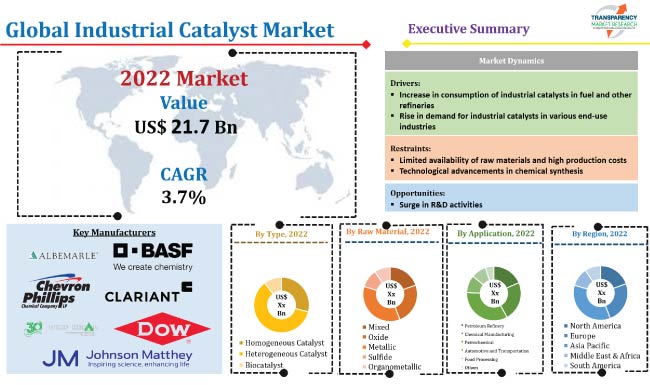
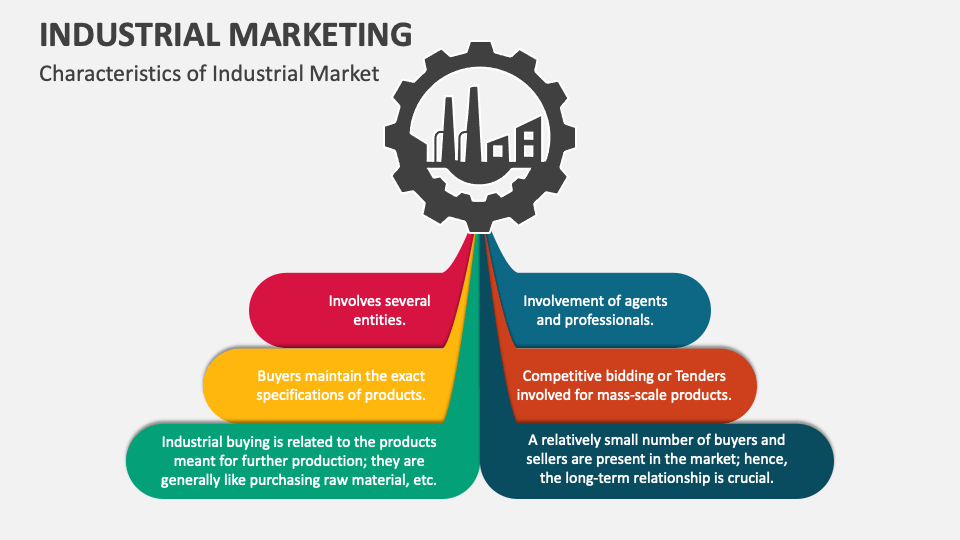
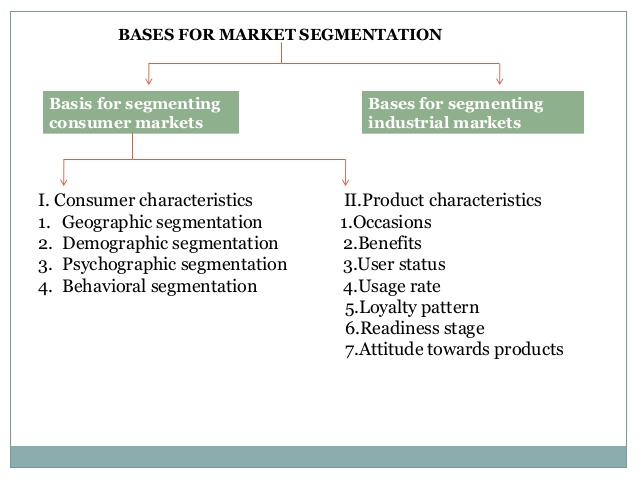
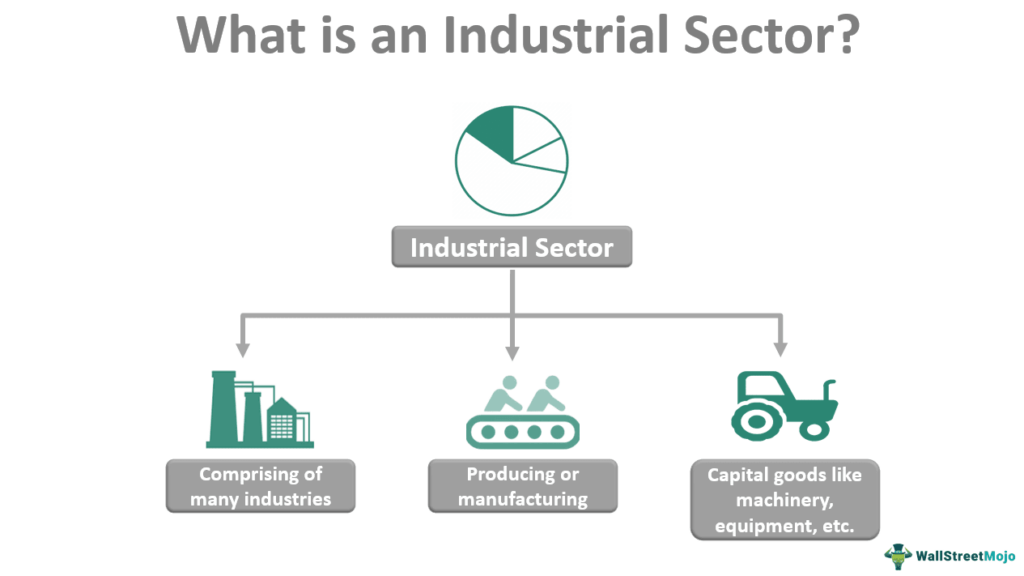
Industrial Markets Can Change Due To Which Of The Following

The hum of machinery, the clang of metal, the logistical ballet of trucks and trains – these are the sounds and sights of industrial markets, the backbone of our modern economy. But like a complex organism, these markets are constantly adapting, evolving in response to a myriad of internal and external forces. Imagine a bustling factory floor suddenly silenced, not by a malfunction, but by a shift in global trade winds. This scenario, though dramatic, underscores the vulnerability and dynamism inherent in industrial markets.
Industrial markets, encompassing everything from manufacturing and energy to construction and transportation, are profoundly susceptible to change. Several key factors can dramatically reshape these sectors, including technological advancements, shifts in government policy, fluctuations in raw material prices, evolving consumer demands, and, increasingly, geopolitical events. Understanding these drivers is crucial for businesses, policymakers, and anyone seeking to navigate the complexities of the modern industrial landscape.
The Foundation: A Shifting Landscape
Industrial markets, unlike consumer markets, deal with goods and services used by other businesses. Think of steel mills supplying automotive manufacturers, or chemical plants providing raw materials for the pharmaceutical industry. This business-to-business (B2B) nature means that changes in one sector can have cascading effects across the entire industrial ecosystem.
Historically, industrial markets were often characterized by long-term contracts and established relationships. However, globalization and technological disruption have created a more fluid and competitive environment. Companies are now more likely to source materials and services from around the world, and they are constantly seeking ways to improve efficiency and reduce costs.
Technological Advancements: The Disruptive Force
Perhaps the most significant driver of change in industrial markets is technology. Automation, artificial intelligence (AI), and the Internet of Things (IoT) are revolutionizing manufacturing processes, supply chain management, and product development.
Automation, for example, is enabling companies to produce goods more quickly and efficiently, with fewer errors and lower labor costs. AI is being used to optimize production schedules, predict equipment failures, and even design new products. IoT devices are providing real-time data on everything from machine performance to inventory levels, allowing companies to make more informed decisions.
"The Fourth Industrial Revolution, characterized by the fusion of technologies that is blurring the lines between the physical, digital, and biological spheres, is fundamentally altering the way we live, work, and relate to one another,"notes a report by the World Economic Forum. This statement underscores the profound impact of technology on industrial markets.
Government Policy: Setting the Stage
Government policies, including regulations, trade agreements, and tax incentives, play a crucial role in shaping industrial markets. Environmental regulations, for example, can force companies to invest in cleaner technologies and reduce their carbon footprint.
Trade agreements can open up new markets for industrial goods and services, while tariffs can restrict trade and protect domestic industries. Tax incentives can encourage companies to invest in research and development, or to locate their operations in specific regions.
Recently, government initiatives focusing on reshoring and supply chain resilience have gained prominence, aiming to bring manufacturing back to domestic shores and diversify sourcing to mitigate risks from global disruptions.
Raw Material Prices: The Economic Undercurrent
Industrial markets are heavily influenced by the prices of raw materials such as oil, steel, and minerals. Fluctuations in these prices can have a significant impact on production costs and profitability.
A sudden increase in the price of oil, for example, can raise transportation costs and make it more expensive to manufacture goods. Similarly, a shortage of a key mineral can disrupt production and lead to higher prices for finished products.
The volatility of raw material prices can create uncertainty for businesses and make it difficult to plan for the future. Companies often use hedging strategies to mitigate the risk of price fluctuations.
Consumer Demand: The Ultimate Driver
While industrial markets are not directly focused on consumers, their operations are ultimately driven by consumer demand. Changes in consumer preferences and buying habits can have a ripple effect throughout the industrial ecosystem.
For example, the growing demand for electric vehicles is driving investment in battery technology and the mining of lithium and other rare earth minerals. Similarly, the increasing popularity of online shopping is fueling the growth of the logistics and warehousing industries.
Understanding consumer trends is essential for industrial companies to anticipate future demand and adapt their production accordingly. This requires careful market research and a willingness to invest in new technologies and capabilities.
Geopolitical Events: The Unforeseen Disruptors
Geopolitical events, such as wars, political instability, and trade disputes, can have a significant impact on industrial markets. These events can disrupt supply chains, create uncertainty, and lead to higher prices.
The COVID-19 pandemic, for example, exposed the vulnerabilities of global supply chains and highlighted the importance of diversification. Similarly, the war in Ukraine has disrupted energy markets and led to increased inflation.
Businesses need to be aware of these risks and have contingency plans in place to mitigate their impact. This may involve diversifying their supply chains, investing in risk management tools, and closely monitoring geopolitical developments.
Looking Ahead: Embracing Change
The factors influencing industrial markets are complex and interconnected. Navigating this dynamic landscape requires a proactive and strategic approach.
Companies need to invest in technology, build resilient supply chains, and stay informed about government policies and geopolitical events. They also need to be flexible and adaptable, willing to change their strategies as the market evolves.
Ultimately, the companies that succeed in the industrial markets of the future will be those that embrace change and are able to anticipate and respond to the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead. It's about building agility, fostering innovation, and understanding that the only constant is adaptation itself. By doing so, these vital sectors can continue to drive economic growth and improve our quality of life, ensuring the hum of industry continues for generations to come.