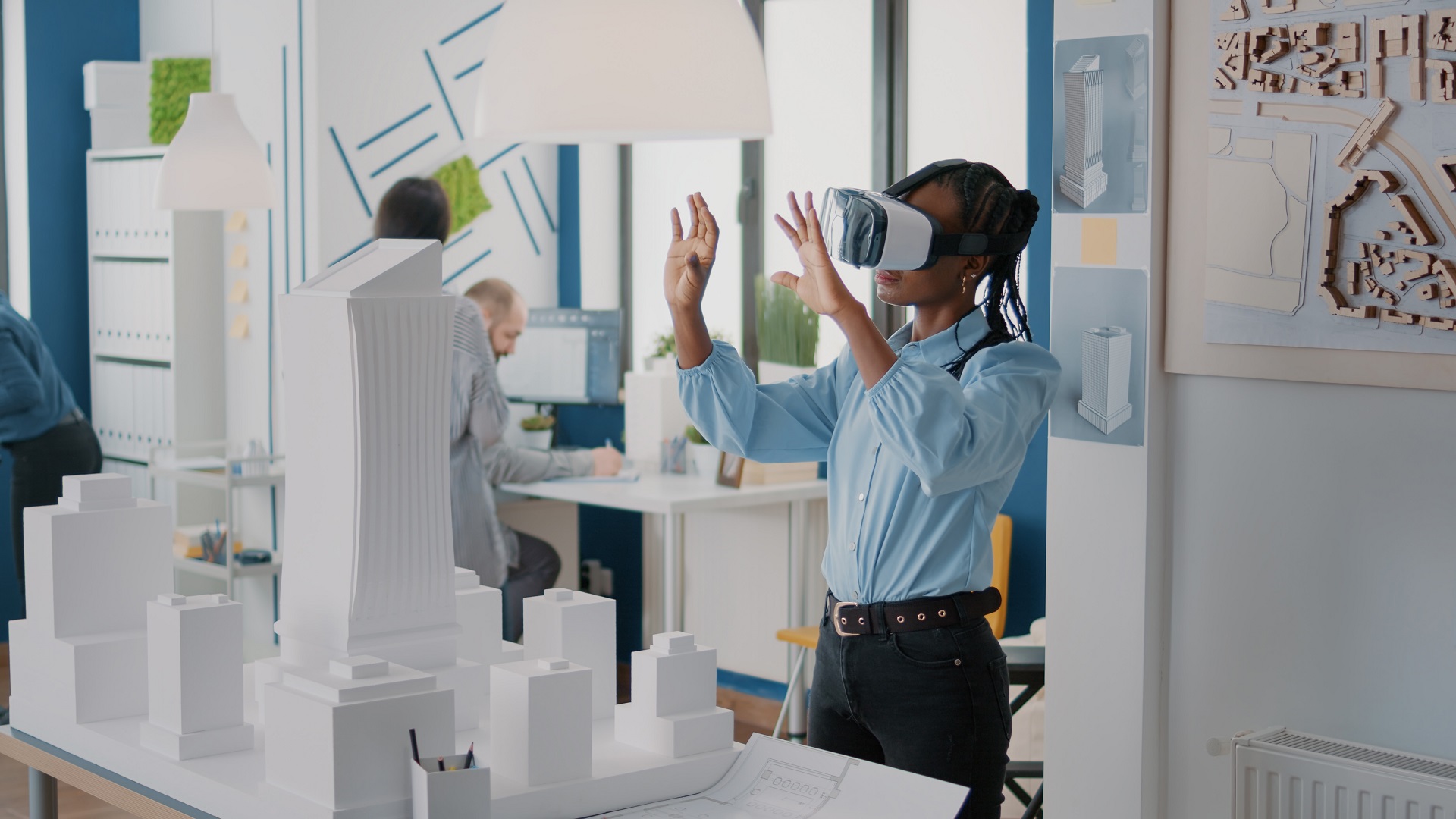
Involves A Virtual Reality Model Of The World

The Earth is facing unprecedented challenges, from climate change-induced disasters to rapidly escalating urbanization. Now, imagine a world where policymakers, scientists, and citizens alike can step inside a perfectly replicated virtual Earth, testing solutions and visualizing consequences before they play out in reality. This is no longer science fiction; a growing consortium of organizations are building sophisticated VR models poised to revolutionize our understanding and management of global issues.
At the heart of this ambitious project is a deep integration of climate data, socioeconomic indicators, and complex system modeling. This virtual Earth – sometimes referred to as a “digital twin” – offers a platform for simulated policy interventions and predictive analytics, potentially offering insights unavailable through traditional methods. The project aims to provide a tool to aid in preemptive action against potential global catastrophes.
The Genesis of a Digital Earth
The initiative is not the product of a single entity. It is a collaborative effort involving governmental agencies, research institutions, and tech giants worldwide. The European Space Agency (ESA), for instance, is contributing vast amounts of satellite data for terrain mapping and environmental monitoring.
Universities such as MIT and Oxford are providing cutting-edge algorithms for predictive modelling. Several private tech companies are developing the VR infrastructure needed to make the digital Earth accessible to users globally.
Core Technologies and Data Integration
The virtual Earth's foundation rests on a complex architecture of interconnected technologies. Geospatial data acquired from satellites, drones, and ground-based sensors forms the backbone, painting a detailed picture of the planet's surface, atmosphere, and oceans. This data is then processed using advanced machine learning algorithms.
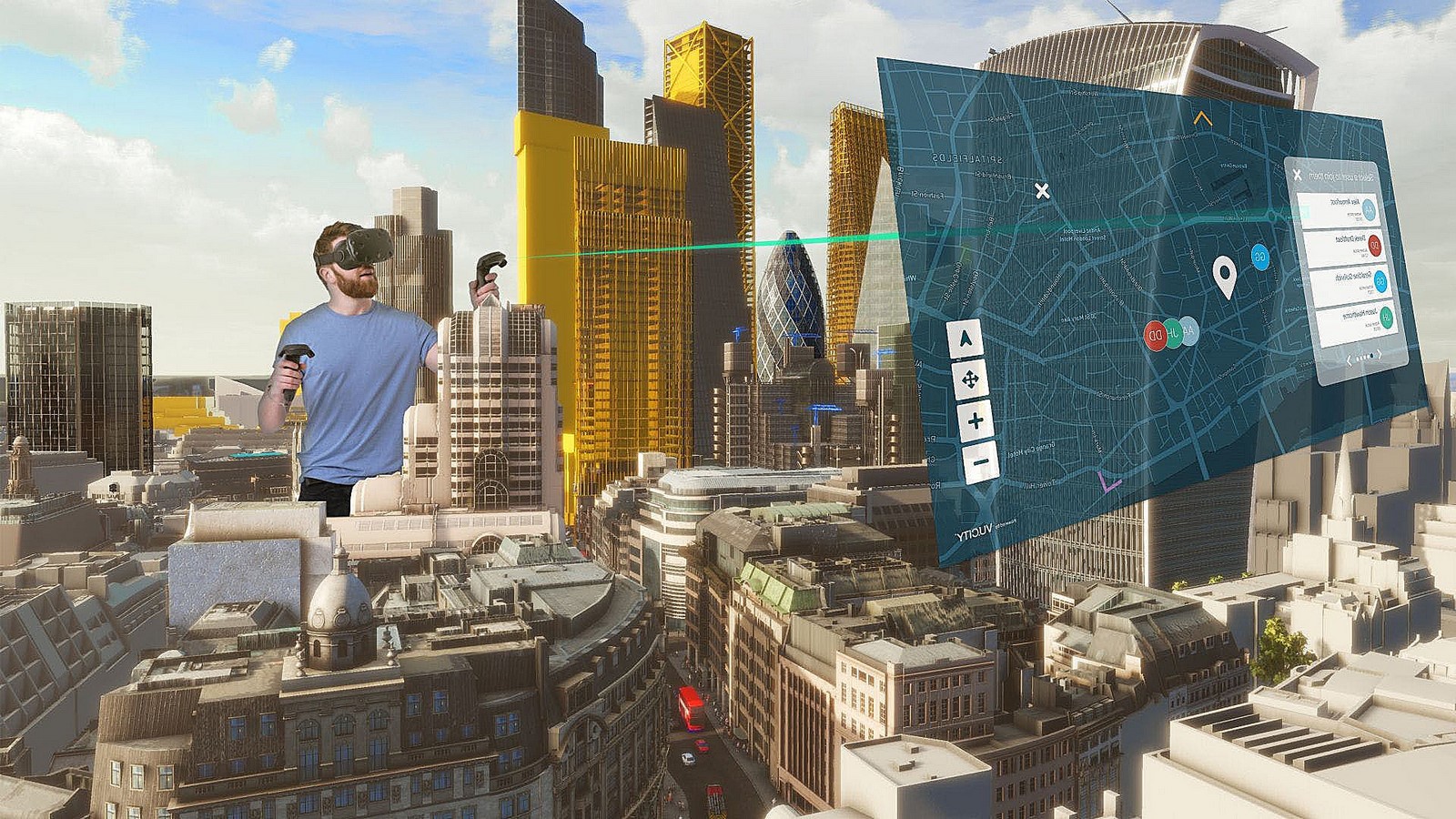
The AI is trained to identify patterns, predict future trends, and simulate the impact of various scenarios. The VR component, often powered by sophisticated gaming engines, allows users to explore the virtual Earth in a 3D environment.
It can range from a bird’s-eye view of global climate patterns to street-level visualizations of urban development.
Applications and Use Cases
The potential applications of this digital Earth are vast and far-reaching. One of the most critical use cases lies in climate change mitigation and adaptation. Users can simulate the effects of rising sea levels on coastal communities, assess the effectiveness of carbon sequestration strategies, or model the spread of wildfires under different climate scenarios.
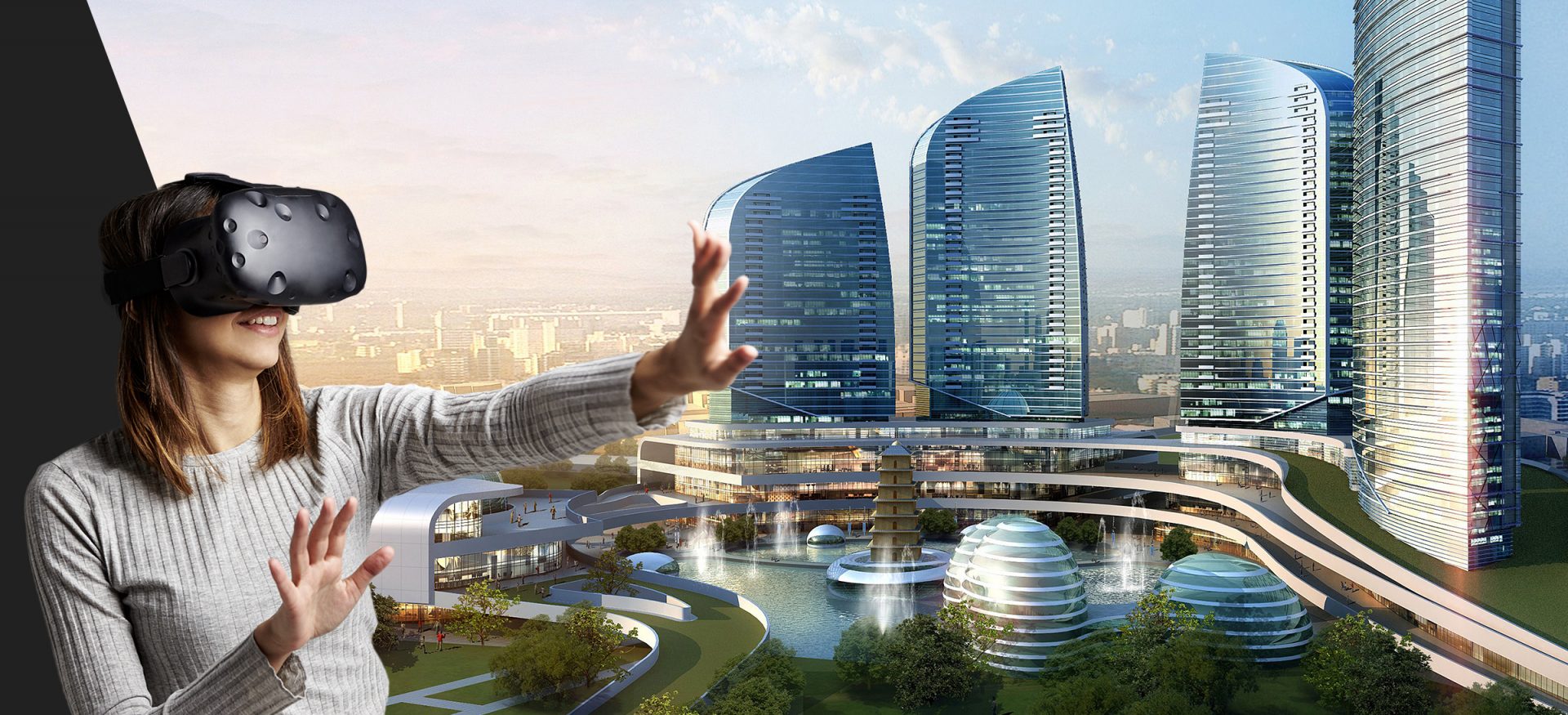
Urban planning is another area ripe for transformation. Architects and city planners can use the virtual Earth to design sustainable infrastructure, optimize traffic flow, and evaluate the impact of new developments on the environment.
The model also presents new opportunities for disaster preparedness and response. By simulating the impact of earthquakes, hurricanes, and other natural disasters, emergency responders can develop more effective evacuation plans and allocate resources more efficiently.
Policy Implications and Ethical Considerations
While the benefits of a virtual Earth are undeniable, the project also raises important policy and ethical questions. One key concern is data privacy. The model relies on massive amounts of data, much of which is personal and sensitive. Ensuring that this data is used responsibly and ethically is paramount.
The accuracy and reliability of the model are also critical considerations. If the simulations are based on flawed data or biased algorithms, they could lead to misguided policies with serious consequences. This concern requires rigorous validation processes and ongoing efforts to improve the model's accuracy.
Furthermore, access to the digital Earth could become a source of inequality. If only wealthy nations and organizations have access to this powerful tool, it could exacerbate existing disparities and create new forms of digital divide.
Challenges and Future Directions
Building and maintaining a virtual Earth is an enormous undertaking, fraught with technical and logistical challenges. One of the biggest hurdles is the sheer volume of data that needs to be collected, processed, and integrated.
Standardizing data formats and ensuring data interoperability are also crucial. The model also requires significant computing power. Cloud computing and edge computing solutions are being explored to address this challenge.
Looking ahead, the developers envision a future where the digital Earth is constantly evolving, incorporating new data streams, and becoming more sophisticated over time. They also hope to make the model more accessible to a wider audience.
The goal is to create a tool that empowers citizens to participate in shaping the future of their communities and the planet as a whole. The project's success hinges on international collaboration. This global effort aims to benefit all of humankind.
Expert Opinions and Perspectives
"The digital Earth represents a paradigm shift in how we understand and manage our planet. It offers a unique opportunity to test solutions in a virtual environment before implementing them in the real world," says Dr. Emily Carter, a leading climate scientist at Princeton University.
However, some experts caution against overreliance on virtual models. They emphasize the importance of ground-truthing simulations with real-world data and incorporating human judgment into decision-making processes.
Dr. David Miller, a professor of urban planning at the University of Toronto, notes, "The digital Earth is a powerful tool, but it should not replace on-the-ground research and community engagement. It is essential to ensure that virtual models reflect the lived experiences of people in diverse communities."
Conclusion
The development of a virtual reality model of the Earth is a monumental undertaking with the potential to reshape our world. The project faces technical, ethical, and political challenges, but the potential benefits are too significant to ignore.
As the model continues to evolve, it is crucial to ensure that it is used responsibly, ethically, and equitably. The digital Earth could become a pivotal tool for addressing global challenges and building a more sustainable future for all.
Ultimately, the virtual Earth represents a bold vision of how technology can be used to understand, protect, and improve our planet. It requires careful stewardship and global cooperation to realize its full potential.