Is Delta 9 Stronger Than Thca

Imagine a sun-drenched afternoon, the air thick with the scent of summer, and conversations buzzing about the latest trends. Among them, a recurring question floats: "Is Delta 9 really stronger than THCA?" It's a question that sparks curiosity and, sometimes, a little confusion, as the world of cannabinoids continues to unfold its intricate secrets.
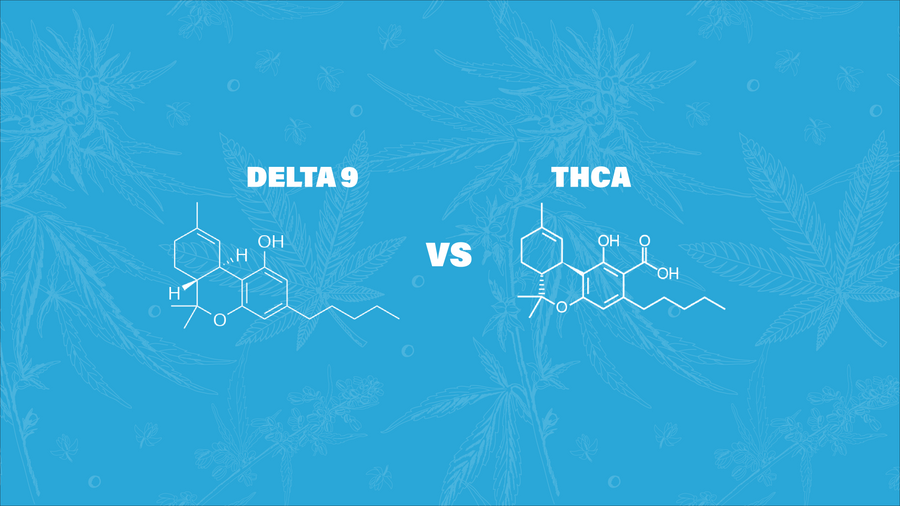
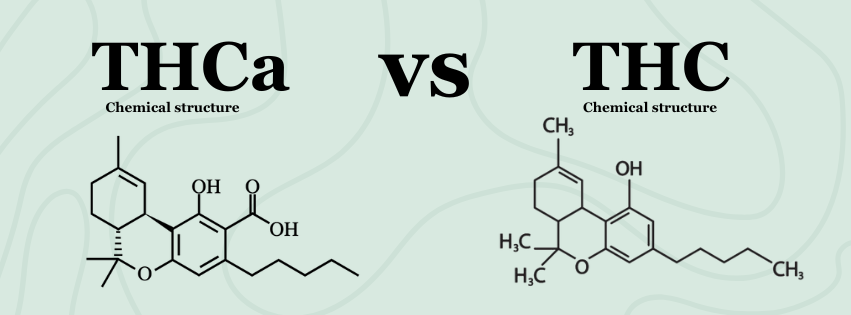
At the heart of this query lies a simple yet significant distinction: Delta 9 is known for its psychoactive effects, while THCA, in its raw form, is not. This article will delve into the nuances of these two compounds, exploring their chemical structures, effects, and legal statuses, to provide a clearer understanding of their respective strengths and roles.
Understanding THCA: The Precursor
THCA, or tetrahydrocannabinolic acid, is the non-psychoactive precursor to Delta 9 THC found in raw cannabis plants. In its natural state, THCA doesn't produce the "high" associated with cannabis use.
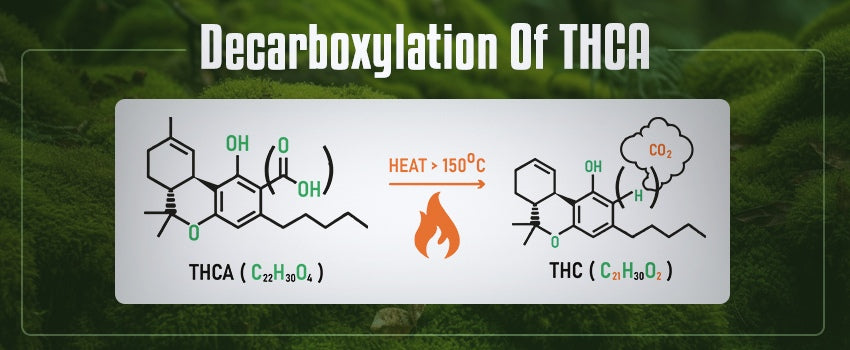
Think of THCA as a sleeping giant, holding the potential for psychoactivity but requiring a key to unlock it. That key is heat, a process called decarboxylation.
Decarboxylation occurs when THCA is exposed to heat, such as through smoking, vaping, or baking. This process removes a carboxyl group from the molecule, converting it into Delta 9 THC.
Delta 9 THC: The Psychoactive Compound
Delta 9 THC, or tetrahydrocannabinol, is the primary psychoactive component in cannabis. It's responsible for the euphoric and altered states of consciousness that cannabis is known for.
Delta 9 interacts with the body's endocannabinoid system, specifically binding to CB1 receptors in the brain and nervous system. This interaction leads to a cascade of effects, including altered mood, perception, and cognitive function.
The strength of Delta 9's effects can vary widely depending on factors such as dosage, individual tolerance, and method of consumption. Factors like genetics and metabolism also play crucial roles.
The Strength Showdown: THCA vs. Delta 9
In a direct comparison, Delta 9 THC is definitively stronger than THCA in terms of psychoactive effects. This is because THCA, in its raw form, doesn't readily bind to the CB1 receptors in the brain.
However, it's essential to understand that THCA is not inactive. Research suggests that THCA may possess its own therapeutic properties, independent of its conversion to Delta 9. Studies have explored its potential anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective, and anti-emetic effects.
Therefore, when considering "strength," it's important to clarify whether you're referring to psychoactive potency or therapeutic potential. Delta 9 wins the psychoactive battle, but THCA may hold its own in other areas.
Decarboxylation: Transforming THCA into Delta 9
The transformation of THCA into Delta 9 through decarboxylation is a crucial step in understanding their relationship. This process unlocks the psychoactive potential of cannabis.
Different methods of decarboxylation can affect the final potency and profile of the resulting Delta 9. Lower temperatures and longer heating times tend to preserve terpenes, the aromatic compounds that contribute to the overall experience.
Understanding decarboxylation allows consumers to control the potency and effects of their cannabis products. By carefully managing the heating process, users can tailor the experience to their preferences.
The Legal Landscape
The legal status of THCA and Delta 9 varies significantly depending on location. Delta 9 THC is often subject to stricter regulations due to its psychoactive properties.
In many jurisdictions, cannabis products containing more than a certain percentage of Delta 9 THC are considered controlled substances. However, the legality of THCA can be less clear-cut.
Some argue that THCA, in its raw form, should be legal since it's non-psychoactive. Others maintain that its potential to be converted into Delta 9 warrants regulation. It's vital to stay informed about the laws in your specific area.
Beyond Psychoactivity: Exploring Potential Benefits
While Delta 9 is primarily known for its psychoactive effects, both Delta 9 and THCA are being studied for their potential therapeutic benefits. Research into cannabinoids is continuously evolving.
Delta 9 THC has been investigated for its potential to relieve pain, reduce nausea, and stimulate appetite. It's often prescribed to patients undergoing chemotherapy.
THCA is gaining attention for its potential anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective properties. Studies have suggested its potential role in managing conditions like arthritis and neurodegenerative diseases, though more research is needed. According to the *National Cancer Institute*, THCA is being investigated for its potential role in cancer treatment.
The Future of Cannabinoid Research
The study of cannabinoids is a rapidly growing field, with new discoveries being made all the time. As research progresses, our understanding of THCA and Delta 9 will continue to evolve.
Scientists are exploring the synergistic effects of different cannabinoids and terpenes, known as the "entourage effect." This phenomenon suggests that the combined effects of these compounds may be greater than the sum of their individual effects.
The future of cannabinoid research holds immense promise for developing new and effective treatments for a wide range of conditions. By continuing to unlock the secrets of these compounds, we can harness their therapeutic potential to improve human health and well-being.
Conclusion
Ultimately, the question of whether Delta 9 is stronger than THCA depends on how "strength" is defined. In terms of psychoactive effects, Delta 9 is the clear winner.
However, THCA is not without its own merits. Its potential therapeutic benefits and its role as the precursor to Delta 9 make it an important compound in its own right.
As the world of cannabis continues to evolve, a deeper understanding of these and other cannabinoids will empower consumers to make informed choices and unlock the full potential of this remarkable plant. It encourages continuous learning and responsible engagement with cannabis and its derivatives.