Is Oats Good For Building Muscle

The quest for optimal muscle growth fuels countless hours in gyms and meticulous dietary planning. Among the staple foods often touted for their health benefits, oats frequently appear on the list of potential muscle-building allies. But is this humble grain truly a powerhouse for those seeking to pack on size, or is its reputation more hype than substance? The answer, as with most aspects of nutrition, is nuanced and depends heavily on individual needs and goals.
This article delves into the role of oats in muscle building, examining its nutritional profile, benefits, and limitations. We'll explore how oats stack up against other common muscle-building foods, and offer practical advice for incorporating them into a balanced diet designed to support muscle growth. Understanding the science behind oats can empower individuals to make informed decisions about their nutrition and achieve their fitness aspirations.
The Nutritional Profile of Oats
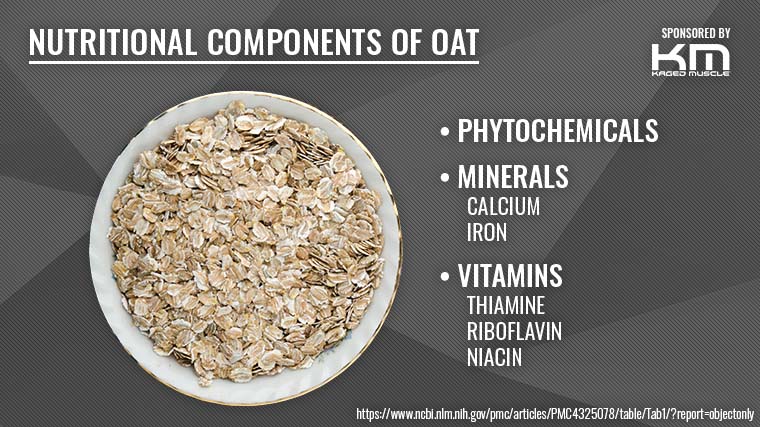
Oats are a whole grain prized for their fiber content, particularly beta-glucan. They are also a source of carbohydrates, which are essential for providing energy during workouts and replenishing glycogen stores after exercise. Furthermore, oats contain a moderate amount of protein and various micronutrients.
A typical serving (around half a cup dry) of rolled oats provides roughly 150 calories, 5 grams of protein, 27 grams of carbohydrates, and 2.5 grams of fat. That same serving boasts approximately 4 grams of fiber, contributing significantly to daily fiber intake, which aids digestion and promotes feelings of fullness. Oats also contain important vitamins and minerals like magnesium, iron, and zinc.
Oats and Muscle Growth: The Benefits
Oats offer several potential benefits for individuals striving to build muscle. The complex carbohydrates in oats provide a sustained energy release, which can be particularly useful during long or intense workouts. This helps maintain energy levels and delay fatigue.
The fiber content in oats supports healthy digestion, which is crucial for nutrient absorption. Optimal nutrient absorption ensures that the body can effectively utilize the protein and other nutrients necessary for muscle repair and growth. Oats also contribute to satiety, potentially aiding in calorie control, an important factor for both bulking and cutting phases.
Glycogen Replenishment
After an intense workout, the body's glycogen stores are depleted. Replenishing these stores is crucial for recovery and future performance. Oats, being a good source of carbohydrates, can effectively help replenish glycogen levels.
Faster glycogen replenishment allows for quicker muscle recovery and reduces muscle breakdown, paving the way for muscle growth. Combining oats with a protein source post-workout can further enhance this recovery process.
Protein Content
While not a primary source of protein, oats do contribute a small amount of this essential macronutrient. Every little bit counts when you're trying to maximize your gains.
Pairing oats with other protein-rich foods like eggs, Greek yogurt, or protein powder can create a complete meal that supports muscle protein synthesis. While the amount of protein in oats is not significant enough for building muscle, it contributes to your overall intake.
Limitations and Considerations
While oats offer certain benefits for muscle building, it's crucial to acknowledge their limitations. Oats are not a high-protein food, and protein is the cornerstone of muscle growth. Relying solely on oats for protein would be insufficient for most individuals seeking to gain muscle mass.
Oats are primarily a carbohydrate source. While carbohydrates are important, prioritizing protein intake is paramount for muscle protein synthesis. Some individuals may also find that oats don't provide enough satiety on their own, potentially leading to overeating of other, less healthy foods.
Digestibility and Individual Tolerance
Some individuals may experience digestive issues like bloating or gas after consuming oats. This can be due to the high fiber content or individual sensitivities. It's essential to assess individual tolerance and adjust intake accordingly.
If digestive issues arise, starting with smaller portions and gradually increasing intake can help the body adapt. Choosing rolled oats or quick oats over steel-cut oats can also improve digestibility for some.
Oats vs. Other Muscle-Building Foods
Compared to protein-rich foods like chicken, beef, eggs, and whey protein, oats fall short in terms of their muscle-building potential. These protein sources provide a higher concentration of essential amino acids, the building blocks of muscle tissue. However, oats can complement these protein sources by providing energy and fiber.
Compared to simple carbohydrates like white bread or sugary cereals, oats offer a more sustained energy release and greater nutritional value. This makes them a preferable carbohydrate source for fueling workouts and supporting overall health. Oats also provide more fiber and important micronutrients.
Incorporating Oats into a Muscle-Building Diet
To effectively incorporate oats into a muscle-building diet, consider the following tips. Combine oats with a protein source, such as protein powder, Greek yogurt, or nuts, to create a more complete meal. Experiment with different preparation methods, such as overnight oats, baked oats, or adding oats to smoothies.
Time your oat consumption strategically, such as pre-workout for sustained energy or post-workout to replenish glycogen stores. Pay attention to portion sizes to ensure you're meeting your overall calorie and macronutrient goals. Consider adding fruits, nuts, and seeds for additional nutrients and flavor.
The Future of Oats in Sports Nutrition
Ongoing research continues to explore the potential benefits of oats, including its impact on gut health and its role in modulating inflammation. Future studies may uncover new insights into how oats can be optimized for muscle building and athletic performance.
As the demand for plant-based protein sources continues to grow, oats may become increasingly popular as a supplementary ingredient in protein bars and other sports nutrition products. The food industry is already exploring ways to enhance the protein content and bioavailability of oats.
Conclusion
Oats can be a valuable addition to a well-rounded muscle-building diet, providing sustained energy, fiber, and essential nutrients. However, it's important to recognize its limitations as a protein source and prioritize adequate protein intake from other sources. By strategically incorporating oats into a balanced diet and considering individual needs, individuals can leverage its benefits to support their muscle-building goals. Ultimately, a holistic approach that combines proper training, adequate rest, and a nutrient-rich diet, including foods like oats, is key to achieving optimal muscle growth.