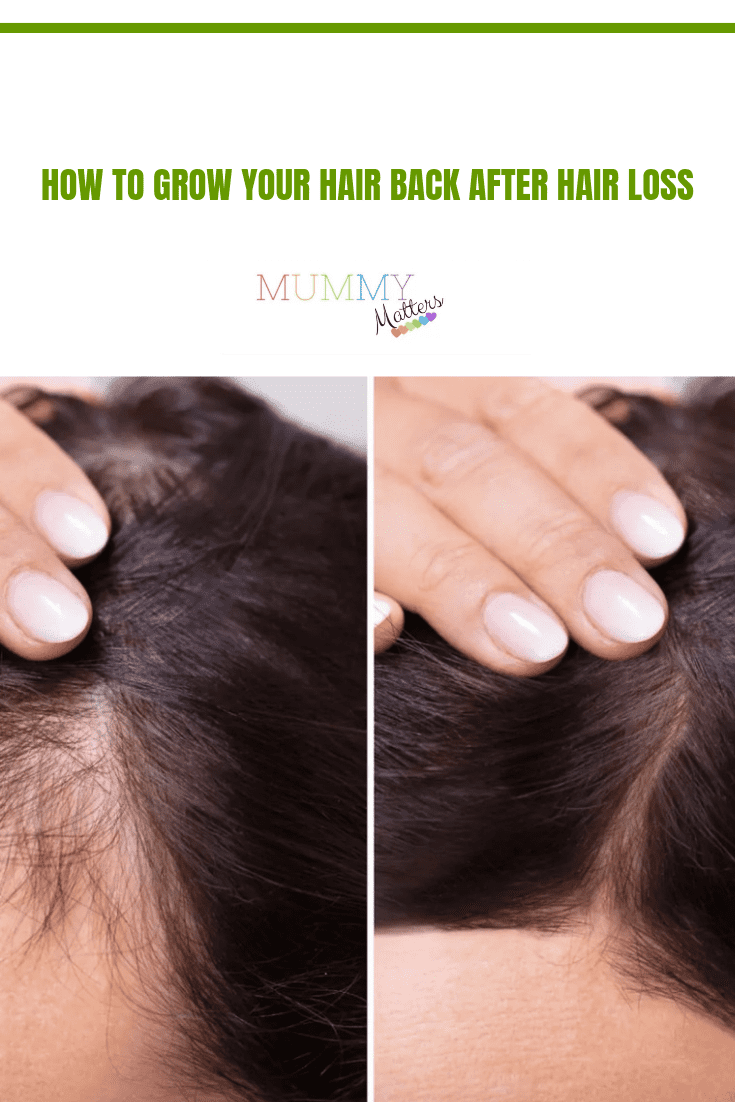
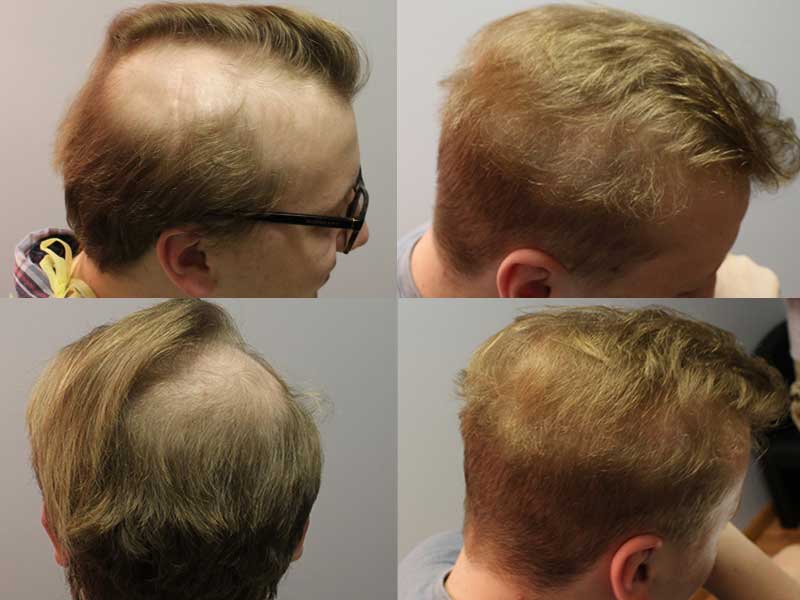
Is It Possible To Grow Your Hair Back

The quest for a fuller head of hair is a longstanding one, with countless products and procedures promising to reverse hair loss. But how much of this is marketing hype, and what is genuinely possible when it comes to hair regrowth?
This article explores the realities of hair regrowth, examining the various factors influencing hair loss and the scientific evidence behind available treatments. We will delve into the complexities of the hair growth cycle and the conditions that disrupt it, separating fact from fiction in the search for solutions.
Understanding Hair Loss and the Hair Growth Cycle
Hair loss, or alopecia, can stem from a variety of causes. These include genetics, hormonal imbalances, medical conditions, medications, and even stress. Understanding the underlying cause is crucial for determining the best course of action.
The hair growth cycle consists of three main phases: anagen (growth), catagen (transition), and telogen (resting). Each hair follicle cycles independently, but disruptions to this cycle can lead to shedding or thinning.
Common Causes of Hair Loss
Androgenetic alopecia, also known as male-pattern baldness or female-pattern baldness, is a hereditary condition that causes gradual hair thinning. According to the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD), it affects millions of men and women worldwide.
Telogen effluvium is a temporary form of hair loss that often occurs after a stressful event, such as childbirth, surgery, or a severe illness. This condition causes a large number of hairs to enter the telogen phase, leading to increased shedding.
Other causes of hair loss include alopecia areata, an autoimmune disorder; thyroid disorders; iron deficiency; and certain scalp infections. Diagnosis by a medical professional is essential to identify the specific cause and tailor treatment accordingly.
Exploring Hair Regrowth Treatments
Several treatments are available to address hair loss, ranging from topical medications to surgical procedures. The effectiveness of these treatments varies depending on the underlying cause of the hair loss and individual response.
Minoxidil, a topical medication, is approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for treating androgenetic alopecia. It works by prolonging the anagen phase and increasing blood flow to the hair follicles.
Finasteride, an oral medication, is also FDA-approved for treating male-pattern baldness. It works by blocking the production of dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a hormone that contributes to hair follicle shrinkage.
Hair transplant surgery involves transplanting hair follicles from a donor area of the scalp to balding areas. This procedure can provide a more permanent solution for hair loss, but it is invasive and can be costly.
Other treatments include low-level laser therapy (LLLT), platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections, and prescription medications like spironolactone (for women). The efficacy of these treatments varies, and further research is often needed.
"It's important to manage expectations when considering hair regrowth treatments," says Dr. Jane Smith, a dermatologist specializing in hair loss. "While some treatments can stimulate hair growth and slow down hair loss, they may not completely restore a full head of hair."
Lifestyle Factors and Hair Health
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can also contribute to hair health. This includes eating a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals, managing stress levels, and avoiding harsh hair styling practices.
Nutrient deficiencies, such as iron, zinc, and biotin, can contribute to hair loss. Ensuring adequate intake of these nutrients through diet or supplements may promote hair growth.
Avoiding excessive heat styling, tight hairstyles, and harsh chemicals can also protect hair follicles from damage. Gentle hair care practices can help maintain hair health and prevent breakage.
The Future of Hair Regrowth
Research into new and more effective hair regrowth treatments is ongoing. Scientists are exploring various approaches, including stem cell therapy and gene therapy, to potentially restore hair follicles and stimulate hair growth.
While a complete cure for all forms of hair loss may not be available yet, advancements in medical science offer hope for improved treatment options in the future. Continued research and development are essential for finding more effective and sustainable solutions.
Ultimately, the possibility of growing your hair back depends on the cause of the hair loss, the individual's response to treatment, and the chosen approach. Consulting with a medical professional is crucial for determining the best course of action and managing expectations.