Internet Providers Based On Zip Code
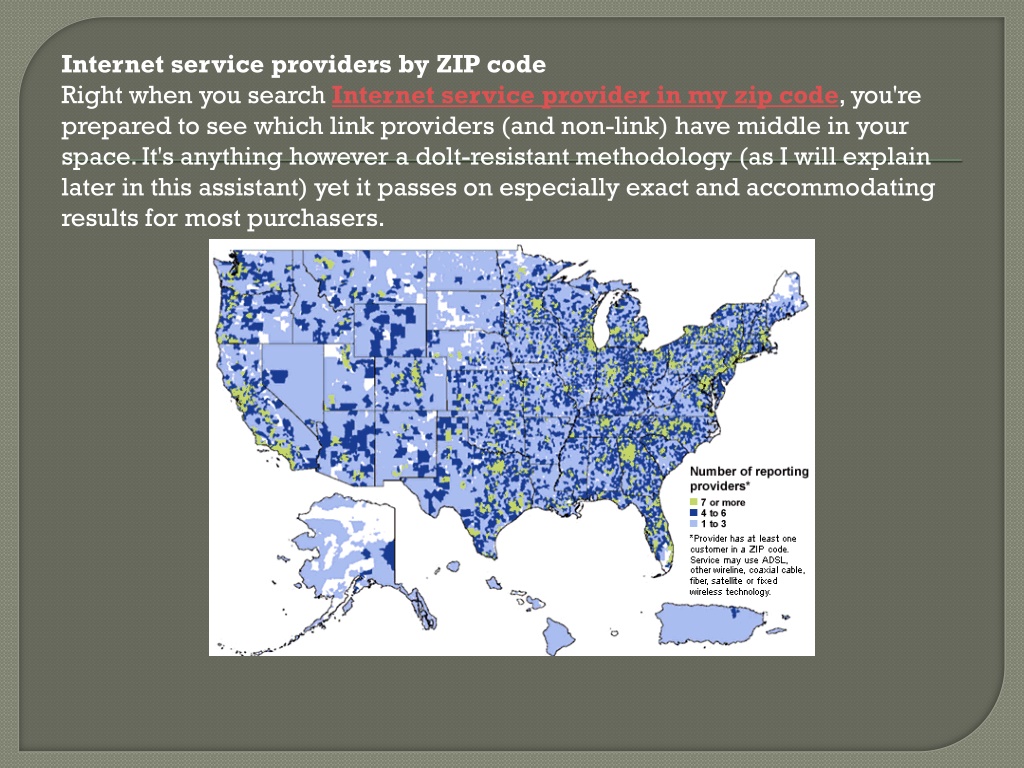
Millions face internet access inequality, with options dictated by zip code. Limited choices translate to higher prices and slower speeds for many Americans.
This article exposes how location dictates internet provider options, impacting affordability and service quality, based on recent FCC data and consumer reports.
The Digital Divide: Zip Code Lottery
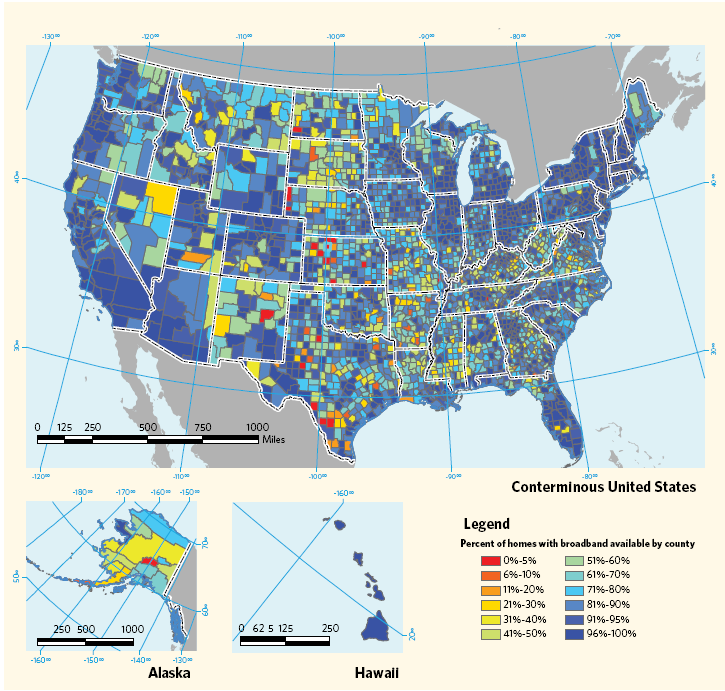
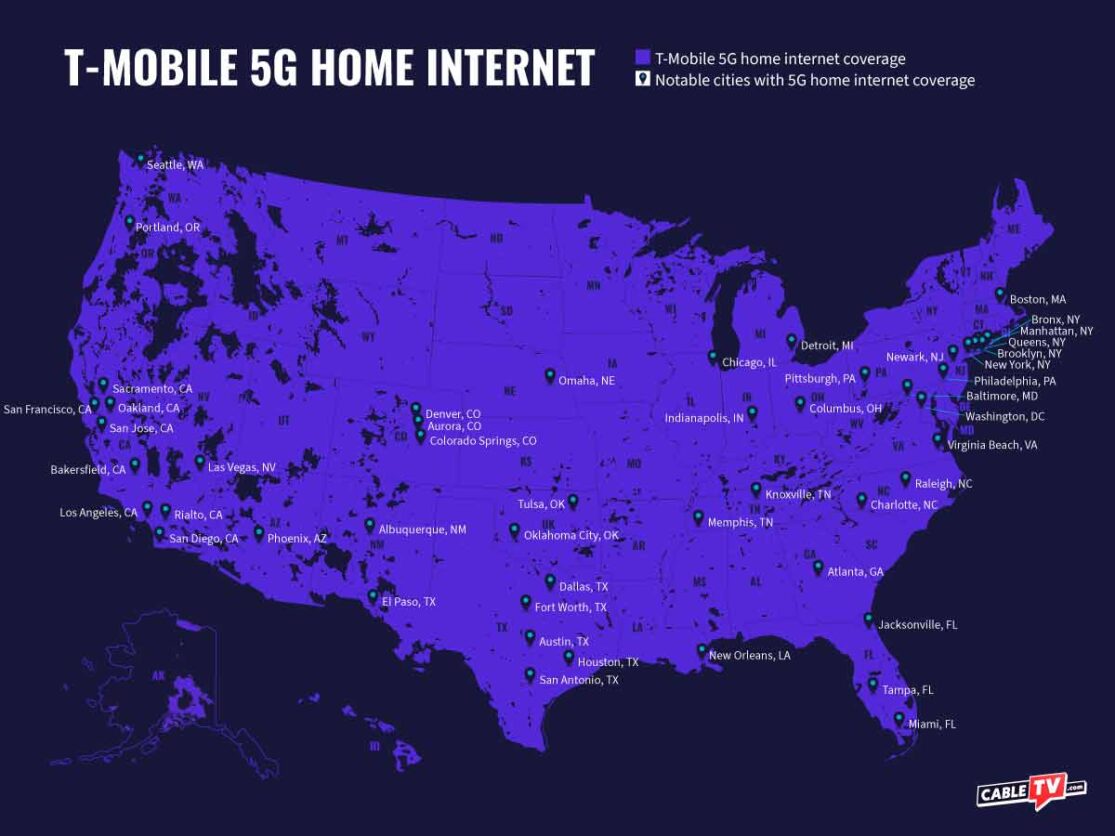
The FCC's National Broadband Map reveals stark disparities. Residents in rural areas, and even some urban neighborhoods, often have access to only one or two providers.
This lack of competition allows providers to set prices without consumer pressure. Consequently, those with fewer options pay more for subpar internet service.
Consider zip code 90210 in Beverly Hills, CA. Here, residents typically have access to multiple high-speed internet providers, including Spectrum and Verizon Fios.
Contrast this with zip code 73032 in rural Oklahoma. Residents there often rely on a single provider, like Rise Broadband, with slower speeds and higher costs.
Price and Speed Discrepancies
Data from Consumer Reports indicates a direct correlation between provider competition and pricing. Areas with only one provider see average monthly internet bills exceeding $80.
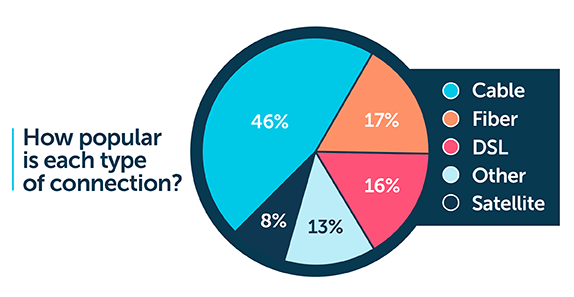
In competitive markets, similar speed tiers are available for $50-$60 per month. The speed also greatly vary.
Furthermore, the digital divide is not solely a rural issue. Low-income urban areas often face similar constraints. Comcast and other major providers may offer limited, slower service in these regions.
This is often attributed to lower potential profits due to demographic factors. It deepens the existing socio-economic inequalities.
Impact on Education and Economy
Limited internet access hampers educational opportunities for students. Online learning, research, and homework completion become significantly harder.
Economically, individuals in these areas struggle to participate in the digital economy. Telecommuting, online job searching, and e-commerce are severely limited.
According to a study by the National Digital Inclusion Alliance, the lack of affordable, reliable internet costs the U.S. economy billions annually.
Businesses also suffer, hindering innovation and growth in affected areas. Small business cannot compete in the market.
Government Intervention and Future Plans
The Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act aims to address this issue. The Act allocated billions of dollars for broadband expansion and affordability programs.
The Affordable Connectivity Program (ACP), part of the Act, provides eligible households with monthly discounts on internet service. However, program’s long term funding is uncertain.
Advocacy groups like Public Knowledge are urging Congress to ensure the ACP's continued funding. They emphasize the program’s crucial role in bridging the digital divide.
States are also implementing local initiatives to promote broadband expansion. These include offering incentives to providers to expand service in underserved areas.
Consumers are encouraged to check the FCC's Broadband Map to assess their internet options. They should also compare prices and speeds from different providers.
Contacting local representatives to advocate for better internet access is also very important. The fight for digital equality continues.