Conclusion: Corporations are integral to modern society, contributing significantly to economic growth, innovation, and job creation. While they face legitimate criticisms and challenges, their potential for positive impact is undeniable. By embracing Corporate Social Responsibility and prioritizing stakeholder value, corporations can play a vital role in building a more sustainable and equitable future.



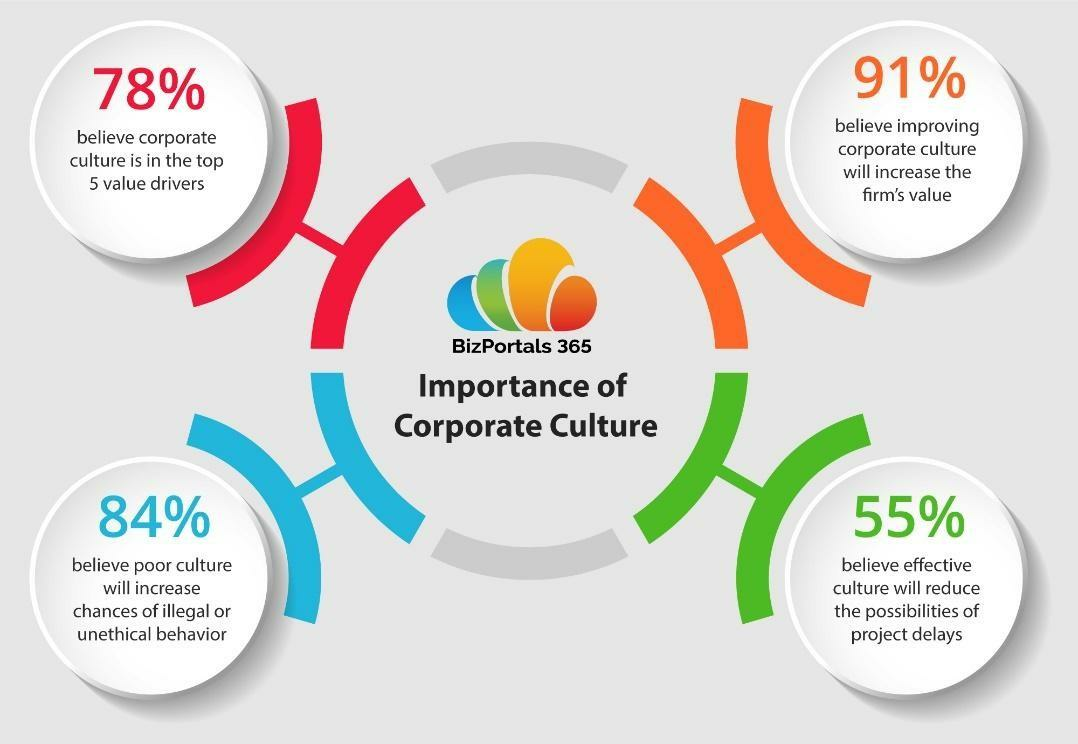
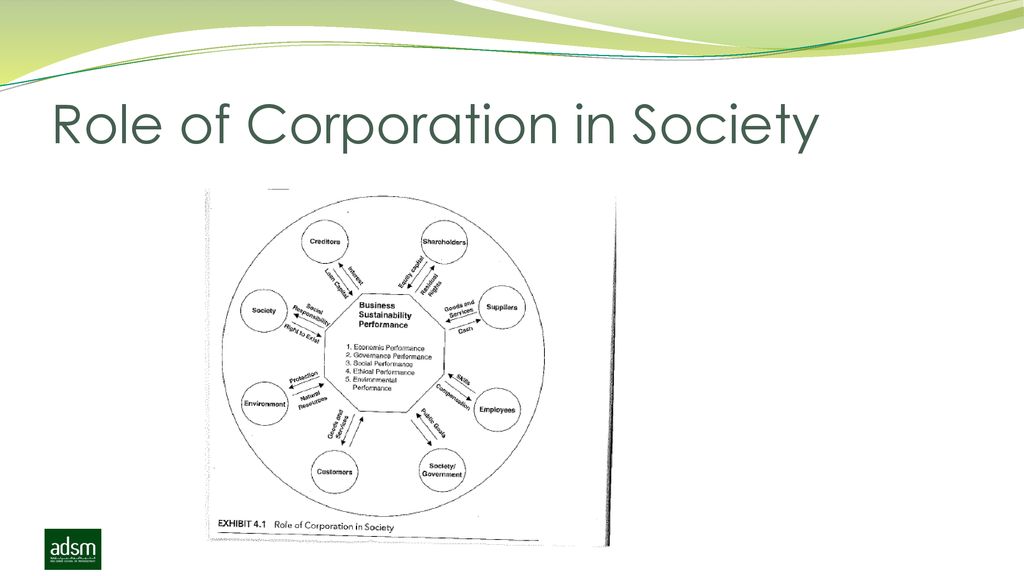





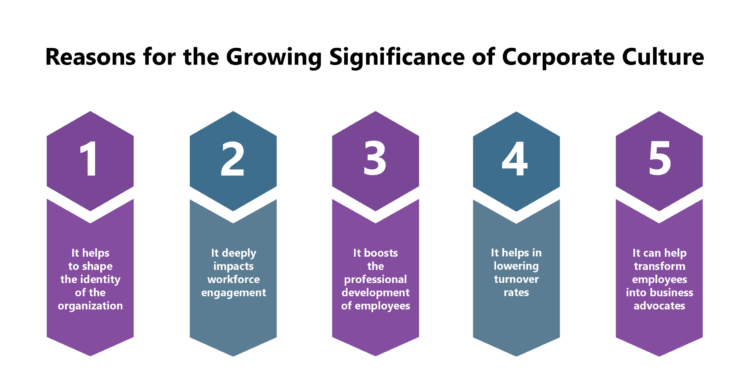
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/CorporateCulture_Final_4198720-5744ada285de4eba81cc976525d00c4d.jpg)