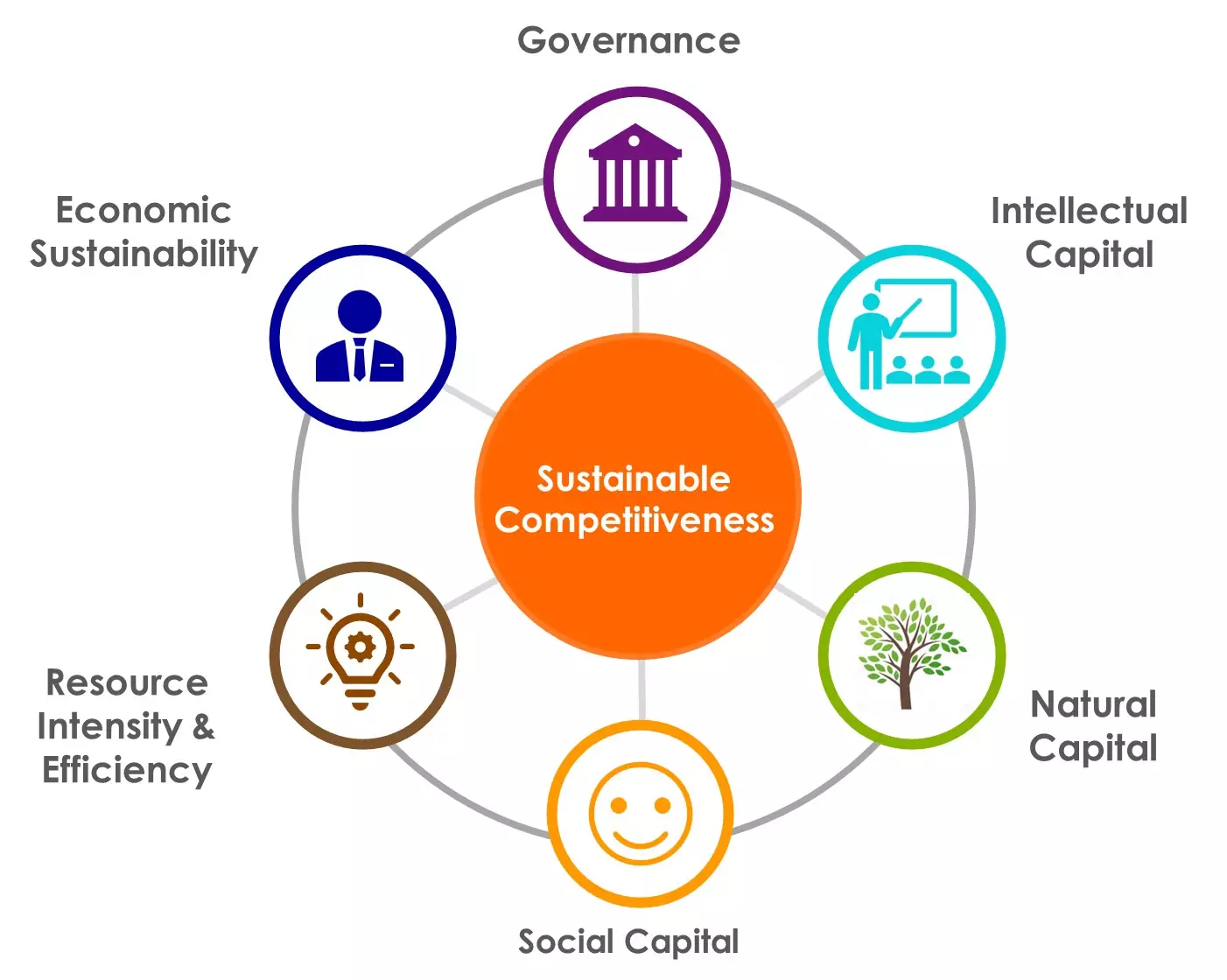
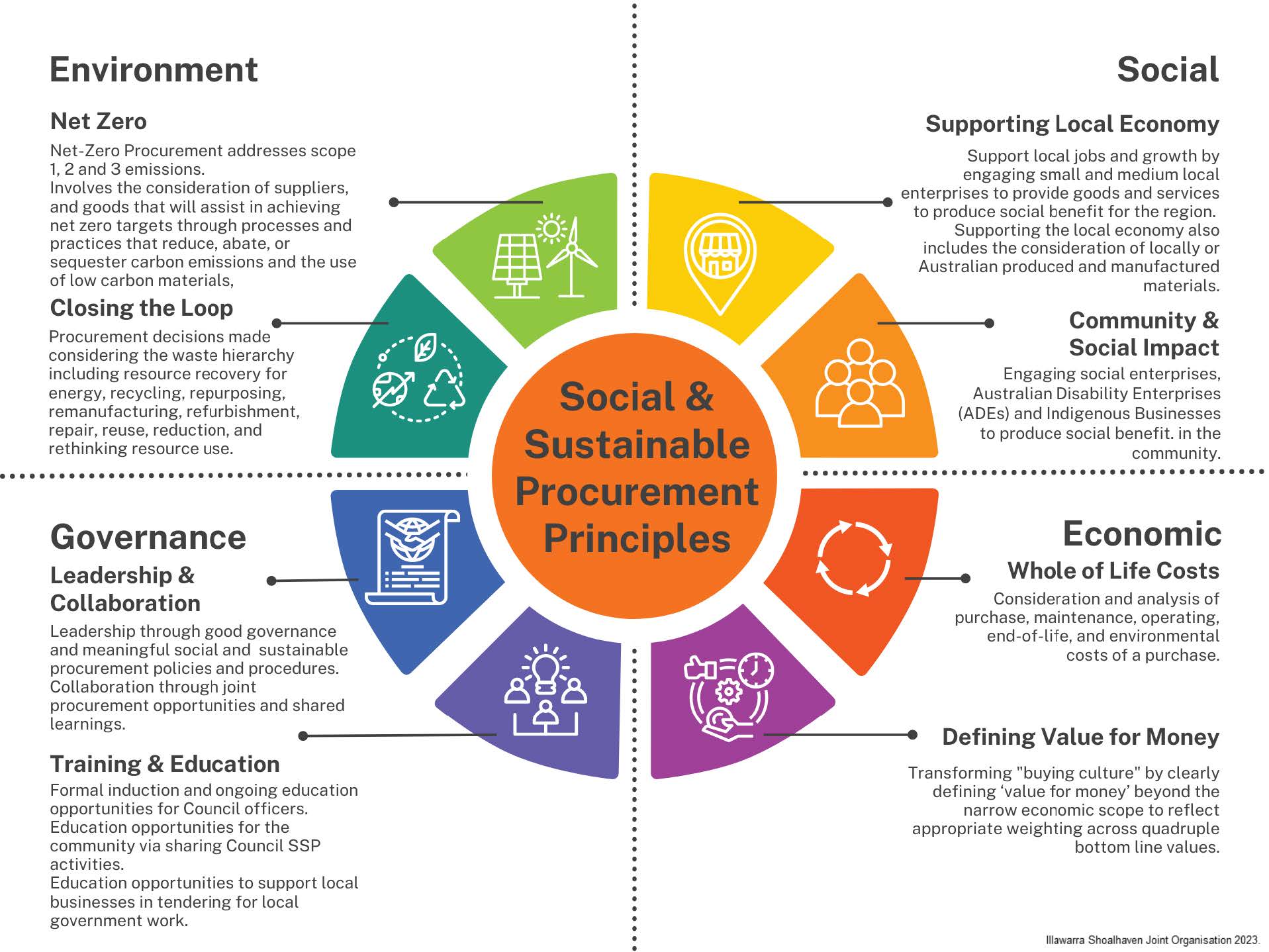
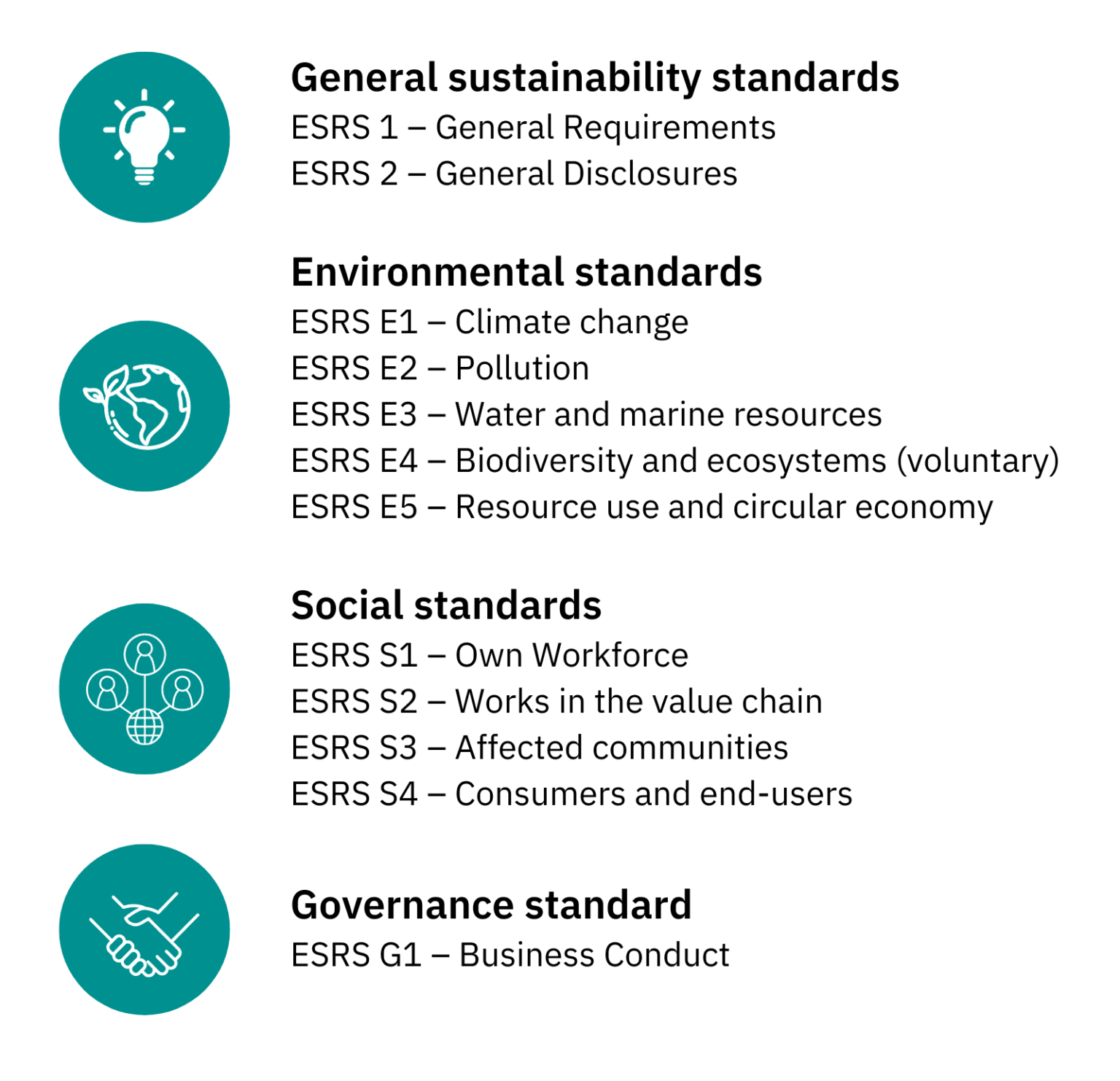
In The Context Of Contracts With Sustainable Requirements

Contracts with sustainability requirements are facing unprecedented scrutiny as global supply chains falter and greenwashing accusations surge. The urgency to enforce genuine environmental and social responsibility is intensifying, pushing businesses and governments to overhaul contractual frameworks.
This crisis demands immediate action to redefine contract clauses and ensure verifiable sustainability benchmarks.
Mounting Pressure on Sustainable Contracts
The pressure on businesses to demonstrate genuine sustainability is reaching a boiling point. Consumers, investors, and regulators are demanding concrete evidence, not just promises.
This increased scrutiny is forcing companies to re-evaluate their contractual obligations and the sustainability claims they make.
Many existing contracts lack the specificity and enforcement mechanisms needed to ensure genuine environmental and social responsibility.
The Rise of Greenwashing Accusations
A wave of greenwashing accusations is sweeping across industries, targeting companies that exaggerate or misrepresent their sustainability efforts.
These accusations often stem from vague or unenforceable sustainability clauses in contracts with suppliers and partners.
A recent report by TerraChoice, updated in 2023, found that a significant percentage of products marketed as "green" or "sustainable" contained deceptive or misleading claims, highlighting the inadequacy of current oversight mechanisms.
Supply Chain Vulnerabilities Expose Weaknesses
The fragility of global supply chains, exacerbated by geopolitical instability and climate change, is exposing significant weaknesses in sustainable sourcing practices.
Contracts that lack robust due diligence provisions and clear risk mitigation strategies are failing to protect businesses from reputational and financial damage.
The COVID-19 pandemic and ongoing conflicts have disrupted supply chains, forcing companies to scramble for alternative sources, often compromising their sustainability commitments.
Redefining Contractual Frameworks
To address these challenges, businesses and governments are actively working to redefine contractual frameworks. The goal is to incorporate more stringent sustainability requirements.
This includes strengthening due diligence processes, establishing verifiable metrics, and implementing robust enforcement mechanisms.
The focus is on creating contracts that are not only legally binding but also aligned with globally recognized sustainability standards.
Strengthening Due Diligence
Enhanced due diligence is crucial to ensure that suppliers and partners meet the required sustainability standards. This involves thorough audits, site visits, and independent verification.
Companies are increasingly using technology to track and monitor their supply chains, providing greater transparency and accountability.
Blockchain technology, for example, is being explored to create tamper-proof records of product origins and environmental impact.
Establishing Verifiable Metrics
Vague promises of sustainability are no longer sufficient. Contracts must include specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) metrics.
These metrics should cover a range of environmental and social factors, such as carbon emissions, water usage, waste generation, and labor practices.
Organizations like the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) and the Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB) provide frameworks for reporting and measuring sustainability performance.
Implementing Robust Enforcement Mechanisms
To ensure compliance, contracts must include clear enforcement mechanisms. This includes penalties for non-compliance, termination clauses, and dispute resolution processes.
Companies are also exploring the use of insurance policies to protect themselves against the risks associated with unsustainable supply chains.
Collaboration between businesses, governments, and civil society organizations is essential to ensure effective enforcement of sustainable contract requirements.
Next Steps and Ongoing Developments
The drive to strengthen sustainable contracts is an ongoing process. Businesses must act now to review and revise their contractual frameworks, prioritizing transparency, accountability, and measurable results.
Government regulations are expected to become stricter, and consumer expectations will continue to rise.
The European Union's Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD), which mandates comprehensive sustainability reporting for a wide range of companies, is setting a new global standard.
The ongoing developments will shape the future of sustainable business practices and the role of contracts in driving positive change.
Businesses that fail to adapt risk reputational damage, financial losses, and legal challenges.